Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2697 - Infliximab-Associated Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy in a Patient With Ulcerative Colitis
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Syed Ahmad Adil, MD
Henry Ford Health
Shelby Township, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Syed Ahmad Adil, MD1, Ammad Javaid. Chaudhary, MD2, Jeffery Tang, MD2, Najwa El-Nachef, MD2
1Henry Ford Health, Shelby Township, MI; 2Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI
Introduction: Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors have been associated with heart failure, myocarditis, and acute myocardial infarction (MI). Takotsubo (stress-induced) cardiomyopathy (TC) is characterized by transient regional systolic dysfunction and mimics MI but without evidence of obstructive coronary artery disease. While emotional stressors are commonly implicated in TC, there is increasing recognition of pharmacological triggers. Data, however, is scarce on the association of anti-TNF therapy with TC. Here, we present a case of a 53-year-old female with ulcerative colitis admitted to our hospital with TC, thought to be related to infliximab.
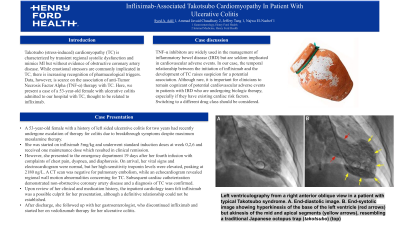
Case Description/Methods: A 53-year-old female with a history of left sided ulcerative colitis for two years had recently undergone escalation of therapy for colitis due to breakthrough symptoms despite maximum mesalamine therapy. She was started on infliximab 5mg/kg and underwent standard induction doses at week 0,2,6 and received one maintenance dose which resulted in clinical remission. However, she presented to the emergency department 19 days after her fourth infusion with complaints of chest pain, dyspnea, and diaphoresis. On arrival, her vital signs and electrocardiogram were normal, but her high-sensitivity troponin levels were elevated, peaking at 2180 ng/L. A CT scan was negative for pulmonary embolism, while an echocardiogram revealed regional wall motion abnormalities concerning for TC. Subsequent cardiac catheterization demonstrated non-obstructive coronary artery disease and a diagnosis of TC was confirmed. Upon review of her clinical and medication history, the inpatient cardiology team felt infliximab was a possible culprit for her presentation, although a definitive relationship could not be established. After discharge, she followed up with her gastroenterologist, who discontinued infliximab and started her on vedolizumab therapy for her ulcerative colitis.
Discussion: TNF-α inhibitors are widely used in the management of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) but are seldom implicated in cardiovascular adverse events. In our case, the temporal relationship between the initiation of infliximab and the development of TC raises suspicion for a potential association. Although rare, it is important for clinicians to remain cognizant of potential cardiovascular adverse events in patients with IBD who are undergoing biologic therapy, especially if they have existing cardiac risk factors. Switching to a different drug class should be considered.
Disclosures:
Syed Ahmad Adil, MD1, Ammad Javaid. Chaudhary, MD2, Jeffery Tang, MD2, Najwa El-Nachef, MD2. P2697 - Infliximab-Associated Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy in a Patient With Ulcerative Colitis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Henry Ford Health, Shelby Township, MI; 2Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI
Introduction: Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) inhibitors have been associated with heart failure, myocarditis, and acute myocardial infarction (MI). Takotsubo (stress-induced) cardiomyopathy (TC) is characterized by transient regional systolic dysfunction and mimics MI but without evidence of obstructive coronary artery disease. While emotional stressors are commonly implicated in TC, there is increasing recognition of pharmacological triggers. Data, however, is scarce on the association of anti-TNF therapy with TC. Here, we present a case of a 53-year-old female with ulcerative colitis admitted to our hospital with TC, thought to be related to infliximab.
Case Description/Methods: A 53-year-old female with a history of left sided ulcerative colitis for two years had recently undergone escalation of therapy for colitis due to breakthrough symptoms despite maximum mesalamine therapy. She was started on infliximab 5mg/kg and underwent standard induction doses at week 0,2,6 and received one maintenance dose which resulted in clinical remission. However, she presented to the emergency department 19 days after her fourth infusion with complaints of chest pain, dyspnea, and diaphoresis. On arrival, her vital signs and electrocardiogram were normal, but her high-sensitivity troponin levels were elevated, peaking at 2180 ng/L. A CT scan was negative for pulmonary embolism, while an echocardiogram revealed regional wall motion abnormalities concerning for TC. Subsequent cardiac catheterization demonstrated non-obstructive coronary artery disease and a diagnosis of TC was confirmed. Upon review of her clinical and medication history, the inpatient cardiology team felt infliximab was a possible culprit for her presentation, although a definitive relationship could not be established. After discharge, she followed up with her gastroenterologist, who discontinued infliximab and started her on vedolizumab therapy for her ulcerative colitis.
Discussion: TNF-α inhibitors are widely used in the management of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) but are seldom implicated in cardiovascular adverse events. In our case, the temporal relationship between the initiation of infliximab and the development of TC raises suspicion for a potential association. Although rare, it is important for clinicians to remain cognizant of potential cardiovascular adverse events in patients with IBD who are undergoing biologic therapy, especially if they have existing cardiac risk factors. Switching to a different drug class should be considered.
Disclosures:
Syed Ahmad Adil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ammad Chaudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeffery Tang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Najwa El-Nachef: Abbvie – Grant/Research Support. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Syed Ahmad Adil, MD1, Ammad Javaid. Chaudhary, MD2, Jeffery Tang, MD2, Najwa El-Nachef, MD2. P2697 - Infliximab-Associated Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy in a Patient With Ulcerative Colitis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
