Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1806 - Development of IgG4-Related Disease and Autoimmune Pancreatitis-Like Changes on Cross-Sectional Imaging After GLP-1 Agonist
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Vikarsh Bhardwaj, MBBS
Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College
New Dehli, Delhi, India
Presenting Author(s)
Vikarsh Bhardwaj, MBBS1, Dhanush Shimoga, MBBS2, Raguraj Chandradevan, MBBS2, Natasha Savage, MD2, Amol Sharma, MS, MD, FACG2
1Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, New Dehli, Delhi, India; 2Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, GA
Introduction: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) was described in 2001 as autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) and is now known to involve every organ. Significant weight loss and lymphadenopathy occur in patients with Type 1 AIP. Here, we present a case of IgG4-RD triggered by initiation of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA).
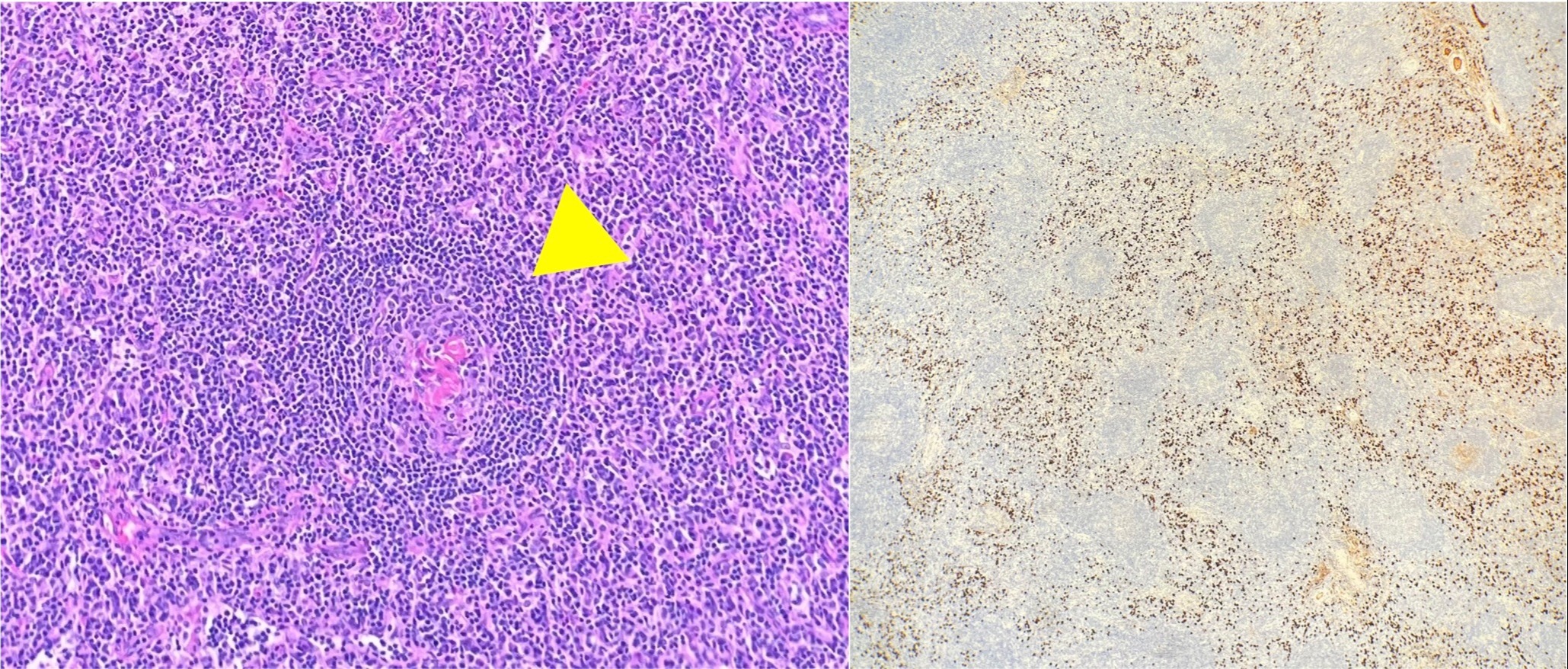
Case Description/Methods: A 77-year-old female with a history of T2DM who started treatment with semaglutide developed 65-lb unintentional weight loss (35% body weight) over 6 months. Physical examination revealed inguinal lymphadenopathy. CT A/P showed peritoneal soft tissue densities suggestive of primary peritoneal carcinoma and a ‘sausage-shaped’ appearance of peripancreatic inflammation. PET scan demonstrated multiple mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy, omental soft tissue density, and a swollen pancreas all with mildly increased FDG uptake. Ozempic after 6 weeks total exposure was switched to sitagliptin. A repeat PET scan 4 months later showed an interval increase in metabolic activity of lymph nodes in the neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and inguinal regions. . An excisional biopsy of the left inguinal node revealed over 40% IgG4 cells and prominent plasma cells (Fig 1), in setting of normal IL-6, consistent with IgG4-related disease. Sitagliptin was discontinued. Azathioprine was initiated and the patient was able to gain 10 lb with a persistent borderline elevation of IgG4.
Discussion: The pathophysiology of type I AIP, IgG4-RD, and anti-inflammatory actions of GLP-1RA are poorly understood. The initiation of GLP-1RA resulted in greater than expected weight loss and prominent lymphadenopathy with the development of IgG4-RD. Weight loss and lymphadenopathy continued to progress after switching to a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, another medication targeting the same incretin pathway as GLP-1RAs. Eventual discontinuation of DPP-4 inhibitor and initiation of azathioprine improved the patient’s condition. Even though clinical pancreatitis did not develop, evidence of a characteristic ‘sausage-shaped’ pancreas was appreciated on cross-sectional imaging and progressive inflammation with continuation of GLP-1RA may have progressed to clinical pancreatitis. In conclusion, this case suggests that IgG4 and antigen hypersensitivity pathways could play a crucial role in the development of IgG4-RD and AIP and may underlie the anti-inflammatory actions of GLP-1RAs.
Disclosures:
Vikarsh Bhardwaj, MBBS1, Dhanush Shimoga, MBBS2, Raguraj Chandradevan, MBBS2, Natasha Savage, MD2, Amol Sharma, MS, MD, FACG2. P1806 - Development of IgG4-Related Disease and Autoimmune Pancreatitis-Like Changes on Cross-Sectional Imaging After GLP-1 Agonist, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, New Dehli, Delhi, India; 2Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, GA
Introduction: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) was described in 2001 as autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) and is now known to involve every organ. Significant weight loss and lymphadenopathy occur in patients with Type 1 AIP. Here, we present a case of IgG4-RD triggered by initiation of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA).
Case Description/Methods: A 77-year-old female with a history of T2DM who started treatment with semaglutide developed 65-lb unintentional weight loss (35% body weight) over 6 months. Physical examination revealed inguinal lymphadenopathy. CT A/P showed peritoneal soft tissue densities suggestive of primary peritoneal carcinoma and a ‘sausage-shaped’ appearance of peripancreatic inflammation. PET scan demonstrated multiple mediastinal and hilar lymphadenopathy, omental soft tissue density, and a swollen pancreas all with mildly increased FDG uptake. Ozempic after 6 weeks total exposure was switched to sitagliptin. A repeat PET scan 4 months later showed an interval increase in metabolic activity of lymph nodes in the neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and inguinal regions. . An excisional biopsy of the left inguinal node revealed over 40% IgG4 cells and prominent plasma cells (Fig 1), in setting of normal IL-6, consistent with IgG4-related disease. Sitagliptin was discontinued. Azathioprine was initiated and the patient was able to gain 10 lb with a persistent borderline elevation of IgG4.
Discussion: The pathophysiology of type I AIP, IgG4-RD, and anti-inflammatory actions of GLP-1RA are poorly understood. The initiation of GLP-1RA resulted in greater than expected weight loss and prominent lymphadenopathy with the development of IgG4-RD. Weight loss and lymphadenopathy continued to progress after switching to a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor, another medication targeting the same incretin pathway as GLP-1RAs. Eventual discontinuation of DPP-4 inhibitor and initiation of azathioprine improved the patient’s condition. Even though clinical pancreatitis did not develop, evidence of a characteristic ‘sausage-shaped’ pancreas was appreciated on cross-sectional imaging and progressive inflammation with continuation of GLP-1RA may have progressed to clinical pancreatitis. In conclusion, this case suggests that IgG4 and antigen hypersensitivity pathways could play a crucial role in the development of IgG4-RD and AIP and may underlie the anti-inflammatory actions of GLP-1RAs.

Figure: Fig 1a. Morphologic examination of the excised lymph node revealed an enlarged lymph node without effacement, but many follicles showed an "onion-skinning" pattern with concentric rings of mantle zone B-cells surrounding atretic germinal centers (yellow triangle). (Hematoxylin and Eosin; original magnification, 200x); 1b. Between follicles, a prominent proliferation of plasma cells was noted without morphologic atypia. These plasma cells expressed IgG and a major subset expressed IgG4. (IgG4 immunohistochemical stain; original magnification, 40x)
Disclosures:
Vikarsh Bhardwaj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dhanush Shimoga indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raguraj Chandradevan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Natasha Savage indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amol Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikarsh Bhardwaj, MBBS1, Dhanush Shimoga, MBBS2, Raguraj Chandradevan, MBBS2, Natasha Savage, MD2, Amol Sharma, MS, MD, FACG2. P1806 - Development of IgG4-Related Disease and Autoimmune Pancreatitis-Like Changes on Cross-Sectional Imaging After GLP-1 Agonist, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
