Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P4484 - Stereomicroscopic On-Site Evaluation in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition of Upper GI and Pancreatic Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

- FJ
Fouad Jaber, MD, MS
University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine
Kansas City, MO
Presenting Author(s)
Fouad Jaber, MD, MS1, Mohammad Jaber, MD2, Saqr Alsakarneh, MD1, Ahmed Fares, MD3, Tala Alsharaeh, MD4, Ahmed-Jordan Salahat, MD4, Mohammed Ayyad, MD5, Yazan Sallam, MD6, Anas Alselek, MD7, Raed Darwish, MD8, Laith Numan, MD, MS9, Wasseem Skef, MD10, Shifa Umar, MD10
1University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 2Al-Azhar University, Gaza, Palestinian Territories; 3Tufts Medical Center, Boston, MA; 4The University of Jordan, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 5Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ; 6University of Missouri, Kansas City, MO; 7Cairo University School of Medicine, Cairo, Al Jizah, Egypt; 8Ain Shams University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt; 9Saint Louis University, St. Louis, MO; 10Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Introduction: Macroscopic on-site evaluation (MOSE) during endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy (EUS-FNB) shows promise, yet a standardized approach remains elusive. Stereomicroscopic on-site evaluation (SOSE), which assesses EUS-guided tissue acquisition (EUS-TA) quality by detecting stereomicroscopically visible white cores (SVWC) ≥4 mm, has shown high diagnostic sensitivity in limited studies. This systematic review evaluates SOSE's efficacy in enhancing diagnostic accuracy during EUS-TA of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions (SELs) and pancreatic lesions (PLs).
Methods: A systematic literature review was conducted across Cochrane, SCOPUS, PubMed, and EMBASE from inception to March 2024. Studies evaluating SOSE for diagnosing gastrointestinal and PLs via EUS- fine-needle aspiration (FNA) or FNB were included. Primary outcomes included sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy. Secondary outcomes included positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), tissue sampling rate, and adverse events. The pooled analysis utilized random effects models and heterogeneity was interpreted using I2 statistics.
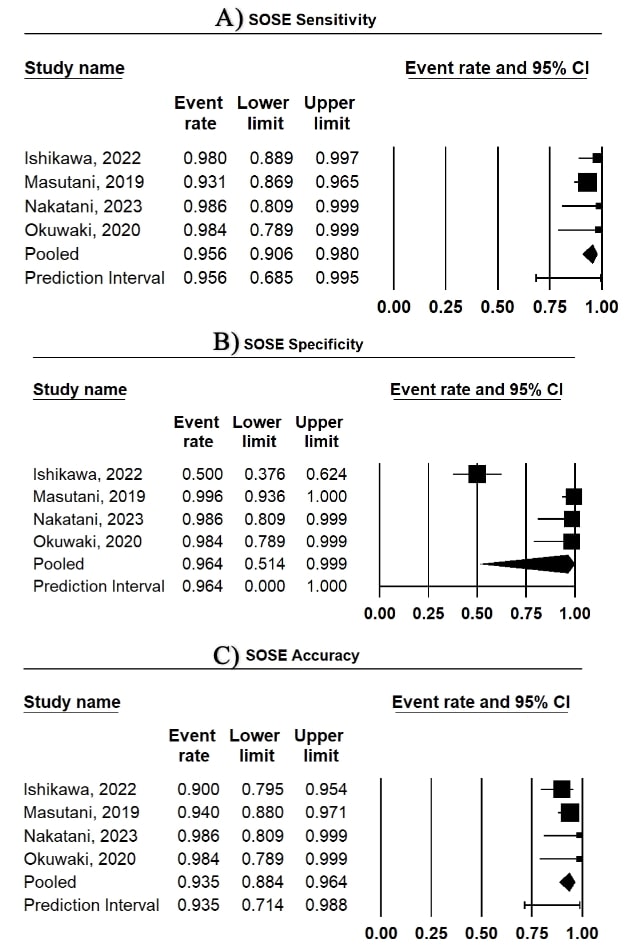
Results: Six studies involving 368 patients were analyzed, with most lesions being PLs (57.3%) and SELs (41%). All studies used 22-gauge needles for EUS-TA, with four studies using fine-needle biopsy (FNB) and two using both FNB and FNA. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of SOSE were 95.6%, 96.4%, and 93.5%, respectively (Figure 1). The pooled diagnostic accuracy, PPV, and NPV were 91.9%, 97.5%, and 86.7%. The pooled rate for obtaining microscopic tissue cells/tissue fragments per lesion was 96.2% (confidence interval [CI]: 77%-99.5%), and per pass was 93.5% (CI: 89%-96.2%)(Table 1). The pooled tissue sampling rate per lesion and per pass was 99% (CI: 96.5%-99.7%) and 93.7% (CI: 88.2%-96.7%), respectively (Table 1). The pooled rate for achieving the presence of SVWC per lesion was 98.9% (CI: 96.6%-99.6%) and per pass was 95.6% (CI: 91.3%-97.8%). The only reported adverse events across all studies were cases of bleeding, with a pooled rate of 3% (CI: 1.4%-6.2%) (Table 1).
Discussion: Our analysis highlights the efficacy of SOSE in improving diagnostic outcomes of SELs and PLs during EUS-TA. With its high diagnostic sensitivity, SOSE emerges as a viable alternative, particularly beneficial for accurate pathological diagnosis of pancreatic and subepithelial lesions in settings lacking rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) capabilities.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Fouad Jaber, MD, MS1, Mohammad Jaber, MD2, Saqr Alsakarneh, MD1, Ahmed Fares, MD3, Tala Alsharaeh, MD4, Ahmed-Jordan Salahat, MD4, Mohammed Ayyad, MD5, Yazan Sallam, MD6, Anas Alselek, MD7, Raed Darwish, MD8, Laith Numan, MD, MS9, Wasseem Skef, MD10, Shifa Umar, MD10. P4484 - Stereomicroscopic On-Site Evaluation in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition of Upper GI and Pancreatic Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 2Al-Azhar University, Gaza, Palestinian Territories; 3Tufts Medical Center, Boston, MA; 4The University of Jordan, Amman, 'Amman, Jordan; 5Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ; 6University of Missouri, Kansas City, MO; 7Cairo University School of Medicine, Cairo, Al Jizah, Egypt; 8Ain Shams University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt; 9Saint Louis University, St. Louis, MO; 10Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Introduction: Macroscopic on-site evaluation (MOSE) during endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy (EUS-FNB) shows promise, yet a standardized approach remains elusive. Stereomicroscopic on-site evaluation (SOSE), which assesses EUS-guided tissue acquisition (EUS-TA) quality by detecting stereomicroscopically visible white cores (SVWC) ≥4 mm, has shown high diagnostic sensitivity in limited studies. This systematic review evaluates SOSE's efficacy in enhancing diagnostic accuracy during EUS-TA of upper gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions (SELs) and pancreatic lesions (PLs).
Methods: A systematic literature review was conducted across Cochrane, SCOPUS, PubMed, and EMBASE from inception to March 2024. Studies evaluating SOSE for diagnosing gastrointestinal and PLs via EUS- fine-needle aspiration (FNA) or FNB were included. Primary outcomes included sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic accuracy. Secondary outcomes included positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), tissue sampling rate, and adverse events. The pooled analysis utilized random effects models and heterogeneity was interpreted using I2 statistics.
Results: Six studies involving 368 patients were analyzed, with most lesions being PLs (57.3%) and SELs (41%). All studies used 22-gauge needles for EUS-TA, with four studies using fine-needle biopsy (FNB) and two using both FNB and FNA. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of SOSE were 95.6%, 96.4%, and 93.5%, respectively (Figure 1). The pooled diagnostic accuracy, PPV, and NPV were 91.9%, 97.5%, and 86.7%. The pooled rate for obtaining microscopic tissue cells/tissue fragments per lesion was 96.2% (confidence interval [CI]: 77%-99.5%), and per pass was 93.5% (CI: 89%-96.2%)(Table 1). The pooled tissue sampling rate per lesion and per pass was 99% (CI: 96.5%-99.7%) and 93.7% (CI: 88.2%-96.7%), respectively (Table 1). The pooled rate for achieving the presence of SVWC per lesion was 98.9% (CI: 96.6%-99.6%) and per pass was 95.6% (CI: 91.3%-97.8%). The only reported adverse events across all studies were cases of bleeding, with a pooled rate of 3% (CI: 1.4%-6.2%) (Table 1).
Discussion: Our analysis highlights the efficacy of SOSE in improving diagnostic outcomes of SELs and PLs during EUS-TA. With its high diagnostic sensitivity, SOSE emerges as a viable alternative, particularly beneficial for accurate pathological diagnosis of pancreatic and subepithelial lesions in settings lacking rapid on-site evaluation (ROSE) capabilities.

Figure: Figure 1: Forest plots for SOSE showing pooled A. Sensitivity. B. Specificity. C. Accuracy.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Fouad Jaber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Jaber indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saqr Alsakarneh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Fares indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tala Alsharaeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed-Jordan Salahat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Ayyad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Sallam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anas Alselek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raed Darwish indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laith Numan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wasseem Skef indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shifa Umar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fouad Jaber, MD, MS1, Mohammad Jaber, MD2, Saqr Alsakarneh, MD1, Ahmed Fares, MD3, Tala Alsharaeh, MD4, Ahmed-Jordan Salahat, MD4, Mohammed Ayyad, MD5, Yazan Sallam, MD6, Anas Alselek, MD7, Raed Darwish, MD8, Laith Numan, MD, MS9, Wasseem Skef, MD10, Shifa Umar, MD10. P4484 - Stereomicroscopic On-Site Evaluation in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition of Upper GI and Pancreatic Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
