Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P4498 - Long-Term Clinical Outcomes After Endoscopic Stapling System Therapy of Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Tarek G. Aridi, MD
Indiana University School of Medicine
Indianapolis, IN
Presenting Author(s)
Tarek G. Aridi, MD1, Gail McNulty, RN, BSN, CCRC1, Glen Lehman, MD, FACG1, William Kessler, MD, FACG2, Mark A. Gromski, MD1
1Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 2Indiana University School of Medicine, Zionsville, IN
Introduction: The MUSETM (MEDIGUS) endoscopic stapling device has been shown to improve GERD symptoms over 6-month (Zacherl et al. Surg Endosc 29(1):220–229, 2014) and 4-year (Kim et al. Surg Endosc 30(8):3402–3408, 2015) time periods. This study aims to explore the long-term outcomes of this treatment after 10 years of follow up.
Methods: 25 patients with GERD underwent MUSE procedure between years 2008 and 2016. 8 evaluable patients were lost to follow up between years 1 and 9. Efficacy data over a 10-year follow up period was analyzed at annual intervals and compared to baseline. The primary outcome was an improvement in GERD health-related quality of life (HRQL) score. Secondary outcomes included GERD medication dose reduction measured by omeprazole equivalents annually over the duration of follow up.
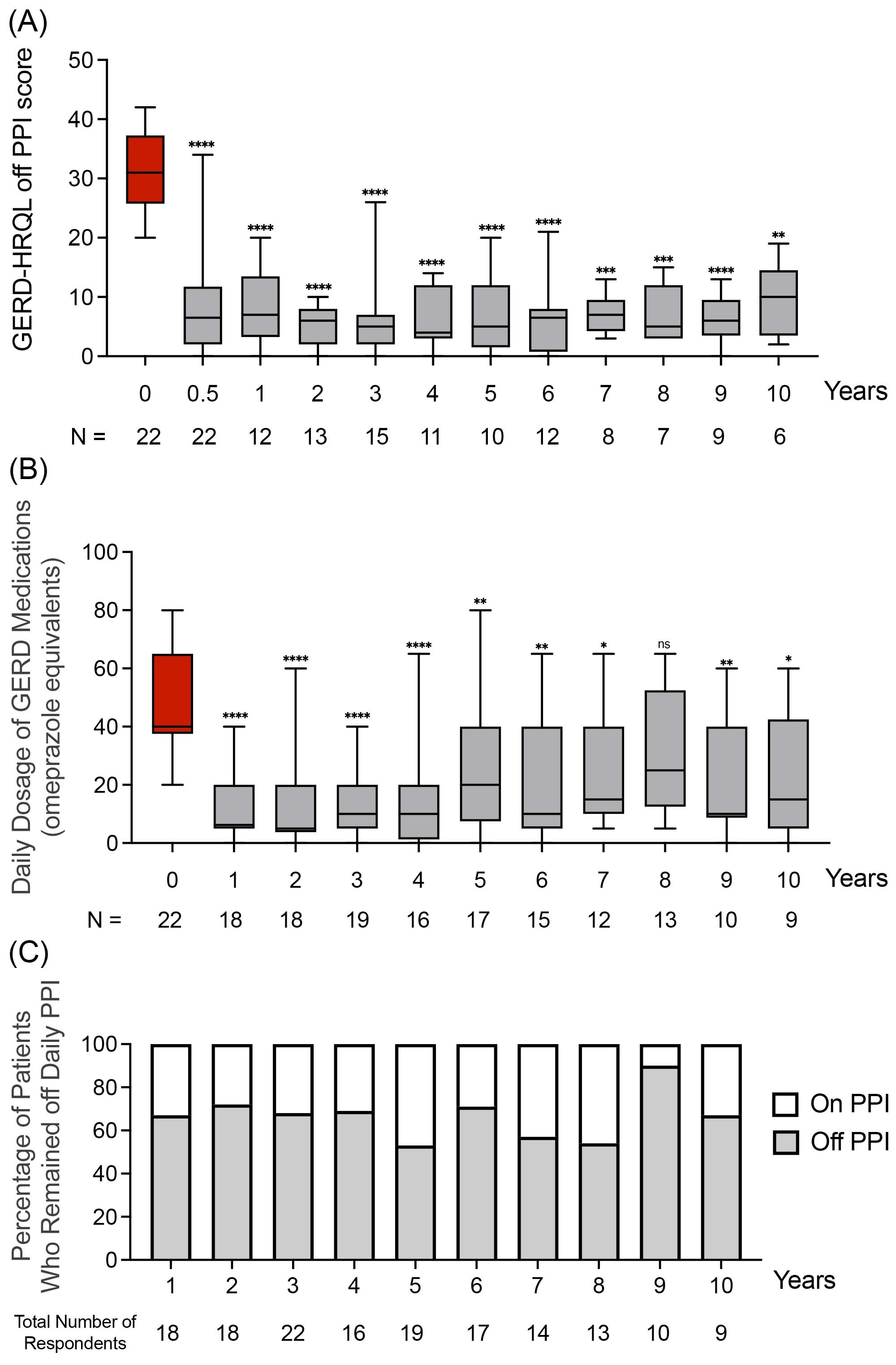
Results: The GERD-HRQL scores (mean ± SD) off PPI post-procedure were significantly lower at each annual follow up visit (7.07 ± 5.74) when compared to baseline scores (31.27 ± 6.45; Figure 1A). The dose of GERD medications, measured annually by omeprazole equivalents (mean ± SD), was significantly reduced at post-procedure follow up visits (21.19 ± 18.77) when compared to pre-procedure baseline (47.73 ± 21.37; Figure 1B). The average proportion of patients who remained off PPI during the follow up period was 70.8% ± 10.7% (Figure 1C).
Discussion: In this prospective study, the efficacy profile of the MUSETM endoscopic stapling device was shown to be preserved for at least 10 years post-procedure. The measures include improved GERD symptom scores as well as decreased GERD medication dosages. Future research with larger sample sizes and controls are needed to better compare and evaluate the efficacy and safety outcomes of the MUSETM stapling device.
Disclosures:
Tarek G. Aridi, MD1, Gail McNulty, RN, BSN, CCRC1, Glen Lehman, MD, FACG1, William Kessler, MD, FACG2, Mark A. Gromski, MD1. P4498 - Long-Term Clinical Outcomes After Endoscopic Stapling System Therapy of Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 2Indiana University School of Medicine, Zionsville, IN
Introduction: The MUSETM (MEDIGUS) endoscopic stapling device has been shown to improve GERD symptoms over 6-month (Zacherl et al. Surg Endosc 29(1):220–229, 2014) and 4-year (Kim et al. Surg Endosc 30(8):3402–3408, 2015) time periods. This study aims to explore the long-term outcomes of this treatment after 10 years of follow up.
Methods: 25 patients with GERD underwent MUSE procedure between years 2008 and 2016. 8 evaluable patients were lost to follow up between years 1 and 9. Efficacy data over a 10-year follow up period was analyzed at annual intervals and compared to baseline. The primary outcome was an improvement in GERD health-related quality of life (HRQL) score. Secondary outcomes included GERD medication dose reduction measured by omeprazole equivalents annually over the duration of follow up.
Results: The GERD-HRQL scores (mean ± SD) off PPI post-procedure were significantly lower at each annual follow up visit (7.07 ± 5.74) when compared to baseline scores (31.27 ± 6.45; Figure 1A). The dose of GERD medications, measured annually by omeprazole equivalents (mean ± SD), was significantly reduced at post-procedure follow up visits (21.19 ± 18.77) when compared to pre-procedure baseline (47.73 ± 21.37; Figure 1B). The average proportion of patients who remained off PPI during the follow up period was 70.8% ± 10.7% (Figure 1C).
Discussion: In this prospective study, the efficacy profile of the MUSETM endoscopic stapling device was shown to be preserved for at least 10 years post-procedure. The measures include improved GERD symptom scores as well as decreased GERD medication dosages. Future research with larger sample sizes and controls are needed to better compare and evaluate the efficacy and safety outcomes of the MUSETM stapling device.

Figure: A) GERD-HRQL scores, off PPI, at follow up visits post-procedure compared to pre-procedure baseline, B) daily dose of GERD medications measured in omeprazole equivalents at follow up visits post-procedure compared to pre-procedure baseline, by ANOVA-Kruskal-Walls tests. C) Proportion of patients who remained off daily PPI annually measured as a percentage of total number of patients who reported their GERD medications at each follow up visit. P-values: ✱✱✱✱: p<0.0001, ✱✱✱: p<0.001, ✱✱: p<0.01, ✱: p<0.05, ns: not significant. N: the number of patients completing the HRQL scoring or reported GERD medication dosages at each follow up visit.
Disclosures:
Tarek Aridi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gail McNulty indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Glen Lehman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
William Kessler indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mark Gromski: Allurion – Grant/Research Support. Ambu – Consultant. Boston Scientific – Consultant. Cook Medical – Grant/Research Support. Fractyl – Grant/Research Support.
Tarek G. Aridi, MD1, Gail McNulty, RN, BSN, CCRC1, Glen Lehman, MD, FACG1, William Kessler, MD, FACG2, Mark A. Gromski, MD1. P4498 - Long-Term Clinical Outcomes After Endoscopic Stapling System Therapy of Patients With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
