Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Stomach
P5042 - The Effect of GLP-1 RA Use on Gastric Emptying and Gastroparesis Symptoms in Patients With Diabetic Gastroparesis: A Systematic Review
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Sudheer M. Dhoop, MD
University of Toledo College Medicine and Life Sciences
Toledo, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Jacob Itkin, BS1, Sudheer M.. Dhoop, MD2, Thomas Sodeman, MD3
1University of Toledo College Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH; 2University of Toledo College Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, MI; 3University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Gastroparesis (GP) is a condition characterized by delayed gastric emptying without mechanical obstruction commonly observed in patients with diabetes mellitus, often due to autonomic neuropathy. The use of GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in diabetes management is on the risk and has raised concerns about their potential to exacerbate gastroparesis. This review aims to summarize the findings from various studies investigating the relationship between GLP-1 RAs and Gastric Emptying in Diabetic Gastroparesis.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in Embase (Embase.com, Elsevier) on 23 May 2024 by an experienced health sciences librarian (W.L.S.) using various advanced search techniques. The search was replicated in MEDLINE (OVID), Cochrane Central, Web of Science Core Collection, Korean Citation Index, SciELO, and Global Index Medicus (see Supplementary Table 1), with no publication date or language limits. Results were exported to EndNote 20, where duplicates were removed using EndNote's algorithms and manual inspection (see Supplementary Table 2). We included all studies with a population of patients with diabetic gastroparesis where GLP-1 RAs were studied as an intervention and measured gastric emptying by breath or gastric emptying testing and considered retrospective and prospective studies as well as randomized controlled trials. Other reviews were excluded.
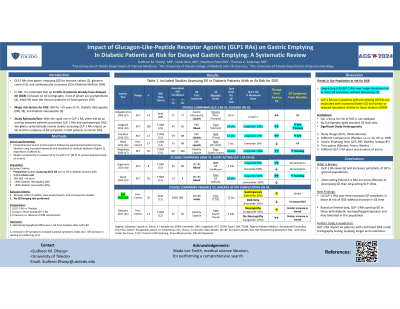
Results: 10 studies from 2003 to 2024 including 3 with breath testing, 6 with various gastric emptying tests, and 1 with ultrasound were included. 6 out of 10 studies found a significant association between GLP-1 RA use and gastroparesis symptoms but only 4 out 10 studies found a significant association between GLP-1 RA use and delayed gastric emptying measured by imaging test.
Discussion: There is conflicting data on the effect GLP-1 RAs have on gastroparesis symptoms and gastric emptying on patients with diabetic gastroparesis and higher quality data including randomized controlled trials are needed.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Jacob Itkin, BS1, Sudheer M.. Dhoop, MD2, Thomas Sodeman, MD3. P5042 - The Effect of GLP-1 RA Use on Gastric Emptying and Gastroparesis Symptoms in Patients With Diabetic Gastroparesis: A Systematic Review, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Toledo College Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH; 2University of Toledo College Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, MI; 3University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Gastroparesis (GP) is a condition characterized by delayed gastric emptying without mechanical obstruction commonly observed in patients with diabetes mellitus, often due to autonomic neuropathy. The use of GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in diabetes management is on the risk and has raised concerns about their potential to exacerbate gastroparesis. This review aims to summarize the findings from various studies investigating the relationship between GLP-1 RAs and Gastric Emptying in Diabetic Gastroparesis.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in Embase (Embase.com, Elsevier) on 23 May 2024 by an experienced health sciences librarian (W.L.S.) using various advanced search techniques. The search was replicated in MEDLINE (OVID), Cochrane Central, Web of Science Core Collection, Korean Citation Index, SciELO, and Global Index Medicus (see Supplementary Table 1), with no publication date or language limits. Results were exported to EndNote 20, where duplicates were removed using EndNote's algorithms and manual inspection (see Supplementary Table 2). We included all studies with a population of patients with diabetic gastroparesis where GLP-1 RAs were studied as an intervention and measured gastric emptying by breath or gastric emptying testing and considered retrospective and prospective studies as well as randomized controlled trials. Other reviews were excluded.
Results: 10 studies from 2003 to 2024 including 3 with breath testing, 6 with various gastric emptying tests, and 1 with ultrasound were included. 6 out of 10 studies found a significant association between GLP-1 RA use and gastroparesis symptoms but only 4 out 10 studies found a significant association between GLP-1 RA use and delayed gastric emptying measured by imaging test.
Discussion: There is conflicting data on the effect GLP-1 RAs have on gastroparesis symptoms and gastric emptying on patients with diabetic gastroparesis and higher quality data including randomized controlled trials are needed.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Jacob Itkin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sudheer Dhoop indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thomas Sodeman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jacob Itkin, BS1, Sudheer M.. Dhoop, MD2, Thomas Sodeman, MD3. P5042 - The Effect of GLP-1 RA Use on Gastric Emptying and Gastroparesis Symptoms in Patients With Diabetic Gastroparesis: A Systematic Review, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
