Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P4258 - Clinical Effectiveness of Vedolizumab in Chinese Patients With Crohn's Disease: Interim Results From the VALUE study
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
- LL
Li Li
The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University
Guangzhou, Guizhou, China
Presenting Author(s)
Li Li, 1, Xiaoqi Zhang, 2, Yaqiu Hu, 3, Li Xie, 4, Minhu Chen, MD, PhD5
1The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guizhou, China; 2Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China; 3Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Shanghai, Shanghai, China; 4Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd., Shanghai, Shanghai, China; 5The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Introduction: Vedolizumab (VDZ), an advanced therapy with a unique gut-selective anti-lymphocyte trafficking (GSALT) mechanism of action, was approved to treat moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC) patients in China in 2020. However, there is a lack of effectiveness and safety data for VDZ in Chinese inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients. The VALUE study aims to evaluate the real-world safety and effectiveness of VDZ in patients with IBD.
Methods: VALUE is a prospective, multicentre, single-armed observational study with a total enrolment of 500 IBD adult patients to evaluate the effectiveness of VDZ in Chinese patients (NCT04872491). This study evaluated the effectiveness of VDZ during a maximum of 54 weeks observation period. Clinical response, clinical remission, and endoscopic remission were assessed at weeks 14, 30, and 54. This is the second interim analysis of VALUE study in CD patients. Safety results are presented in another VALUE abstract (ID:1859655).
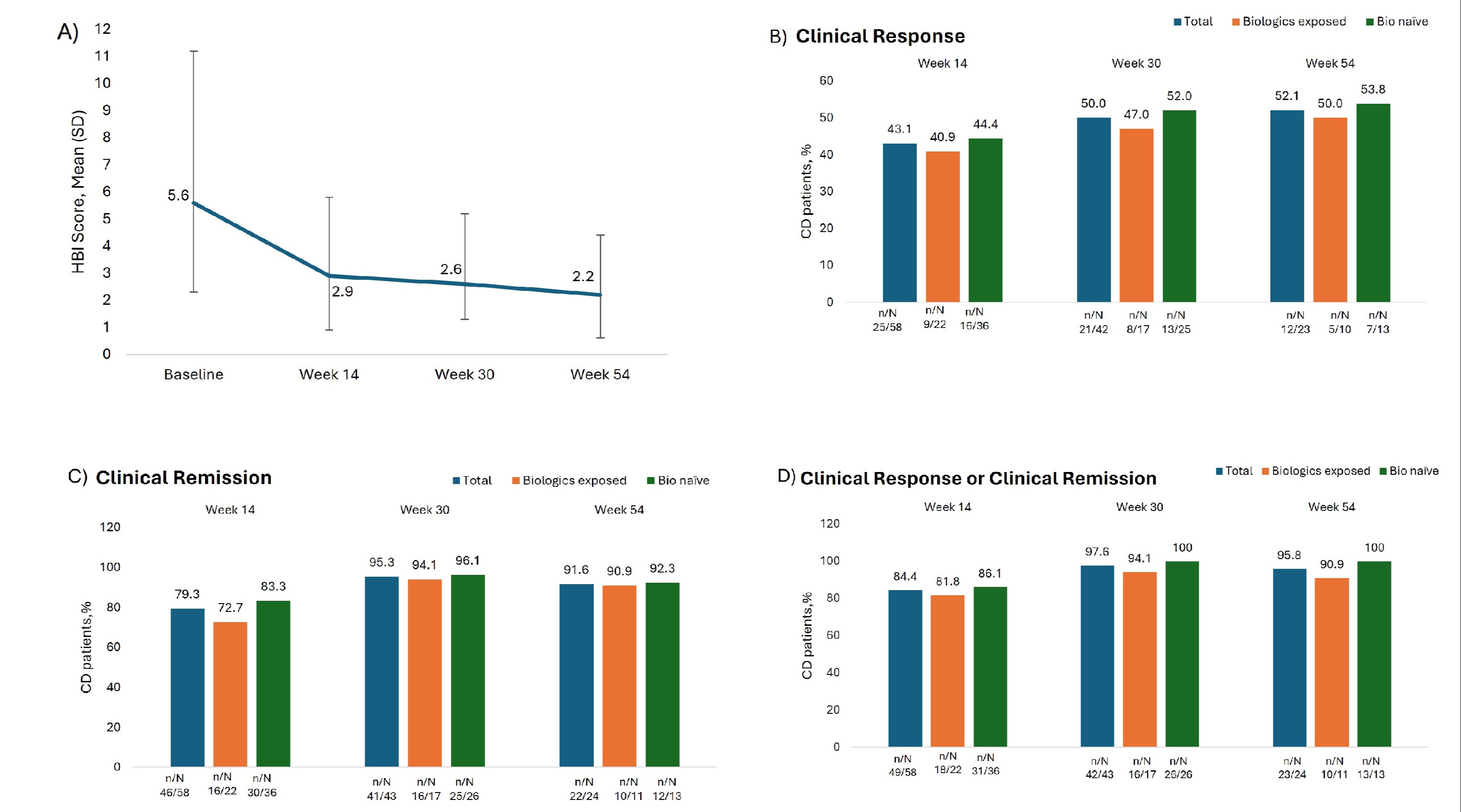
Results: Among 91 CD patients enrolled in this interim analysis, 89 (97.80%) were included in the effectiveness analysis set. Median CD duration was 2 years, 37.36% had prior biologic use (Table 1). After initiating VDZ treatment, the HBI score (Mean ± SD) decreased from 5.6 ± 3.37 to 2.9±2.04,2.6 ±1.35 and 2.2±1.61 at weeks 14, 30 and 54, respectively (Fig 1A). The proportion of patients who achieved clinical response at weeks 14, 30, and 54 were: 43.10% (25/58), 50% (21/42), and 52.17% (12/23), respectively (Fig1B). Clinical remission was achieved by 79.31% (46/58), 95.35% (41/43), and 91.67% (22/24) of patients at weeks 14, 30, and 54, respectively. (Fig 1C) The proportion of patients who either achieved clinical response or clinical remission at weeks 14, 30, and 54 was 84.48% (49/58), 97.67% (42/43), and 95.83% (23/24), respectively (Fig 1D). Endoscopic remission was achieved in 4 of 8 patients, and 3 of 8 patients at weeks 14 and 30, respectively. Subgroup results based on biologics history and baseline severity are shown in Fig 1B-D. For patients with concomitant IBD steroids use at baseline, 2 out of 6 at week 14 and 3 out of 3 at week 54 achieved clinical remission without steroids.
Discussion: This study demonstrated the effectiveness of VDZ in management of CD in Chinese patients.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Li Li, 1, Xiaoqi Zhang, 2, Yaqiu Hu, 3, Li Xie, 4, Minhu Chen, MD, PhD5. P4258 - Clinical Effectiveness of Vedolizumab in Chinese Patients With Crohn's Disease: Interim Results From the VALUE study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guizhou, China; 2Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China; 3Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Shanghai, Shanghai, China; 4Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd., Shanghai, Shanghai, China; 5The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Introduction: Vedolizumab (VDZ), an advanced therapy with a unique gut-selective anti-lymphocyte trafficking (GSALT) mechanism of action, was approved to treat moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC) patients in China in 2020. However, there is a lack of effectiveness and safety data for VDZ in Chinese inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients. The VALUE study aims to evaluate the real-world safety and effectiveness of VDZ in patients with IBD.
Methods: VALUE is a prospective, multicentre, single-armed observational study with a total enrolment of 500 IBD adult patients to evaluate the effectiveness of VDZ in Chinese patients (NCT04872491). This study evaluated the effectiveness of VDZ during a maximum of 54 weeks observation period. Clinical response, clinical remission, and endoscopic remission were assessed at weeks 14, 30, and 54. This is the second interim analysis of VALUE study in CD patients. Safety results are presented in another VALUE abstract (ID:1859655).
Results: Among 91 CD patients enrolled in this interim analysis, 89 (97.80%) were included in the effectiveness analysis set. Median CD duration was 2 years, 37.36% had prior biologic use (Table 1). After initiating VDZ treatment, the HBI score (Mean ± SD) decreased from 5.6 ± 3.37 to 2.9±2.04,2.6 ±1.35 and 2.2±1.61 at weeks 14, 30 and 54, respectively (Fig 1A). The proportion of patients who achieved clinical response at weeks 14, 30, and 54 were: 43.10% (25/58), 50% (21/42), and 52.17% (12/23), respectively (Fig1B). Clinical remission was achieved by 79.31% (46/58), 95.35% (41/43), and 91.67% (22/24) of patients at weeks 14, 30, and 54, respectively. (Fig 1C) The proportion of patients who either achieved clinical response or clinical remission at weeks 14, 30, and 54 was 84.48% (49/58), 97.67% (42/43), and 95.83% (23/24), respectively (Fig 1D). Endoscopic remission was achieved in 4 of 8 patients, and 3 of 8 patients at weeks 14 and 30, respectively. Subgroup results based on biologics history and baseline severity are shown in Fig 1B-D. For patients with concomitant IBD steroids use at baseline, 2 out of 6 at week 14 and 3 out of 3 at week 54 achieved clinical remission without steroids.
Discussion: This study demonstrated the effectiveness of VDZ in management of CD in Chinese patients.

Figure: Fig. 1: A) Mean HBI score at baseline, week 14, week 30, and week 54; (B) Clinical response, C) Clinical remission and D) Clinical response or clinical remission of CD patients after 14,30 and 54 weeks of VDZ therapy. HBI: Harvey-Bradshaw index.
aClinical response defined as ≥3-point decrease in the HBI score; bClinical remission defined as HBI score of ≤4.
Abbreviations: 5-ASA: 5-Aminosalicylic Acids; HBI: Harvey-Bradshaw Index; IMM: immunosuppressants; TNF-α-Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alfa.
aClinical response defined as ≥3-point decrease in the HBI score; bClinical remission defined as HBI score of ≤4.
Abbreviations: 5-ASA: 5-Aminosalicylic Acids; HBI: Harvey-Bradshaw Index; IMM: immunosuppressants; TNF-α-Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alfa.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Li Li indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Xiaoqi Zhang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yaqiu Hu: Takeda China – Employee, Stock Options.
Li Xie: Takeda China – Employee, Stock Options.
Minhu Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Li Li, 1, Xiaoqi Zhang, 2, Yaqiu Hu, 3, Li Xie, 4, Minhu Chen, MD, PhD5. P4258 - Clinical Effectiveness of Vedolizumab in Chinese Patients With Crohn's Disease: Interim Results From the VALUE study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
