Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P4350 - Efficacy of Guselkumab vs Placebo In Crohn’s Disease Based on Prior Response/Exposure to Biologic Therapy: Results of the GALAXI 2 and 3 Phase 3 Studies
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Bruce E. Sands, MD, FACG
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Bruce E.. Sands, MD, FACG1, Geert R. D'Haens, MD, PhD2, Silvio Danese, MD, PhD3, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD4, Walter Reinisch, MD, PhD5, Natalie A. Terry, MD, PhD6, Leonardo Salese, MD7, Rian Van Rampelbergh, MD8, Zijiang Yang, PhD9, Jewel Johanns, PhD6, George DuVall, MD10, Niazy Abu Farsakh, MBBCh, MRCP11, Remo Panaccione, MD12
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 2Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Limburg, Netherlands; 3Humanitas Clinical and Research Center - IRCCS, Rozzano and Humanitas University, Pieve Emanuele, Milan, Lombardia, Italy; 4Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 5Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Wien, Austria; 6Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Spring House, PA; 7Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Horsham, PA; 8Janssen Research and Development, Antwerp, Antwerpen, Belgium; 9Janssen Research and Development, Horsham, PA; 10Tyler Research Institute, LLC, Tyler, TX; 11King Abdullah University Hospital, Irbid, Irbid, Jordan; 12University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada
Introduction: GALAXI 2 & 3 are identically designed 48-week, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo (PBO)- and active-comparator, treat-through registrational trials assessing the efficacy and safety of IV induction and SC maintenance therapy with guselkumab (GUS), a dual-acting IL-23p19 subunit inhibitor, in participants (pts) with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease (CD). Primary results of each study were previously reported; here we explore the impact of biologic therapy exposure on efficacy outcomes with GUS compared to PBO in the pooled GALAXI 2 & 3 dataset.
Methods: Pts with inadequate response or intolerance to conventional therapy or biologic therapy (BIO-ir), active CD (CDAI 220–450 + mean daily SF >3 or AP >1), and SES-CD≥6 (≥4 for isolated ileal disease) were randomly assigned 2:2:2:1 at week (Wk) 0 to GUS 200mg IV q4w (x3)→100mg SC q8w, GUS 200mg IV q4w (x3)→200mg SC q4w, UST IV→SC, or PBO. In each trial, the composite co-primary endpoints were 1) clinical response at Wk12 and clinical remission at Wk48, and 2) clinical response at Wk12 and endoscopic response at Wk48, comparing each GUS regimen to PBO. Major secondary endpoints included clinical remission at Wk12 and endoscopic response at Wk12. Analyses of BIO-ir and BIO-naïve subgroups in the individual trials were prespecified; pooled analyses were performed post hoc.
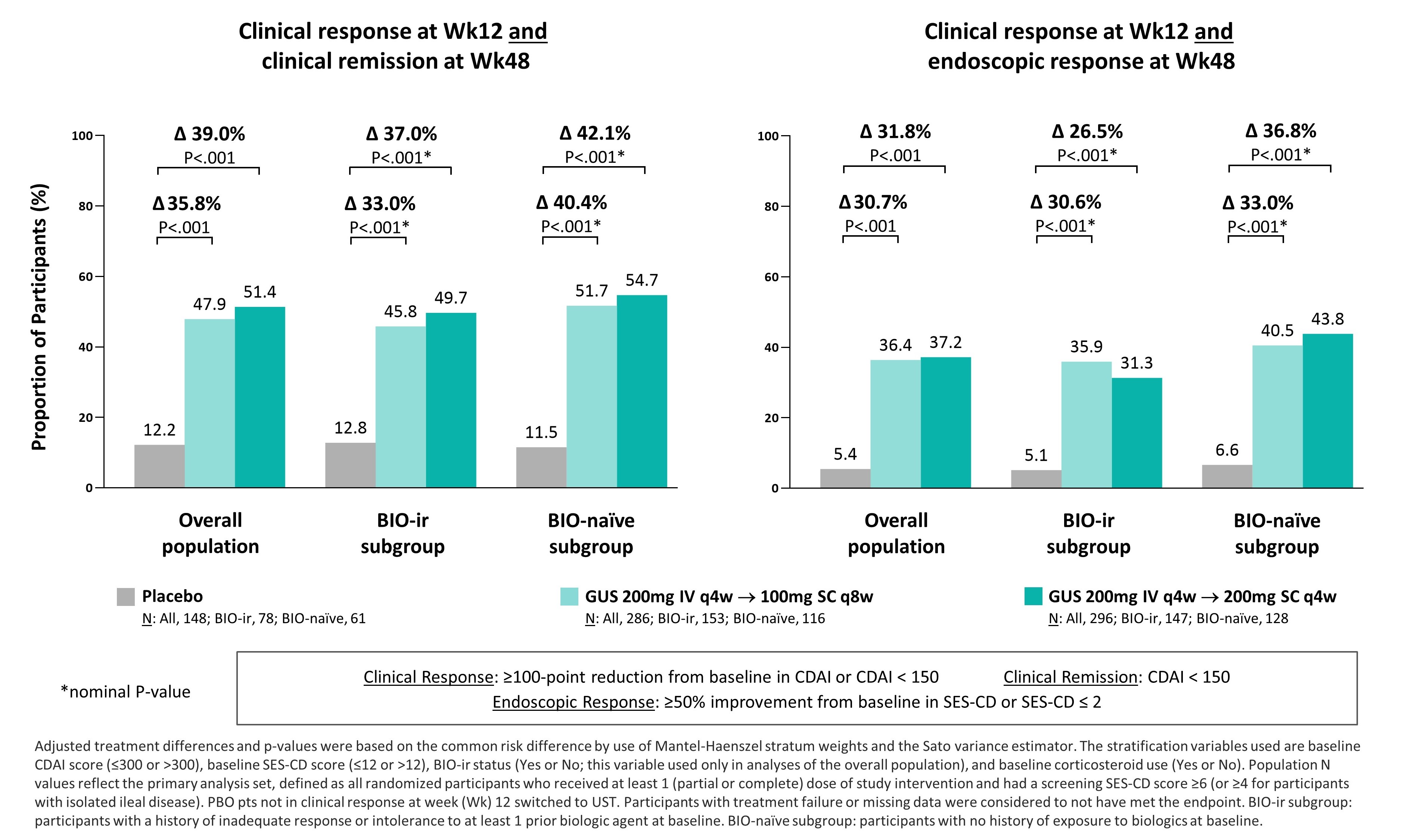
Results: In the pooled dataset, 52% (378/730) of pts randomized to PBO or GUS had a prior history of BIO-ir and 42% (305/730) were BIO-naïve (6% [47/730] had prior exposure to biologics but no documented failure). At Wk12, GUS achieved higher rates of clinical remission and endoscopic response compared to PBO in the overall population and BIO-ir and BIO-naïve subgroups (Table). For the composite co-primary endpoints, both GUS regimens also achieved higher rates of 1) clinical response at Wk12 and clinical remission at Wk48 and 2) clinical response at Wk12 and endoscopic response at Wk48 compared to PBO in the overall population and BIO-ir and BIO-naïve subgroups (Figure).
Discussion: In pooled analyses of the double-blind GALAXI 2 & 3 trials, GUS was efficacious versus PBO in pts with CD regardless of prior biologic therapy exposure in both short-term (Wk12) endpoints and long-term (Wk12 and Wk48) composite endpoints.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Bruce E.. Sands, MD, FACG1, Geert R. D'Haens, MD, PhD2, Silvio Danese, MD, PhD3, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD4, Walter Reinisch, MD, PhD5, Natalie A. Terry, MD, PhD6, Leonardo Salese, MD7, Rian Van Rampelbergh, MD8, Zijiang Yang, PhD9, Jewel Johanns, PhD6, George DuVall, MD10, Niazy Abu Farsakh, MBBCh, MRCP11, Remo Panaccione, MD12. P4350 - Efficacy of Guselkumab vs Placebo In Crohn’s Disease Based on Prior Response/Exposure to Biologic Therapy: Results of the GALAXI 2 and 3 Phase 3 Studies, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 2Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Limburg, Netherlands; 3Humanitas Clinical and Research Center - IRCCS, Rozzano and Humanitas University, Pieve Emanuele, Milan, Lombardia, Italy; 4Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 5Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Wien, Austria; 6Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Spring House, PA; 7Janssen Research & Development, LLC, Horsham, PA; 8Janssen Research and Development, Antwerp, Antwerpen, Belgium; 9Janssen Research and Development, Horsham, PA; 10Tyler Research Institute, LLC, Tyler, TX; 11King Abdullah University Hospital, Irbid, Irbid, Jordan; 12University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada
Introduction: GALAXI 2 & 3 are identically designed 48-week, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo (PBO)- and active-comparator, treat-through registrational trials assessing the efficacy and safety of IV induction and SC maintenance therapy with guselkumab (GUS), a dual-acting IL-23p19 subunit inhibitor, in participants (pts) with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease (CD). Primary results of each study were previously reported; here we explore the impact of biologic therapy exposure on efficacy outcomes with GUS compared to PBO in the pooled GALAXI 2 & 3 dataset.
Methods: Pts with inadequate response or intolerance to conventional therapy or biologic therapy (BIO-ir), active CD (CDAI 220–450 + mean daily SF >3 or AP >1), and SES-CD≥6 (≥4 for isolated ileal disease) were randomly assigned 2:2:2:1 at week (Wk) 0 to GUS 200mg IV q4w (x3)→100mg SC q8w, GUS 200mg IV q4w (x3)→200mg SC q4w, UST IV→SC, or PBO. In each trial, the composite co-primary endpoints were 1) clinical response at Wk12 and clinical remission at Wk48, and 2) clinical response at Wk12 and endoscopic response at Wk48, comparing each GUS regimen to PBO. Major secondary endpoints included clinical remission at Wk12 and endoscopic response at Wk12. Analyses of BIO-ir and BIO-naïve subgroups in the individual trials were prespecified; pooled analyses were performed post hoc.
Results: In the pooled dataset, 52% (378/730) of pts randomized to PBO or GUS had a prior history of BIO-ir and 42% (305/730) were BIO-naïve (6% [47/730] had prior exposure to biologics but no documented failure). At Wk12, GUS achieved higher rates of clinical remission and endoscopic response compared to PBO in the overall population and BIO-ir and BIO-naïve subgroups (Table). For the composite co-primary endpoints, both GUS regimens also achieved higher rates of 1) clinical response at Wk12 and clinical remission at Wk48 and 2) clinical response at Wk12 and endoscopic response at Wk48 compared to PBO in the overall population and BIO-ir and BIO-naïve subgroups (Figure).
Discussion: In pooled analyses of the double-blind GALAXI 2 & 3 trials, GUS was efficacious versus PBO in pts with CD regardless of prior biologic therapy exposure in both short-term (Wk12) endpoints and long-term (Wk12 and Wk48) composite endpoints.

Figure: Figure. Efficacy of guselkumab (GUS) and placebo (PBO) for long-term (Wk 12 and Wk 48) clinical and endoscopic endpoints in all participants and BIO-ir and BIO-naïve subgroups in the pooled GALAXI 2 & 3 dataset
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Bruce Sands: AbbVie – Consultant. Abivax – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Adiso Therapeutics – Consultant. Agomab – Consultant. Alimentiv – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant. AnaptysBio – Consultant. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Artugen Therapeutics – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Biolojic Design – Consultant. Biora Therapeutics – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Boston Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Other support, Speakers Bureau. Calibr – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. ClostraBio – Consultant. Enthera – Consultant. Envied Biosciences – Consultant. Equilium – Consultant. Evommune – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Fiat – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant. Genentech (Roche) – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. Glaxo SmithKline – Consultant. Gossamer Bio – Consultant. Imhotex – Consultant. Index Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Innovation Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Other support, Speakers Bureau. Kaleido – Consultant. Kallyope – Consultant. Lilly – Consultant, other support, Speakers Bureau. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA – Consultant. Microba – Consultant. Mobius Care – Consultant. Morphic Therapeutics – Consultant. MRM Health – Consultant. Nexus Therapeutics – Consultant. Nimbus Discovery – Consultant. Odyssey Therapeutics – Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Other support, Speakers Bureau. Progenity – Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant. Prometheus Laboratories – Consultant. Protagonist Therapeutics – Consultant. Q32 Bio – Consultant. Rasayana Therapeutics – Consultant. Recludix Therapeutics – Consultant. Reistone Biopharma – Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Spyre Therapeutics – Consultant. Sun Pharma – Consultant. Surrozen – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Other support, Speakers Bureau. Target RWE – Consultant. Teva – Consultant. Theravance Biopharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. TLL Pharmaceutical – Consultant. Tr1X – Consultant. Union Therapeutics – Consultant. Ventyx Biopharma – Consultant, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Geert D'Haens: AbbVie – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Agomab Therapeutics – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Alimentiv – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Allergan – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Alphabiomics – Advisor or Review Panel Member. AstraZeneca – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Grant/Research Support. Eli Lilly – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Ferring – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Galapagos – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Immunic – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Johnson & Johnson – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer Inc – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Seres – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Takeda – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Tillotts – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Speakers Bureau. Ventyx – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Silvio Danese: AbbVie – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Alimentiv – Consultant. Allergan – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Applied Molecular Transport – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Athos Therapeutics – Consultant. Biogen – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion Healthcare – Consultant. Dr Falk Pharma – Consultant. Eli Lilly and Company – Consultant. Enthera – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Gilead – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Hospira – Consultant. Inotrem – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Johnson & Johnson – Consultant. Morphic – Consultant. MSD – Consultant. Mundipharma – Consultant. Mylan – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer Inc – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Roche – Consultant. Sandoz – Consultant. Sublimity Therapeutics – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Teladoc Health – Consultant. TiGenix – Consultant. UCB Inc. – Consultant. Vial – Consultant. Vifor – Consultant.
Tadakazu Hisamatsu: AbbVie – Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Daiichi-Sankyo – Grant/Research Support. EA Pharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant. JIMRO – Grant/Research Support. Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation – Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Mochida Pharmaceutical – Grant/Research Support. Nippon Kayaku – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Grant/Research Support. Takeda Pharmaceutical – Grant/Research Support, lecture fees.
Walter Reinisch: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. AOP Orphan – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Calyx – Consultant. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Ferring – Speakers Bureau. Galapagos – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Gilead – Consultant. Index Pharma – Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Medahead – Consultant. Microbiotica – Consultant. MSD – Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Roche – Speakers Bureau. Sandoz – Grant/Research Support. Sanofi – Grant/Research Support. Sobi – Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau.
Natalie A. Terry: Janssen Research & Development, LLC – Employee, Stock Options.
Leonardo Salese: Johnson & Johnson – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Rian Van Rampelbergh: Janssen Research & Development (a Johnson & Johnson Company) – Employee, Stock Options.
Zijiang Yang: Janssen Research & Development (a Johnson & Johnson Company) – Employee, Stock Options.
Jewel Johanns: Janssen Research & Development, LLC – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
George DuVall: Janssen Research & Development, LLC – Clinical trial investigator.
Niazy Abu Farsakh: Abbott – Consultant. Amgen – Consultant. Antanea medical services – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Hikma – Consultant. Janssen – Clinical trial investigator. Pfizer – Consultant.
Remo Panaccione: Élan – Consultant. Abbivax – Consultant. Abbott – Consultant. AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaking Fees. Alimentiv – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. AstraZeneca – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Biogen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Celgene – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Celltrion – Consultant. Cosmos Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Eisai – Consultant. Ferring – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Fresenius Kabi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Galapagos – Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. GlaxoSmithKline – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. JAMP Bio – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Merck – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Mylan – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Novartis – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Oppilan Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Organon – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Pandion Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pendopharm – Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Progenity – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant. Protagonist Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Satisfai Health – Consultant. Shire – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Sublimity Therapeutics – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speaker Fees. Theravance – Consultant. Trellus – Consultant. UCB – Consultant. Ventyx – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Viatris – Consultant.
Bruce E.. Sands, MD, FACG1, Geert R. D'Haens, MD, PhD2, Silvio Danese, MD, PhD3, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD4, Walter Reinisch, MD, PhD5, Natalie A. Terry, MD, PhD6, Leonardo Salese, MD7, Rian Van Rampelbergh, MD8, Zijiang Yang, PhD9, Jewel Johanns, PhD6, George DuVall, MD10, Niazy Abu Farsakh, MBBCh, MRCP11, Remo Panaccione, MD12. P4350 - Efficacy of Guselkumab vs Placebo In Crohn’s Disease Based on Prior Response/Exposure to Biologic Therapy: Results of the GALAXI 2 and 3 Phase 3 Studies, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
