Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P4651 - Implementing MASLD Screening Using FIB-4 Index in Diabetic Patients: PI/QI Project in a Resident-Driven Clinic in Trenton, NJ
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Lucinda Dass, MD
Capital Health Regional Medical Center
Trenton, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Lucinda Dass, MD, MPH, Mahmoud Abdelwahab, MBBCh, Deep Mehta, MD, Syeda Afzal, MD, Nazish Najeeb, MD, Narine Misakyan, MD, Anand Kaji, MD
Capital Health Regional Medical Center, Trenton, NJ
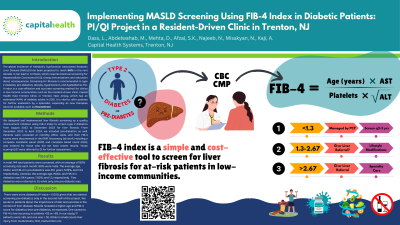
Introduction: The global incidence of Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) has been projected to reach 56% in the next decade. It can lead to cirrhosis, which requires biannual screening for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), timely immunizations, and education about consequences. Screening for fibrosis is recommended in type 2 diabetics (T2DM), pre-diabetics, obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. FIB-4 index is a cost-effective and accurate screening method for clinics in low-income communities such as the resident-driven clinic, Capital Health East Trenton Clinic, in Trenton, New Jersey. Trenton has an estimated 14.4% of diabetic adults in 2021. It is vital to refer patients to a specialist, especially as new therapies become available, such as Resmetirom.
Methods: We designed and implemented liver fibrosis screening as a quality improvement initiative using FIB-4 index to screen type 2 diabetics from August 2023 to December 2023 for liver fibrosis. From December 2023 to April 2024, we included pre-diabetics as well. Patients were screened at monthly office visits, and their FIB-4 scores were documented in the EMR. Necessary lab work, including a complete metabolic panel (CMP) and complete blood count (CBC), was ordered for those who did not have recent results. Those scoring >2.67 were referred to Gastroenterology (GI) for further assessment.
Results: In total, 144 total patients were screened, with an average of 82% screening rate per month. Overall, 66% were male. The average age, HbA1c, and FIB-4 in pre-diabetics was 45.1 years, 5.78%, and 1.04 respectively. Likewise, the average age, HbA1c, and FIB-4 in diabetics was 54.4 years, 7.62%, and 1.3, respectively. Overall, 3 patients were referred to GI.
Discussion: There was no existing screening process for liver fibrosis at the clinic. We used FIB-4 score as a cost-effective method. There were more diabetics (P-value < 0.001), given that we started screening pre-diabetics only in the second half of the project. We used monthly office visits to start this conversation with patients, stressing the importance of diet and exercise in yet another context. Results reveal a higher age and FIB-4 score for diabetics than prediabetics, as expected. Two diabetics were referred to GI, while only one prediabetic was. We recognized caveats to FIB-4, including low accuracy in patients < 35 or >65. In our study, 17 patients were >65, and one was < 35. Going forward, we will adhere to these parameters to fine-tune our screening.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Lucinda Dass, MD, MPH, Mahmoud Abdelwahab, MBBCh, Deep Mehta, MD, Syeda Afzal, MD, Nazish Najeeb, MD, Narine Misakyan, MD, Anand Kaji, MD. P4651 - Implementing MASLD Screening Using FIB-4 Index in Diabetic Patients: PI/QI Project in a Resident-Driven Clinic in Trenton, NJ, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Capital Health Regional Medical Center, Trenton, NJ
Introduction: The global incidence of Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) has been projected to reach 56% in the next decade. It can lead to cirrhosis, which requires biannual screening for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), timely immunizations, and education about consequences. Screening for fibrosis is recommended in type 2 diabetics (T2DM), pre-diabetics, obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. FIB-4 index is a cost-effective and accurate screening method for clinics in low-income communities such as the resident-driven clinic, Capital Health East Trenton Clinic, in Trenton, New Jersey. Trenton has an estimated 14.4% of diabetic adults in 2021. It is vital to refer patients to a specialist, especially as new therapies become available, such as Resmetirom.
Methods: We designed and implemented liver fibrosis screening as a quality improvement initiative using FIB-4 index to screen type 2 diabetics from August 2023 to December 2023 for liver fibrosis. From December 2023 to April 2024, we included pre-diabetics as well. Patients were screened at monthly office visits, and their FIB-4 scores were documented in the EMR. Necessary lab work, including a complete metabolic panel (CMP) and complete blood count (CBC), was ordered for those who did not have recent results. Those scoring >2.67 were referred to Gastroenterology (GI) for further assessment.
Results: In total, 144 total patients were screened, with an average of 82% screening rate per month. Overall, 66% were male. The average age, HbA1c, and FIB-4 in pre-diabetics was 45.1 years, 5.78%, and 1.04 respectively. Likewise, the average age, HbA1c, and FIB-4 in diabetics was 54.4 years, 7.62%, and 1.3, respectively. Overall, 3 patients were referred to GI.
Discussion: There was no existing screening process for liver fibrosis at the clinic. We used FIB-4 score as a cost-effective method. There were more diabetics (P-value < 0.001), given that we started screening pre-diabetics only in the second half of the project. We used monthly office visits to start this conversation with patients, stressing the importance of diet and exercise in yet another context. Results reveal a higher age and FIB-4 score for diabetics than prediabetics, as expected. Two diabetics were referred to GI, while only one prediabetic was. We recognized caveats to FIB-4, including low accuracy in patients < 35 or >65. In our study, 17 patients were >65, and one was < 35. Going forward, we will adhere to these parameters to fine-tune our screening.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Lucinda Dass indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahmoud Abdelwahab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Deep Mehta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syeda Afzal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nazish Najeeb indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Narine Misakyan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anand Kaji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lucinda Dass, MD, MPH, Mahmoud Abdelwahab, MBBCh, Deep Mehta, MD, Syeda Afzal, MD, Nazish Najeeb, MD, Narine Misakyan, MD, Anand Kaji, MD. P4651 - Implementing MASLD Screening Using FIB-4 Index in Diabetic Patients: PI/QI Project in a Resident-Driven Clinic in Trenton, NJ, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
