Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P4585 - A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Endoscopic Innovations in MASLD Management
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
.jpg)
Raj H. Patel, MD
St. Mary Medical Center
Bensalem, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Raj H. Patel, MD1, Charmy Parikh, MD2, Dev Desai, MBBS3, Maurya Patel, MBBS4, Yug Patel, MBBS5, Truptesh Kothari, MD6
1St. Mary Medical Center, Bensalem, PA; 2Mercy Catholic Medical Center, Darby, PA; 3Montefiore Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY; 4Smt. NHL Municipal Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 5Smt. NHL Municipal Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 6University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY
Introduction: In recent years, MASLD has evolved as one of the leading causes of liver cirrhosis in western countries. Obesity and metabolic syndrome are common predisposing factors for MASLD patients. Various studies have proven reduction in obesity leads to better MASLD outcomes. Recently endobariatrics have emerged as one of the leading interventions for weight loss, and an increasing number of studies have reported positive effects of endobariatric techniques on MASLD. In our study, we aim to examine the comparative effectiveness of these interventions on hospitalized MASLD patients.
Methods: A systematic review and network meta-analysis was conducted following a systematic search across various database using relevant keywords yielding 18 articles involving 953 patients with consideration of inclusion/exclusion criteria, Prisma Guidelines and bias assessments. In the Intervention group, we included DJBS, DMR, ESG, IGB, and lifestyle modifications compared to baseline measures. Key outcomes included HOMA-IR values and ALT levels. RevMan 5.3 was used for analysis with employment of Fixed and Random Effect Model tests with statistical significance set at p< 0.05. For interventions lacking direct comparator groups, we relied on indirect comparisons against other modalities. To facilitate this, League Tables and Mean Rank Tables were generated post-standardization of controls.
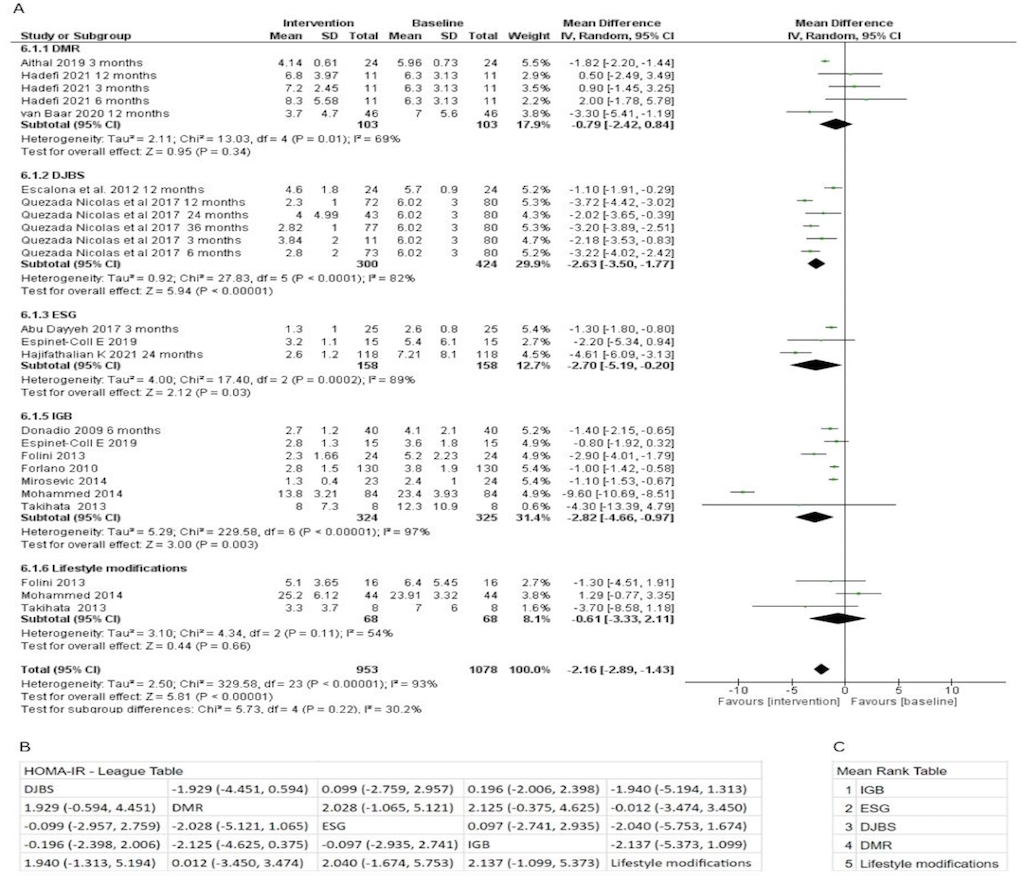
Results: Among the five experimental groups examined, IGB demonstrated the most effective reduction in HOMA-IR, showing a pooled mean difference (MD) of -2.82 (95% CI: -4.66 to -0.97). When comparing within the experimental groups, IGB ranked highest with a mean rank of 1, indicating superior performance compared to Lifestyle modifications, which ranked fifth with a MD of -2.137. ESG showed the greatest improvement in ALT values, although not statistically significant, with an MD of -22 (95% CI: -54.99 to 10.99). DMR had an MD of -10.16, while IGB also demonstrated a significant decrease of -9.97 (95% CI: -14.42 to -5.52) in ALT values. Our systematic review yielded studies that reported MRI-PDFF, HSI, NFS as well as various biopsy scores.Significant reduction in steatosis and steatohepatitis was noted in various surgical studies but given lack of common variables we couldn’t compare that with endoscopic modalities.
Discussion: In conclusion, our study provides valuable insights into the differential effects of EBMTs on MASLD markers, offering practical implications for optimizing treatment approaches in MASLD.
Disclosures:
Raj H. Patel, MD1, Charmy Parikh, MD2, Dev Desai, MBBS3, Maurya Patel, MBBS4, Yug Patel, MBBS5, Truptesh Kothari, MD6. P4585 - A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Endoscopic Innovations in MASLD Management, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1St. Mary Medical Center, Bensalem, PA; 2Mercy Catholic Medical Center, Darby, PA; 3Montefiore Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY; 4Smt. NHL Municipal Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 5Smt. NHL Municipal Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 6University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY
Introduction: In recent years, MASLD has evolved as one of the leading causes of liver cirrhosis in western countries. Obesity and metabolic syndrome are common predisposing factors for MASLD patients. Various studies have proven reduction in obesity leads to better MASLD outcomes. Recently endobariatrics have emerged as one of the leading interventions for weight loss, and an increasing number of studies have reported positive effects of endobariatric techniques on MASLD. In our study, we aim to examine the comparative effectiveness of these interventions on hospitalized MASLD patients.
Methods: A systematic review and network meta-analysis was conducted following a systematic search across various database using relevant keywords yielding 18 articles involving 953 patients with consideration of inclusion/exclusion criteria, Prisma Guidelines and bias assessments. In the Intervention group, we included DJBS, DMR, ESG, IGB, and lifestyle modifications compared to baseline measures. Key outcomes included HOMA-IR values and ALT levels. RevMan 5.3 was used for analysis with employment of Fixed and Random Effect Model tests with statistical significance set at p< 0.05. For interventions lacking direct comparator groups, we relied on indirect comparisons against other modalities. To facilitate this, League Tables and Mean Rank Tables were generated post-standardization of controls.
Results: Among the five experimental groups examined, IGB demonstrated the most effective reduction in HOMA-IR, showing a pooled mean difference (MD) of -2.82 (95% CI: -4.66 to -0.97). When comparing within the experimental groups, IGB ranked highest with a mean rank of 1, indicating superior performance compared to Lifestyle modifications, which ranked fifth with a MD of -2.137. ESG showed the greatest improvement in ALT values, although not statistically significant, with an MD of -22 (95% CI: -54.99 to 10.99). DMR had an MD of -10.16, while IGB also demonstrated a significant decrease of -9.97 (95% CI: -14.42 to -5.52) in ALT values. Our systematic review yielded studies that reported MRI-PDFF, HSI, NFS as well as various biopsy scores.Significant reduction in steatosis and steatohepatitis was noted in various surgical studies but given lack of common variables we couldn’t compare that with endoscopic modalities.
Discussion: In conclusion, our study provides valuable insights into the differential effects of EBMTs on MASLD markers, offering practical implications for optimizing treatment approaches in MASLD.

Figure: (A) Forest Plot showing the change in HOMA-IR scores after different treatment modalities. (B) League table comparing the effectiveness of various modalities on HOMA-IR scores, presented as mean difference with 95% confidence interval. (C ) Mean rank table summarizing the relative effectiveness of each modality on HOMA-IR score.
Disclosures:
Raj Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Charmy Parikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dev Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maurya Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yug Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Truptesh Kothari indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raj H. Patel, MD1, Charmy Parikh, MD2, Dev Desai, MBBS3, Maurya Patel, MBBS4, Yug Patel, MBBS5, Truptesh Kothari, MD6. P4585 - A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Endoscopic Innovations in MASLD Management, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
