Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P4573 - The Evolving Landscape of Drug Induced Liver Injury (DILI): Tracking New Drug Culprits
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Gautam Maddineni, MD
Florida State University
Cape Coral, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Gautam Maddineni, MD1, Silpa Choday, MD2, Fnu Vikash, MD, M.Med3, Chun-Wei Pan, MD4, Yashwitha Sai Pulakurthi, MBBS, MD5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Mihir P. Shah, MD7, Raja Chandra Chakinala, MD8, Vaishnavi Boppana, MD9, Bhaumik Brahmbhatt, MD10
1Florida State University, Cape Coral, FL; 2Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 3Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, NY; 4John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL; 5Saint Michael's Medical Center, Newark, NJ; 6Creighton University School of Medicine, Brooklyn, NY; 7John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Cook County, IL; 8Guthrie Robert Packer Hospital, Sayre, PA; 9University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM; 10Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) presents a significant healthcare challenge that is often challenging to detect in its initial phases. DILI has been increasingly prevalent in recent years, mainly due to the growing availability of designer drugs. Currently, no comprehensive epidemiological study provides details on the incidence of DILI. The occurrence of DILI varies based on geographic location and the drugs involved. Therefore, it is advantageous to be aware of the recent trends regarding drugs that most frequently lead to DILI to facilitate early identification.
Methods: We analyzed 20.2 million adverse events reported in the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database from January 1st, 2014, to March 31st, 2024. Instances of DILI were identified and categorized after excluding reports with missing data. The data was divided into two periods: 2014-2018 and 2019-2024. Demographic information was documented, and the primary outcomes focused on identifying the top 5 causative agents, assessing the mortality rate, and examining the differences in trends between the two subgroups. Additionally, we calculated the Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) using the statistical analysis software STATA 18.
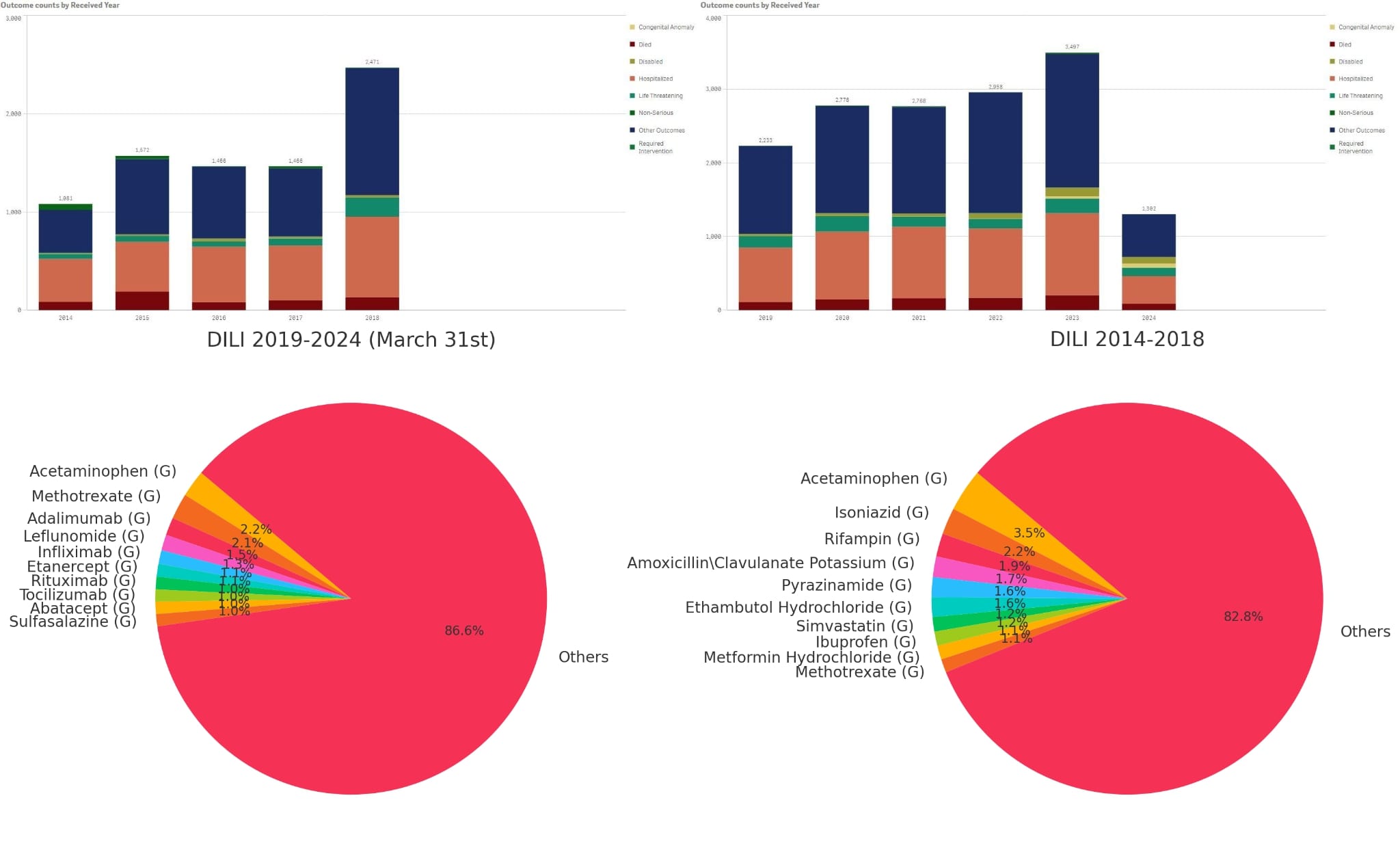
Results: A total of 15,834 cases were identified. Among these, 2014-2018 accounted for 5766 cases, while 2019-2024 had 10,068 cases. The age group most affected was between 18-65 years, constituting 62.94% of the cases. There has been a notable increase in reported cases among females, with a 180% rise. Most of the reported events leading to serious outcomes occurred outside the US. Acetaminophen remained the most commonly reported drug, but its ROR decreased from 16.08 to 8.24. Newer drugs such as Methotrexate (ROR 4.42), Adalimumab (ROR 0.83), Leflunomide (ROR 14.09), and Infliximab (ROR 5.5) have displaced previously major drugs with higher reported cases. Conversely, drugs that previously had high reporting events and ROR in 2014-2018 now have significantly lower cases (494) compared to the newer drugs (1217) from 2019-2024.
Discussion: The rising prevalence of DILI emphasizes its impact on public health. This study highlights the evolving causes, with newer medications increasingly contributing to DILI cases. Despite an overall increase in reported cases, the reduced ROR for previously common drugs like acetaminophen indicates improved awareness and potentially more effective management. Future research should focus on refining diagnostics and exploring preventive measures.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Gautam Maddineni, MD1, Silpa Choday, MD2, Fnu Vikash, MD, M.Med3, Chun-Wei Pan, MD4, Yashwitha Sai Pulakurthi, MBBS, MD5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Mihir P. Shah, MD7, Raja Chandra Chakinala, MD8, Vaishnavi Boppana, MD9, Bhaumik Brahmbhatt, MD10. P4573 - The Evolving Landscape of Drug Induced Liver Injury (DILI): Tracking New Drug Culprits, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Gautam Maddineni, MD1, Silpa Choday, MD2, Fnu Vikash, MD, M.Med3, Chun-Wei Pan, MD4, Yashwitha Sai Pulakurthi, MBBS, MD5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Mihir P. Shah, MD7, Raja Chandra Chakinala, MD8, Vaishnavi Boppana, MD9, Bhaumik Brahmbhatt, MD10
1Florida State University, Cape Coral, FL; 2Creighton University School of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 3Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, NY; 4John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL; 5Saint Michael's Medical Center, Newark, NJ; 6Creighton University School of Medicine, Brooklyn, NY; 7John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Cook County, IL; 8Guthrie Robert Packer Hospital, Sayre, PA; 9University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM; 10Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) presents a significant healthcare challenge that is often challenging to detect in its initial phases. DILI has been increasingly prevalent in recent years, mainly due to the growing availability of designer drugs. Currently, no comprehensive epidemiological study provides details on the incidence of DILI. The occurrence of DILI varies based on geographic location and the drugs involved. Therefore, it is advantageous to be aware of the recent trends regarding drugs that most frequently lead to DILI to facilitate early identification.
Methods: We analyzed 20.2 million adverse events reported in the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database from January 1st, 2014, to March 31st, 2024. Instances of DILI were identified and categorized after excluding reports with missing data. The data was divided into two periods: 2014-2018 and 2019-2024. Demographic information was documented, and the primary outcomes focused on identifying the top 5 causative agents, assessing the mortality rate, and examining the differences in trends between the two subgroups. Additionally, we calculated the Reporting Odds Ratio (ROR) using the statistical analysis software STATA 18.
Results: A total of 15,834 cases were identified. Among these, 2014-2018 accounted for 5766 cases, while 2019-2024 had 10,068 cases. The age group most affected was between 18-65 years, constituting 62.94% of the cases. There has been a notable increase in reported cases among females, with a 180% rise. Most of the reported events leading to serious outcomes occurred outside the US. Acetaminophen remained the most commonly reported drug, but its ROR decreased from 16.08 to 8.24. Newer drugs such as Methotrexate (ROR 4.42), Adalimumab (ROR 0.83), Leflunomide (ROR 14.09), and Infliximab (ROR 5.5) have displaced previously major drugs with higher reported cases. Conversely, drugs that previously had high reporting events and ROR in 2014-2018 now have significantly lower cases (494) compared to the newer drugs (1217) from 2019-2024.
Discussion: The rising prevalence of DILI emphasizes its impact on public health. This study highlights the evolving causes, with newer medications increasingly contributing to DILI cases. Despite an overall increase in reported cases, the reduced ROR for previously common drugs like acetaminophen indicates improved awareness and potentially more effective management. Future research should focus on refining diagnostics and exploring preventive measures.

Figure: DILI Data Comparison: 2014-2018 Vs 2019-2024
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Gautam Maddineni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Silpa Choday indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fnu Vikash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chun-Wei Pan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yashwitha Sai Pulakurthi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikash Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mihir Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raja Chandra Chakinala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vaishnavi Boppana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhaumik Brahmbhatt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gautam Maddineni, MD1, Silpa Choday, MD2, Fnu Vikash, MD, M.Med3, Chun-Wei Pan, MD4, Yashwitha Sai Pulakurthi, MBBS, MD5, Vikash Kumar, MD6, Mihir P. Shah, MD7, Raja Chandra Chakinala, MD8, Vaishnavi Boppana, MD9, Bhaumik Brahmbhatt, MD10. P4573 - The Evolving Landscape of Drug Induced Liver Injury (DILI): Tracking New Drug Culprits, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

