Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0340 - Teriflunomide Induced Dysbiosis and Colitis in a Multiple Sclerosis Patient
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Yashwitha Sai Pulakurthi, MBBS, MD
Saint Michael's Medical Center
Newark, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Yashwitha Sai Pulakurthi, MBBS, MD1, Byron Okwesili, MD2, Charity Iheagwara, MD2, Jihad Slim, MD2, Theodore DaCosta Jr, MD2
1Saint Michael's Medical Center, Newark, NJ; 2New York Medical College - Saint Michael's Medical Center, Newark, NJ
Introduction: Teriflunomide is a disease-modifying therapy (DMT) that selectively inhibits dihydro-orotate dehydrogenase, a mitochondrial enzyme in the de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway. Teriflunomide is among the few orally administered therapies available for Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (RRMS), alongside Dimethyl fumarate, Fingolimod, etc. It is an immunomodulator recently implicated in gut microbiota dysbiosis. Here, we present a case of Clostridium difficile colitis followed by Proteus colitis in a patient taking Teriflunomide
Case Description/Methods: A 49-year-old female with a medical history of Multiple Sclerosis, lymphedema, and seizures presented to the hospital with abdominal pain and diarrhea lasting six days. Her medications included Teriflunomide for MS initiated in February, along with Levetiracetam, Baclofen, Amlodipine, and Lisinopril. Physical examination revealed decreased bowel sounds and 1+ pitting edema in both legs.
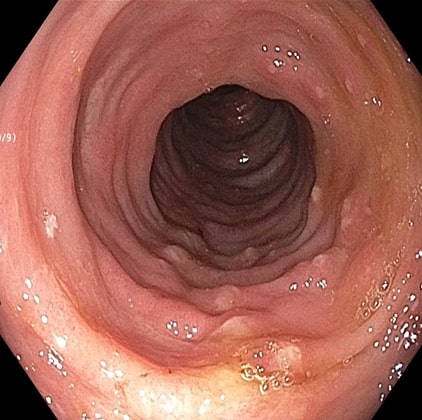
Initial labs showed a leukocyte count of 26,400 cells with neutrophilic predominance. CT abdomen pelvis showed diffuse colitis with fluid-filled portions. C. difficile toxin assay, antigen PCR, stool for ova and parasites, fecal lactoferrin, and calprotectin, stool culture were performed. All the tests were unremarkable while C. difficile PCR tested positive with negative toxin assay. A diagnosis of probable C. difficile infection (CDI) was made and oral vancomycin was administered. The patient's condition improved clinically, with stools becoming more formed, less frequent, She was discharged. She was readmitted to the hospital 3 weeks later with similar complaints, C.diff PCR was negative, stool culture was positive for Proteus infection. Colonoscopy was done for possible IBD which showed colitis with ulcerations in the descending and sigmoid colons and rectum. Biopsies showed focal acute colitis, benign lymphoid aggregates. Patient was started on antibiotic therapy after which her symptoms improved and later was discharged.
Discussion: Studies have implicated DMTs in gut microbiome alterations. According to a prospective study, they observed decreasing populations of Lachnospiraceae, Oscillospira, and Butyricimonas in patients taking Teriflunomide, bacteria crucial in controlling C. difficile populations. Additionally, they reported an increasing population of Enterococci and Enterobacteriaceae, associated with C. difficile infection. This incidence supports the notion that Teriflunomide induces gut microbiota dysbiosis
Disclosures:
Yashwitha Sai Pulakurthi, MBBS, MD1, Byron Okwesili, MD2, Charity Iheagwara, MD2, Jihad Slim, MD2, Theodore DaCosta Jr, MD2. P0340 - Teriflunomide Induced Dysbiosis and Colitis in a Multiple Sclerosis Patient, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Saint Michael's Medical Center, Newark, NJ; 2New York Medical College - Saint Michael's Medical Center, Newark, NJ
Introduction: Teriflunomide is a disease-modifying therapy (DMT) that selectively inhibits dihydro-orotate dehydrogenase, a mitochondrial enzyme in the de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway. Teriflunomide is among the few orally administered therapies available for Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (RRMS), alongside Dimethyl fumarate, Fingolimod, etc. It is an immunomodulator recently implicated in gut microbiota dysbiosis. Here, we present a case of Clostridium difficile colitis followed by Proteus colitis in a patient taking Teriflunomide
Case Description/Methods: A 49-year-old female with a medical history of Multiple Sclerosis, lymphedema, and seizures presented to the hospital with abdominal pain and diarrhea lasting six days. Her medications included Teriflunomide for MS initiated in February, along with Levetiracetam, Baclofen, Amlodipine, and Lisinopril. Physical examination revealed decreased bowel sounds and 1+ pitting edema in both legs.
Initial labs showed a leukocyte count of 26,400 cells with neutrophilic predominance. CT abdomen pelvis showed diffuse colitis with fluid-filled portions. C. difficile toxin assay, antigen PCR, stool for ova and parasites, fecal lactoferrin, and calprotectin, stool culture were performed. All the tests were unremarkable while C. difficile PCR tested positive with negative toxin assay. A diagnosis of probable C. difficile infection (CDI) was made and oral vancomycin was administered. The patient's condition improved clinically, with stools becoming more formed, less frequent, She was discharged. She was readmitted to the hospital 3 weeks later with similar complaints, C.diff PCR was negative, stool culture was positive for Proteus infection. Colonoscopy was done for possible IBD which showed colitis with ulcerations in the descending and sigmoid colons and rectum. Biopsies showed focal acute colitis, benign lymphoid aggregates. Patient was started on antibiotic therapy after which her symptoms improved and later was discharged.
Discussion: Studies have implicated DMTs in gut microbiome alterations. According to a prospective study, they observed decreasing populations of Lachnospiraceae, Oscillospira, and Butyricimonas in patients taking Teriflunomide, bacteria crucial in controlling C. difficile populations. Additionally, they reported an increasing population of Enterococci and Enterobacteriaceae, associated with C. difficile infection. This incidence supports the notion that Teriflunomide induces gut microbiota dysbiosis

Figure: Ulcerations in the descending colon
Disclosures:
Yashwitha Sai Pulakurthi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Byron Okwesili indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Charity Iheagwara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jihad Slim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Theodore DaCosta Jr indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yashwitha Sai Pulakurthi, MBBS, MD1, Byron Okwesili, MD2, Charity Iheagwara, MD2, Jihad Slim, MD2, Theodore DaCosta Jr, MD2. P0340 - Teriflunomide Induced Dysbiosis and Colitis in a Multiple Sclerosis Patient, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
