Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Obesity
P4885 - Combination Therapy of Glucagon-Like-Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Endoscopic Gastric Plication in Obesity Population: A Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Noppachai Siranart, MD
Brigham and Women's Hospital
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Noppachai Siranart, MD1, Patavee Pajareya, MD2, Rinrada Worapongpaiboon, 2, Chanattha Thimphitthaya, MD3, Natchaya Polpichai, MD4, Somkiat Phutinart, 5, Emily Shu-Yen Chan, MD, MSc4, Panisara Fangsaard, MD6, Pojsakorn Danpanichkul, MD7, Ponthakorn Kaewkanha, MD8
1Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA; 2King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Bangkok, Krung Thep, Thailand; 3University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 4Weiss Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL; 5Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Krung Thep, Thailand; 6Bassett Medical Center, Cooperstown, NY; 7Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Lubbock, TX; 8King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Phayathai, Krung Thep, Thailand
Introduction: Recent advancements in obesity treatment have demonstrated promising results with both endoscopic gastric plication (EGP) and glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs). Combining these two therapies may further enhance therapeutic outcomes. This study evaluates the efficacy and safety of the combination therapy (EGP+GLP-1 RAs) in patients with obesity.
Methods: A literature search was conducted up until May 2024 to select studies comparing the outcomes between the combination therapy and EGP monotherapy group. The primary endpoint was total body weight loss (%TBWL). Secondary endpoints were excess weight loss (%EWL) and adverse events. A random-effects model and subgroup analysis were performed to pool mean differences and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
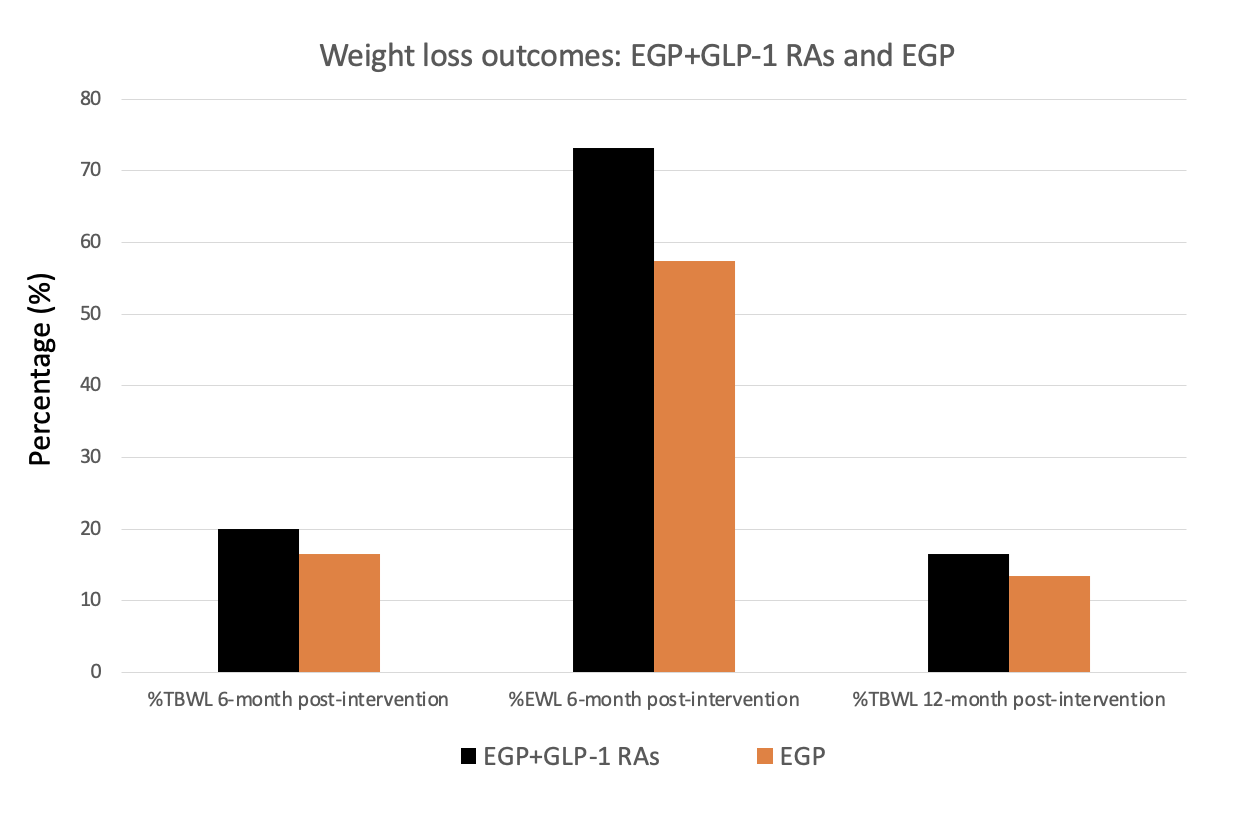
Results: Out of 24,381 search results, a total of 4 studies were included, comprising 1,505 obese adult patients (1,378 EGP, 127 EGP+GLP-1 RAs). In the EGP+GLP-1 RAs group, the patients reached 20.05% [95% CI: 9.38-30.73] TBWL, 73.19% [95% CI: 19.86-126.53] EWL at the 6-month post-intervention, and 16.50% [95% CI: -4.46 to 37.46] TBWL at the 12-month post-intervention. In the EGP group, the patients reached 16.56% [95% CI: 9.28-23.85] TBWL, 57.40% [95% CI: 38.47-76.33] EWL at the 6-month post-intervention, and 13.49% [95% CI: -34.77 to 61.76] TBWL at the 12-month post-intervention. EGP+GLP-1 RAs seem to have higher and long-term durability for weight loss outcome although, insignificant differences were noted between both groups. Subgroup analysis by type of GLP-1 RAs showed that semaglutide seems to have the highest efficacy for weight reduction with 22.01% TBWL, followed by liraglutide with 18.26% TBWL, and dulaglutide with 15.80% TBWL at the 6-month post-intervention. The statistics showed no significant differences between these medications (p = 0.78). Both groups had a low rate of adverse events, with no difference between groups. Most common adverse event is mild nausea in patients who received GLP-1 RAs.
Discussion: GLP-1 RAs are safe when combined with EGP, resulting in significant and sustainable weight loss.
Disclosures:
Noppachai Siranart, MD1, Patavee Pajareya, MD2, Rinrada Worapongpaiboon, 2, Chanattha Thimphitthaya, MD3, Natchaya Polpichai, MD4, Somkiat Phutinart, 5, Emily Shu-Yen Chan, MD, MSc4, Panisara Fangsaard, MD6, Pojsakorn Danpanichkul, MD7, Ponthakorn Kaewkanha, MD8. P4885 - Combination Therapy of Glucagon-Like-Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Endoscopic Gastric Plication in Obesity Population: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA; 2King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Bangkok, Krung Thep, Thailand; 3University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 4Weiss Memorial Hospital, Chicago, IL; 5Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Krung Thep, Thailand; 6Bassett Medical Center, Cooperstown, NY; 7Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, Lubbock, TX; 8King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Phayathai, Krung Thep, Thailand
Introduction: Recent advancements in obesity treatment have demonstrated promising results with both endoscopic gastric plication (EGP) and glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs). Combining these two therapies may further enhance therapeutic outcomes. This study evaluates the efficacy and safety of the combination therapy (EGP+GLP-1 RAs) in patients with obesity.
Methods: A literature search was conducted up until May 2024 to select studies comparing the outcomes between the combination therapy and EGP monotherapy group. The primary endpoint was total body weight loss (%TBWL). Secondary endpoints were excess weight loss (%EWL) and adverse events. A random-effects model and subgroup analysis were performed to pool mean differences and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results: Out of 24,381 search results, a total of 4 studies were included, comprising 1,505 obese adult patients (1,378 EGP, 127 EGP+GLP-1 RAs). In the EGP+GLP-1 RAs group, the patients reached 20.05% [95% CI: 9.38-30.73] TBWL, 73.19% [95% CI: 19.86-126.53] EWL at the 6-month post-intervention, and 16.50% [95% CI: -4.46 to 37.46] TBWL at the 12-month post-intervention. In the EGP group, the patients reached 16.56% [95% CI: 9.28-23.85] TBWL, 57.40% [95% CI: 38.47-76.33] EWL at the 6-month post-intervention, and 13.49% [95% CI: -34.77 to 61.76] TBWL at the 12-month post-intervention. EGP+GLP-1 RAs seem to have higher and long-term durability for weight loss outcome although, insignificant differences were noted between both groups. Subgroup analysis by type of GLP-1 RAs showed that semaglutide seems to have the highest efficacy for weight reduction with 22.01% TBWL, followed by liraglutide with 18.26% TBWL, and dulaglutide with 15.80% TBWL at the 6-month post-intervention. The statistics showed no significant differences between these medications (p = 0.78). Both groups had a low rate of adverse events, with no difference between groups. Most common adverse event is mild nausea in patients who received GLP-1 RAs.
Discussion: GLP-1 RAs are safe when combined with EGP, resulting in significant and sustainable weight loss.

Figure: Figure 1. Weight loss outcomes comparing between EGP monotherapy and EGP+GLP-1 RAs
Disclosures:
Noppachai Siranart indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patavee Pajareya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rinrada Worapongpaiboon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chanattha Thimphitthaya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Natchaya Polpichai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Somkiat Phutinart indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Emily Shu-Yen Chan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Panisara Fangsaard indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pojsakorn Danpanichkul indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ponthakorn Kaewkanha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noppachai Siranart, MD1, Patavee Pajareya, MD2, Rinrada Worapongpaiboon, 2, Chanattha Thimphitthaya, MD3, Natchaya Polpichai, MD4, Somkiat Phutinart, 5, Emily Shu-Yen Chan, MD, MSc4, Panisara Fangsaard, MD6, Pojsakorn Danpanichkul, MD7, Ponthakorn Kaewkanha, MD8. P4885 - Combination Therapy of Glucagon-Like-Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Endoscopic Gastric Plication in Obesity Population: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
