Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P4963 - From SNF to Oncology Clinic: A Patient with Metastatic Duodenal Adenocarcinoma Masquerading as Pancreatic Malignancy
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- NR
Nikhil Roy Chaudhury, MD
Medical City Fort Worth
Fort Worth, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Nikhil Roy Chaudhury, MD1, Adair Kerrison, MS2, Long Hoang, DO3, Monte Trouman, DO2
1Medical City Fort Worth, Fort Worth, TX; 2University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, TX; 3HCA MCFW, Fort Worth, TX
Introduction: Duodenal adenocarcinomas are rare, forming less than 5% of GI cancers despite the small bowel being 90% of the GI tract surface area. It’s rarity and non-specific presentation delays diagnosis with the initial encounter often in the advanced stages of disease. We present a case of metastatic duodenal adenocarcinoma that will add to the current literature to aid diagnosis of this uncommon condition.
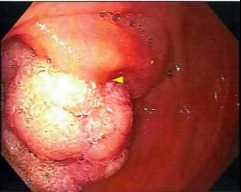
Case Description/Methods: A 59 yo AAM with Hx of sigmoid loop colostomy 2/2 non healing sacral ulcer presented from nursing home with 2 weeks of diffuse non-radiating abdominal pain, reduced appetite, weight loss, chills and nausea. He was unable to eat solid foods but tolerated liquids. He reported "soup like" stools in his colostomy bag. He endorsed twice weekly NSAID use and iron supplementation but denied tobacco, alcohol and Hx of cancer. Exam was notable for diffuse abdominal tenderness and significant volume of loose, tan colored stool in ostomy bag. Admission labs showed elevated ALP 794, AST 189, ALT 82, Tbil 2.5, Hb 9, MCV 77. CT showed left adrenal nodule, many pulmonary lung nodules and nodular liver with many hypodense masses concerning for metastasis; no biliary dilation was noted. Stool studies were positive for CDiff. Tumor markers notable for CEA 124, CA 19-9 51113. Elevated CA19-9 and LFT aberrations suggested pancreatic lesion so EUS was ordered for evaluation. On visualization a large frond-like/villous, fungating, infiltrative and polypoid mass was noted in the 3rd portion of the duodenum. Liver Bx and left adrenal FNA verified pathology of duodenal mass yielding invasive moderately differentiated ACC. No MMR gene defects were noted. Oral antibiotics were started for CDiff and oncology was called for metastatic moderately differentiated duodenal ACC. Outpatient chemotherapy was recommended due to metastatic burden and poor surgical candidacy.
Discussion: The CA19-9 elevation and concomitant CDiff in a rare pathology make this case unique. CA19-9 can differentiate benign and malignant pancreatic disorders but no pancreatic involvement was noted in this patient. The presence of CDiff also raises possible oncogenic contribution. Although no malignant potential has been established akin to H pylori and gastric cancer, there is evidence connecting colonic microbiome disruption to oncogenic induction and a similar process may have occurred in this patient. His chronic conditions and Hx of bowel surgery may have aided induction of oncogenic potential in which CDiff may have contributed.
Disclosures:
Nikhil Roy Chaudhury, MD1, Adair Kerrison, MS2, Long Hoang, DO3, Monte Trouman, DO2. P4963 - From SNF to Oncology Clinic: A Patient with Metastatic Duodenal Adenocarcinoma Masquerading as Pancreatic Malignancy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Medical City Fort Worth, Fort Worth, TX; 2University of North Texas Health Science Center, Fort Worth, TX; 3HCA MCFW, Fort Worth, TX
Introduction: Duodenal adenocarcinomas are rare, forming less than 5% of GI cancers despite the small bowel being 90% of the GI tract surface area. It’s rarity and non-specific presentation delays diagnosis with the initial encounter often in the advanced stages of disease. We present a case of metastatic duodenal adenocarcinoma that will add to the current literature to aid diagnosis of this uncommon condition.
Case Description/Methods: A 59 yo AAM with Hx of sigmoid loop colostomy 2/2 non healing sacral ulcer presented from nursing home with 2 weeks of diffuse non-radiating abdominal pain, reduced appetite, weight loss, chills and nausea. He was unable to eat solid foods but tolerated liquids. He reported "soup like" stools in his colostomy bag. He endorsed twice weekly NSAID use and iron supplementation but denied tobacco, alcohol and Hx of cancer. Exam was notable for diffuse abdominal tenderness and significant volume of loose, tan colored stool in ostomy bag. Admission labs showed elevated ALP 794, AST 189, ALT 82, Tbil 2.5, Hb 9, MCV 77. CT showed left adrenal nodule, many pulmonary lung nodules and nodular liver with many hypodense masses concerning for metastasis; no biliary dilation was noted. Stool studies were positive for CDiff. Tumor markers notable for CEA 124, CA 19-9 51113. Elevated CA19-9 and LFT aberrations suggested pancreatic lesion so EUS was ordered for evaluation. On visualization a large frond-like/villous, fungating, infiltrative and polypoid mass was noted in the 3rd portion of the duodenum. Liver Bx and left adrenal FNA verified pathology of duodenal mass yielding invasive moderately differentiated ACC. No MMR gene defects were noted. Oral antibiotics were started for CDiff and oncology was called for metastatic moderately differentiated duodenal ACC. Outpatient chemotherapy was recommended due to metastatic burden and poor surgical candidacy.
Discussion: The CA19-9 elevation and concomitant CDiff in a rare pathology make this case unique. CA19-9 can differentiate benign and malignant pancreatic disorders but no pancreatic involvement was noted in this patient. The presence of CDiff also raises possible oncogenic contribution. Although no malignant potential has been established akin to H pylori and gastric cancer, there is evidence connecting colonic microbiome disruption to oncogenic induction and a similar process may have occurred in this patient. His chronic conditions and Hx of bowel surgery may have aided induction of oncogenic potential in which CDiff may have contributed.

Figure: Large frond-like/villous, fungating, infiltrative and polypoid mass in the 3rd portion of the duodenum
Disclosures:
Nikhil Roy Chaudhury indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adair Kerrison indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Long Hoang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monte Trouman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nikhil Roy Chaudhury, MD1, Adair Kerrison, MS2, Long Hoang, DO3, Monte Trouman, DO2. P4963 - From SNF to Oncology Clinic: A Patient with Metastatic Duodenal Adenocarcinoma Masquerading as Pancreatic Malignancy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
