Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P4266 - Evening Timing of Inpatient Intravenous Infliximab Administration Is Associated With Worse Disease Outcomes
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- ZP
Zoe Post, MD
Rush University Medical Center
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Zoë Post, MD1, Agnieszka Maniak, MD1, Anthony Demeo, 1, Ali Keshavarzian, MD, MACG2
1Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL; 2Chicago, IL
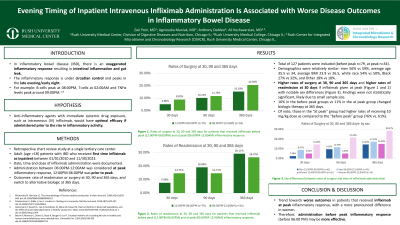
Introduction: In inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), there is an exaggerated inflammatory response resulting in intestinal inflammation and gut leak. This inflammatory response is under control of the circadian rhythm reaches maximum activity in the late evening and early night. For example, peak activity of B-cells and T-cells are at 08:00PM and 02:00AM respectively, and TNFα levels peak around 09:00PM. Based on this diurnal variation in function, we hypothesized that anti-inflammatory agents with immediate systemic drug exposure, such as intravenous (IV) infliximab, would have optimal efficacy if administered prior to the rise in inflammatory activity.
Methods: Adult (age >18) IBD patients who received inpatient infliximab between 01/01/2010 and 11/30/2023 were included in this retrospective study. Date, time and dose of infliximab administration were documented. Administration between 6:00PM and 12:00AM was considered to be at peak inflammatory activity, accounting for infusion times lasting 2-4 hours. Disease outcomes assessed included hospitalization for IBD flare up and need for surgery at 30, 90 and 365 days as well as change in biologic therapy at 365 days. Mann Whitney U test was used to compare time of administration and Fisher’s Exact test was used for proportions.
Results: A total of 127 patients were included in the analysis. A total of 8, 13 and 21 patients required surgery at 30, 90 and 365 days respectively, whereas 13, 24 and 38 patients were readmitted for IBD flare at 30, 90 and 365 days respectively. 18% of patients were switched to an alternative biologic at 365 days. The median time of administration did not differ between the various outcome groups (Table). A greater proportion of patients with either surgery (38% vs 26%) or readmission (38% vs 25%) compared to no surgery or admission at 30 days received infliximab between 6:00PM and 12:00AM.
Discussion: When comparing IBD patients that require surgery or readmission after receiving inpatient IV infliximab to those who do not, there is a trend towards a larger proportion in the surgery/readmission group receiving IV infliximab at the time when the inflammatory response is most active, suggesting that administration before peak inflammatory response (before 6 PM) may be more effective.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Zoë Post, MD1, Agnieszka Maniak, MD1, Anthony Demeo, 1, Ali Keshavarzian, MD, MACG2. P4266 - Evening Timing of Inpatient Intravenous Infliximab Administration Is Associated With Worse Disease Outcomes, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL; 2Chicago, IL
Introduction: In inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), there is an exaggerated inflammatory response resulting in intestinal inflammation and gut leak. This inflammatory response is under control of the circadian rhythm reaches maximum activity in the late evening and early night. For example, peak activity of B-cells and T-cells are at 08:00PM and 02:00AM respectively, and TNFα levels peak around 09:00PM. Based on this diurnal variation in function, we hypothesized that anti-inflammatory agents with immediate systemic drug exposure, such as intravenous (IV) infliximab, would have optimal efficacy if administered prior to the rise in inflammatory activity.
Methods: Adult (age >18) IBD patients who received inpatient infliximab between 01/01/2010 and 11/30/2023 were included in this retrospective study. Date, time and dose of infliximab administration were documented. Administration between 6:00PM and 12:00AM was considered to be at peak inflammatory activity, accounting for infusion times lasting 2-4 hours. Disease outcomes assessed included hospitalization for IBD flare up and need for surgery at 30, 90 and 365 days as well as change in biologic therapy at 365 days. Mann Whitney U test was used to compare time of administration and Fisher’s Exact test was used for proportions.
Results: A total of 127 patients were included in the analysis. A total of 8, 13 and 21 patients required surgery at 30, 90 and 365 days respectively, whereas 13, 24 and 38 patients were readmitted for IBD flare at 30, 90 and 365 days respectively. 18% of patients were switched to an alternative biologic at 365 days. The median time of administration did not differ between the various outcome groups (Table). A greater proportion of patients with either surgery (38% vs 26%) or readmission (38% vs 25%) compared to no surgery or admission at 30 days received infliximab between 6:00PM and 12:00AM.
Discussion: When comparing IBD patients that require surgery or readmission after receiving inpatient IV infliximab to those who do not, there is a trend towards a larger proportion in the surgery/readmission group receiving IV infliximab at the time when the inflammatory response is most active, suggesting that administration before peak inflammatory response (before 6 PM) may be more effective.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Zoë Post indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Agnieszka Maniak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anthony Demeo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Keshavarzian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zoë Post, MD1, Agnieszka Maniak, MD1, Anthony Demeo, 1, Ali Keshavarzian, MD, MACG2. P4266 - Evening Timing of Inpatient Intravenous Infliximab Administration Is Associated With Worse Disease Outcomes, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

