Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P4637 - Safety and Efficacy of Pegozafermin for Treatment of MASH and Hypertriglyceridemia: A Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Muhammad Tayyab Anwar, MD
John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Rameez Akram Tarar, MD1, Hamza Naeem, MD1, Muhammad Tayyab Anwar, MD2, Anzal Abdullah, 3, Sibgha Farooq, MBBS3, Muhammad Bilal Ibrahim, MD2, Ayobami Olafimihan, MD2, Umar Abdul Rehman Khalid, MD1, Khadija Shahjahan, MBBS3, Muhammad Nouman Aslam, MD1, Ahsan Naeem, MBBS3, Zeeshan Tariq Khan, MD4
1King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL; 3University of Health Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Washington State University Elson S. Floyd School of Medicine, Spokane, WA
Introduction: MASLD (Metabolic Associated Steatotic Liver Disease), previously known as NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) is a growing problem worldwide and especially in the United States. It can lead to liver cirrhosis if left untreated. Currently, only lifestyle modifications and one FDA-approved drug are being used as treatment options for MASLD. Among the drugs under testing, the most promising results are shown by Pegozafermin. In this meta-analysis, we discuss the safety and efficacy of this drug in phases 1 and 2 of clinical trials for potential FDA approval.
Methods: We searched Randomized control trials (RCTs) from the start to December 2023 on different databases, including PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, Cochrane Library, Embase, BioMed Central, ICTRP, and ClinicalTrials.gov. The studies meeting the inclusion criteria were included. Data was analyzed and mean differences were calculated.
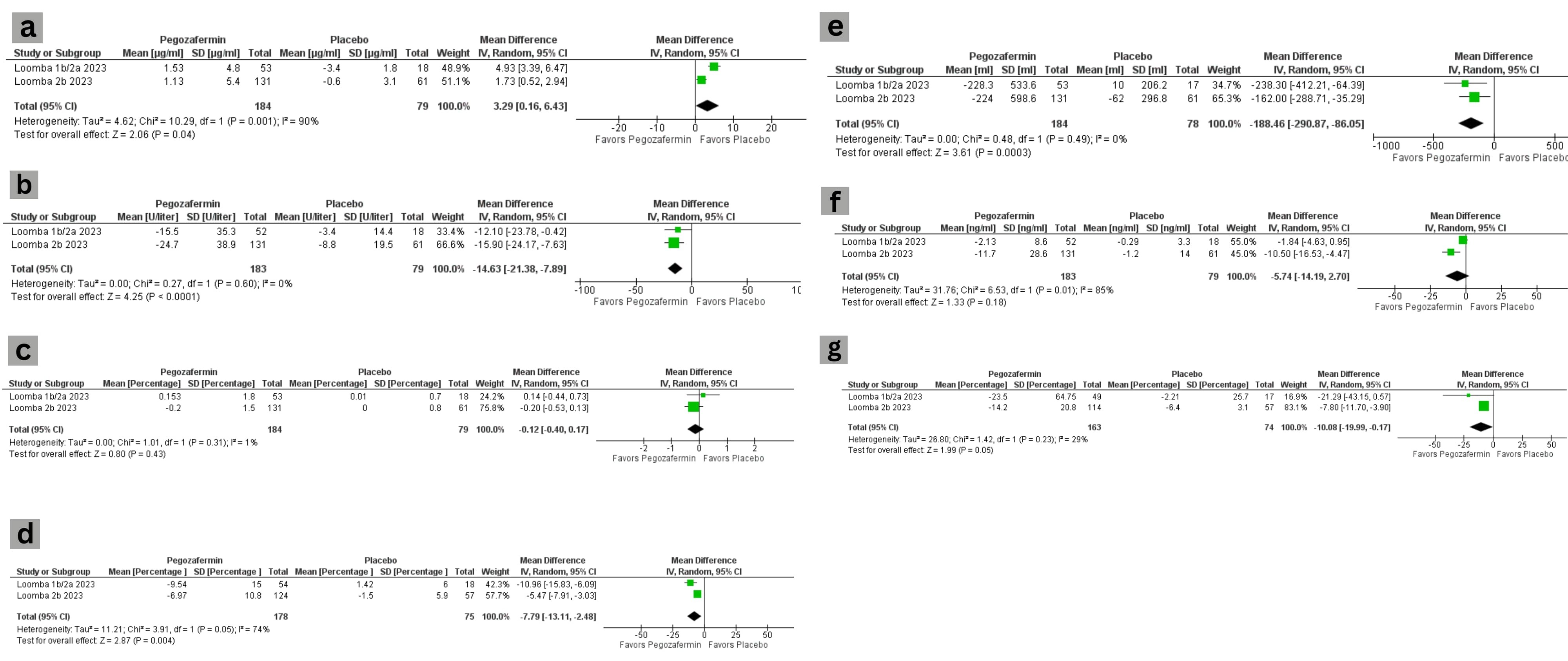
Results: 247 patients in 3 RCTs were included in the study. The results showed that Pegozafermin increased adiponectin levels and decreased ALT levels, serum triglyceride levels. Moreover, it also showed that the Pegozafermin group had decreased liver volume (Combined effect: -208.96 ml, p < 0.0001) and decreased liver fat content (-8.36%) as compared to the placebo as shown in figure 1. The adverse effects only included nausea and increased appetite.
Discussion: Hypertriglyceridemia, liver fat content, and liver volume have a positive correlation with the development of MASLD. The meta-analysis shows that Pegozafermin can manage it by decreasing these parameters significantly as compared to the placebo. Therefore, it holds a promising future in the treatment of MASLD and it has good safety profile.
Disclosures:
Rameez Akram Tarar, MD1, Hamza Naeem, MD1, Muhammad Tayyab Anwar, MD2, Anzal Abdullah, 3, Sibgha Farooq, MBBS3, Muhammad Bilal Ibrahim, MD2, Ayobami Olafimihan, MD2, Umar Abdul Rehman Khalid, MD1, Khadija Shahjahan, MBBS3, Muhammad Nouman Aslam, MD1, Ahsan Naeem, MBBS3, Zeeshan Tariq Khan, MD4. P4637 - Safety and Efficacy of Pegozafermin for Treatment of MASH and Hypertriglyceridemia: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 2John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL; 3University of Health Sciences, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 4Washington State University Elson S. Floyd School of Medicine, Spokane, WA
Introduction: MASLD (Metabolic Associated Steatotic Liver Disease), previously known as NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) is a growing problem worldwide and especially in the United States. It can lead to liver cirrhosis if left untreated. Currently, only lifestyle modifications and one FDA-approved drug are being used as treatment options for MASLD. Among the drugs under testing, the most promising results are shown by Pegozafermin. In this meta-analysis, we discuss the safety and efficacy of this drug in phases 1 and 2 of clinical trials for potential FDA approval.
Methods: We searched Randomized control trials (RCTs) from the start to December 2023 on different databases, including PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, Cochrane Library, Embase, BioMed Central, ICTRP, and ClinicalTrials.gov. The studies meeting the inclusion criteria were included. Data was analyzed and mean differences were calculated.
Results: 247 patients in 3 RCTs were included in the study. The results showed that Pegozafermin increased adiponectin levels and decreased ALT levels, serum triglyceride levels. Moreover, it also showed that the Pegozafermin group had decreased liver volume (Combined effect: -208.96 ml, p < 0.0001) and decreased liver fat content (-8.36%) as compared to the placebo as shown in figure 1. The adverse effects only included nausea and increased appetite.
Discussion: Hypertriglyceridemia, liver fat content, and liver volume have a positive correlation with the development of MASLD. The meta-analysis shows that Pegozafermin can manage it by decreasing these parameters significantly as compared to the placebo. Therefore, it holds a promising future in the treatment of MASLD and it has good safety profile.

Figure: Figure 1. Safety and Efficacy of Pegozafermin for the Treatment of NASH and Hypertriglyceridemia
Disclosures:
Rameez Akram Tarar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hamza Naeem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Tayyab Anwar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anzal Abdullah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sibgha Farooq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Bilal Ibrahim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayobami Olafimihan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Abdul Rehman Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khadija Shahjahan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Nouman Aslam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahsan Naeem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zeeshan Tariq Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rameez Akram Tarar, MD1, Hamza Naeem, MD1, Muhammad Tayyab Anwar, MD2, Anzal Abdullah, 3, Sibgha Farooq, MBBS3, Muhammad Bilal Ibrahim, MD2, Ayobami Olafimihan, MD2, Umar Abdul Rehman Khalid, MD1, Khadija Shahjahan, MBBS3, Muhammad Nouman Aslam, MD1, Ahsan Naeem, MBBS3, Zeeshan Tariq Khan, MD4. P4637 - Safety and Efficacy of Pegozafermin for Treatment of MASH and Hypertriglyceridemia: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
