Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2561 - Risankizumab Sustains Remission and Improves Anti-TNF-Induced Psoriasiform Dermatitis in Well Controlled Crohn's Disease Patients Switched from Anti-TNF Therapy
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Matthew Smyth, MD
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Vancouver, BC, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Matthew Smyth, MD1, Elizabeth Spencer, MD2, Hyder Said, MD2, Ryan C. Ungaro, MD2, Marla C. Dubinsky, MD2
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Vancouver, BC, Canada; 2Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY
Introduction: Paradoxical anti-TNF-induced psoriasiform dermatitis (PD) continues to limit treatment durability, with eczema history increasing risk of PD. Switching to anti-IL-12/23 is effective in some, with emerging evidence for use of anti-IL-4 targets. The efficacy of risankizumab (RZB) for anti-TNF-induced PD in Crohn’s Disease remains unknown.
Methods: A single center retrospective chart review identified CD patients with anti-TNF-induced PD switched from TNF to RZB between June 2022 and November 2023. Patients not in steroid free clinical remission (SFCR) at the time of switch or with < 12 weeks of RZB at last follow-up were excluded. TNF-induced-PD was scored as resolved, mild or severe. The primary outcome was sustained SFCR and PD resolution on RZB at last follow-up. Secondary outcomes included frequency of PD improvement and PD resolution. Descriptive statistics summarized the data (Median [IQR] or frequencies) and univariate tested associations.
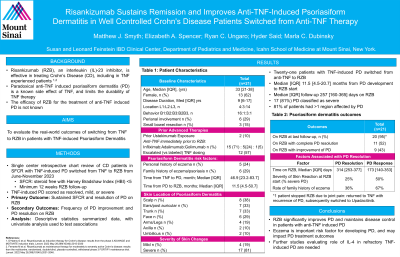
Results: Twenty-one patients with TNF-induced-PD switched from anti-TNF (Infliximab 71%, adalimumab 24%, golimumab 5%) to RZB; 13(62%) female; Median [IQR] age: 33 [21-38] years, disease duration 9 [6-17] years, time from anti-TNF initiation to development of PD 46.9 [23.2-83.7] months, time from developing PD to starting RZB 11.5 [4.5-50.7] months (table). Seventeen (81%) PD reactions were classified as severe. Scalp, ears, and trunk were most frequently affected areas (38%, 33%, 33% respectively), with 81% of patients having >1 affected region. Six (29%) had either a personal and or family history of eczema. All patients were on topical therapy and 1 was on oral antibiotics for their PD at RZB switch. At last follow-up (257 [160-365] days on RZB), all 20 patients remaining on RZB sustained SFCR and had complete resolution (N=11,55%) or improvement in PD (n=9, 45%). Patients not achieving PD resolution had numerically shorter exposure to RZB at follow-up (173 vs 314 days), severe skin reaction at baseline (50% vs 25% mild) and higher reported eczema history (67% vs 36%). One patient stopped RZB secondary to joint pain, returning to anti-TNF with recurrence of their PD, and subsequently switched to upadacitinib with resolution.
Discussion: In patients with anti-TNF-induced PD, RZB significantly improves PD and maintains disease control. Eczema is an important risk factor for developing PD and may impact PD outcomes. IL-4 targeted therapies may be a more biology driven approach to anti-TNF induced PD.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Matthew Smyth, MD1, Elizabeth Spencer, MD2, Hyder Said, MD2, Ryan C. Ungaro, MD2, Marla C. Dubinsky, MD2. P2561 - Risankizumab Sustains Remission and Improves Anti-TNF-Induced Psoriasiform Dermatitis in Well Controlled Crohn's Disease Patients Switched from Anti-TNF Therapy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Vancouver, BC, Canada; 2Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY
Introduction: Paradoxical anti-TNF-induced psoriasiform dermatitis (PD) continues to limit treatment durability, with eczema history increasing risk of PD. Switching to anti-IL-12/23 is effective in some, with emerging evidence for use of anti-IL-4 targets. The efficacy of risankizumab (RZB) for anti-TNF-induced PD in Crohn’s Disease remains unknown.
Methods: A single center retrospective chart review identified CD patients with anti-TNF-induced PD switched from TNF to RZB between June 2022 and November 2023. Patients not in steroid free clinical remission (SFCR) at the time of switch or with < 12 weeks of RZB at last follow-up were excluded. TNF-induced-PD was scored as resolved, mild or severe. The primary outcome was sustained SFCR and PD resolution on RZB at last follow-up. Secondary outcomes included frequency of PD improvement and PD resolution. Descriptive statistics summarized the data (Median [IQR] or frequencies) and univariate tested associations.
Results: Twenty-one patients with TNF-induced-PD switched from anti-TNF (Infliximab 71%, adalimumab 24%, golimumab 5%) to RZB; 13(62%) female; Median [IQR] age: 33 [21-38] years, disease duration 9 [6-17] years, time from anti-TNF initiation to development of PD 46.9 [23.2-83.7] months, time from developing PD to starting RZB 11.5 [4.5-50.7] months (table). Seventeen (81%) PD reactions were classified as severe. Scalp, ears, and trunk were most frequently affected areas (38%, 33%, 33% respectively), with 81% of patients having >1 affected region. Six (29%) had either a personal and or family history of eczema. All patients were on topical therapy and 1 was on oral antibiotics for their PD at RZB switch. At last follow-up (257 [160-365] days on RZB), all 20 patients remaining on RZB sustained SFCR and had complete resolution (N=11,55%) or improvement in PD (n=9, 45%). Patients not achieving PD resolution had numerically shorter exposure to RZB at follow-up (173 vs 314 days), severe skin reaction at baseline (50% vs 25% mild) and higher reported eczema history (67% vs 36%). One patient stopped RZB secondary to joint pain, returning to anti-TNF with recurrence of their PD, and subsequently switched to upadacitinib with resolution.
Discussion: In patients with anti-TNF-induced PD, RZB significantly improves PD and maintains disease control. Eczema is an important risk factor for developing PD and may impact PD outcomes. IL-4 targeted therapies may be a more biology driven approach to anti-TNF induced PD.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Matthew Smyth indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elizabeth Spencer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hyder Said indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan C. Ungaro: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Boehringer Ingelheim – Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Eli Lilly – Grant/Research Support. Inotrem – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Prometheus Labratories – Grant/Research Support. Roivant – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Marla Dubinsky: AbbVie – Consultant. Abivax – Consultant. Arena – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Genentech – Consultant. Gilead – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Consultant. Prometheus Labs – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant.
Matthew Smyth, MD1, Elizabeth Spencer, MD2, Hyder Said, MD2, Ryan C. Ungaro, MD2, Marla C. Dubinsky, MD2. P2561 - Risankizumab Sustains Remission and Improves Anti-TNF-Induced Psoriasiform Dermatitis in Well Controlled Crohn's Disease Patients Switched from Anti-TNF Therapy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
