Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P4660 - Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Electrocardiogram Can Successfully Predict Post-Liver Transplant Atrial Fibrillation
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- IN
Induja R. Nimma, MD
Mayo Clinic
Jacksonville, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Induja R. Nimma, MD1, Lydia A. Mercado, MD1, Anupam Halder, MD2, Kripa Rajak, MD2, Smit Paghdar, MD1, Denise Harnois, DO1, Rohan Goswami, MD1
1Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL; 2UPMC, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Patients with liver disease may carry several risk factors for atrial fibrillation (AF) such as alcohol use, obesity, and diabetes. AF can also develop after liver transplantation (LT) and can lead to devastating patient outcomes. Our goal is to improve patient health by predicting which patients are more likely to develop new onset atrial fibrillation (NOAF), prior to LT, using an artificial intelligence enhanced electrocardiogram model (AIEECG).
Methods: A retrospective review of 234 patients, who underwent liver transplantation from January 2015 to December 2021 at Mayo Clinic, was performed. Patient data was collected on hospital admission and outcomes, particularly focusing on cardiac complications and hospital length of stay. A currently implemented artificial intelligence enhanced electrocardiogram (AIEECG) model was utilized to generate predictive indices with machine learning using cross entropy. Patients with or without NOAF after LT were compared to the original AIEECG prediction for AF risk.
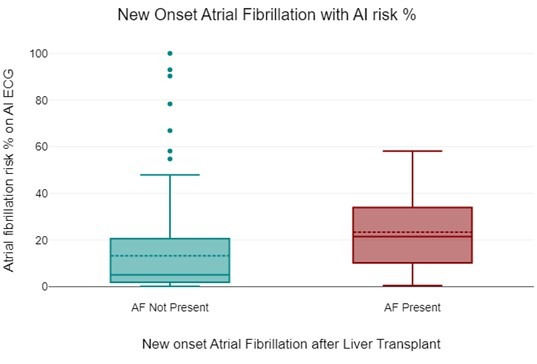
Results: 234 patients underwent LT during our study period and had pre and post operative AIEECG data. Eighteen percent of patients developed NOAF after liver transplantation. Forty percent of patients were female. Majority were caucasian. Mortality was 16% on follow up. Liver failure was most commonly due to MASH (32%), hepatitis C (19%), hepatocellular carcinoma (24%), alcohol associated liver disease (24%), and autoimmune hepatitis (4%). Pre-operative AIEECG prediction of AF risk accurately translated to post-operative observations of NOAF (23% vs 13%), p=.001 with a T(230) of -3.37 and a 95% confidence interval of -16.09 to -4.19. NOAF was also associated with an increased post-LT hospital length of stay (LOS) compared to those without NOAF, 24 vs. 13 days, p = .006 after LT.
Discussion: We demonstrate the novel application of an AIEECG model prior to liver transplant that accurately predicts the development of NOAF after LT. Identifying patients at increased risk through a simple 12 lead ECG may allow improvements in length of stay, post-transplant complications, and health care associated costs in this population.
Disclosures:
Induja R. Nimma, MD1, Lydia A. Mercado, MD1, Anupam Halder, MD2, Kripa Rajak, MD2, Smit Paghdar, MD1, Denise Harnois, DO1, Rohan Goswami, MD1. P4660 - Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Electrocardiogram Can Successfully Predict Post-Liver Transplant Atrial Fibrillation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL; 2UPMC, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Patients with liver disease may carry several risk factors for atrial fibrillation (AF) such as alcohol use, obesity, and diabetes. AF can also develop after liver transplantation (LT) and can lead to devastating patient outcomes. Our goal is to improve patient health by predicting which patients are more likely to develop new onset atrial fibrillation (NOAF), prior to LT, using an artificial intelligence enhanced electrocardiogram model (AIEECG).
Methods: A retrospective review of 234 patients, who underwent liver transplantation from January 2015 to December 2021 at Mayo Clinic, was performed. Patient data was collected on hospital admission and outcomes, particularly focusing on cardiac complications and hospital length of stay. A currently implemented artificial intelligence enhanced electrocardiogram (AIEECG) model was utilized to generate predictive indices with machine learning using cross entropy. Patients with or without NOAF after LT were compared to the original AIEECG prediction for AF risk.
Results: 234 patients underwent LT during our study period and had pre and post operative AIEECG data. Eighteen percent of patients developed NOAF after liver transplantation. Forty percent of patients were female. Majority were caucasian. Mortality was 16% on follow up. Liver failure was most commonly due to MASH (32%), hepatitis C (19%), hepatocellular carcinoma (24%), alcohol associated liver disease (24%), and autoimmune hepatitis (4%). Pre-operative AIEECG prediction of AF risk accurately translated to post-operative observations of NOAF (23% vs 13%), p=.001 with a T(230) of -3.37 and a 95% confidence interval of -16.09 to -4.19. NOAF was also associated with an increased post-LT hospital length of stay (LOS) compared to those without NOAF, 24 vs. 13 days, p = .006 after LT.
Discussion: We demonstrate the novel application of an AIEECG model prior to liver transplant that accurately predicts the development of NOAF after LT. Identifying patients at increased risk through a simple 12 lead ECG may allow improvements in length of stay, post-transplant complications, and health care associated costs in this population.

Figure: Presence of new onset atrial fibrillation (AF) with artificial intelligence enhanced electrocardiogram with AF risk percentage.
Disclosures:
Induja Nimma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lydia Mercado indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anupam Halder indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kripa Rajak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Smit Paghdar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Denise Harnois indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohan Goswami indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Induja R. Nimma, MD1, Lydia A. Mercado, MD1, Anupam Halder, MD2, Kripa Rajak, MD2, Smit Paghdar, MD1, Denise Harnois, DO1, Rohan Goswami, MD1. P4660 - Artificial Intelligence-Enhanced Electrocardiogram Can Successfully Predict Post-Liver Transplant Atrial Fibrillation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

