Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P4423 - Chronic Urticaria in Crohn's Disease: A Rare Phenomenon
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E


Muhammad Jahanzaib Khan, MD
Mather Hospital, Northwell Health
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Muhammad Jahanzaib Khan, MD1, Justin Chuang, MD2, Ramona Rajapakse, MD2
1Mather Hospital, Northwell Health, New York, NY; 2Mather Hospital, Northwell Health, Port Jefferson, NY
Introduction: Crohn's disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, characterized by transmural inflammation and the potential to affect any portion of the digestive tract. Urticaria, conversely, is a cutaneous condition characterized by the sudden onset of pruritic, raised wheals on the skin. The simultaneous occurrence of CD and chronic urticaria is a rare phenomenon and only a limited number of cases have been reported in the literature. Here, we present a case of chronic urticaria associated with CD which responded to Infliximab infusions.
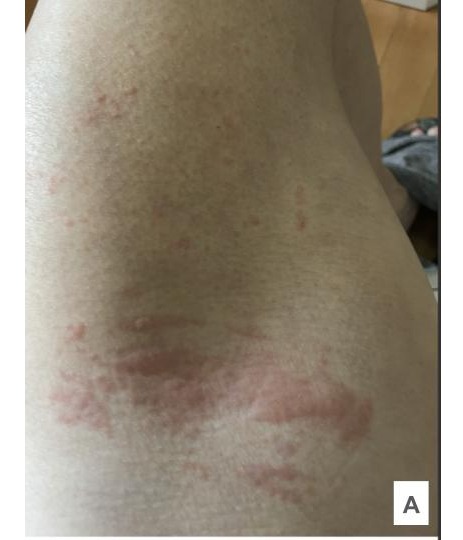
Case Description/Methods: A 63-year-old female with a history of vitiligo, chronic urticaria, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) diagnosed at the age of 40, initially as ulcerative colitis, with a subsequent change to Crohn's disease due to the development of significant ileitis, presented to our office for her initial visit. She reported a recurrent, erythematous rash with well-defined margins (Image A) on various parts of her body, associated with severe itching over the last few months. Despite consulting a dermatologist and receiving steroid treatment, there was no significant relief or improvement in her symptoms. However, she noticed improvement in her symptoms, with decreased frequency and intensity of the rash, after starting Infliximab infusions a few weeks ago, and the rash resolved spontaneously over the next few weeks. She had never been on any treatment for IBD previously.
Discussion: CD is a chronic inflammatory disorder with extraintestinal manifestations, often involving the skin. Shared autoimmune mechanisms and cytokine dysregulation, particularly interleukin-17 (IL-17) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), suggest a common link between chronic urticaria and CD. Limited case reports suggest an association between inflammatory bowel diseases and urticaria. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are biologicals that have revolutionized the management of chronic resistant urticaria (CRU) and are often preferred in chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) resistant to other treatment options. Although Infliximab is not a first-line mAb for the treatment of chronic urticaria, its potential needs to be further evaluated as a treatment option for IBD patients with chronic urticaria.
Disclosures:
Muhammad Jahanzaib Khan, MD1, Justin Chuang, MD2, Ramona Rajapakse, MD2. P4423 - Chronic Urticaria in Crohn's Disease: A Rare Phenomenon, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mather Hospital, Northwell Health, New York, NY; 2Mather Hospital, Northwell Health, Port Jefferson, NY
Introduction: Crohn's disease (CD) is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, characterized by transmural inflammation and the potential to affect any portion of the digestive tract. Urticaria, conversely, is a cutaneous condition characterized by the sudden onset of pruritic, raised wheals on the skin. The simultaneous occurrence of CD and chronic urticaria is a rare phenomenon and only a limited number of cases have been reported in the literature. Here, we present a case of chronic urticaria associated with CD which responded to Infliximab infusions.
Case Description/Methods: A 63-year-old female with a history of vitiligo, chronic urticaria, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) diagnosed at the age of 40, initially as ulcerative colitis, with a subsequent change to Crohn's disease due to the development of significant ileitis, presented to our office for her initial visit. She reported a recurrent, erythematous rash with well-defined margins (Image A) on various parts of her body, associated with severe itching over the last few months. Despite consulting a dermatologist and receiving steroid treatment, there was no significant relief or improvement in her symptoms. However, she noticed improvement in her symptoms, with decreased frequency and intensity of the rash, after starting Infliximab infusions a few weeks ago, and the rash resolved spontaneously over the next few weeks. She had never been on any treatment for IBD previously.
Discussion: CD is a chronic inflammatory disorder with extraintestinal manifestations, often involving the skin. Shared autoimmune mechanisms and cytokine dysregulation, particularly interleukin-17 (IL-17) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), suggest a common link between chronic urticaria and CD. Limited case reports suggest an association between inflammatory bowel diseases and urticaria. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are biologicals that have revolutionized the management of chronic resistant urticaria (CRU) and are often preferred in chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) resistant to other treatment options. Although Infliximab is not a first-line mAb for the treatment of chronic urticaria, its potential needs to be further evaluated as a treatment option for IBD patients with chronic urticaria.

Figure: Well-defined erythematous rash
Disclosures:
Muhammad Jahanzaib Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Justin Chuang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ramona Rajapakse indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Jahanzaib Khan, MD1, Justin Chuang, MD2, Ramona Rajapakse, MD2. P4423 - Chronic Urticaria in Crohn's Disease: A Rare Phenomenon, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
