Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P0824 - Does Starting PPIs Increase the Risk of Complications in IBD Patients on Biologics or Immunomodulators?: A Large Multicenter Cohort Study
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Olanrewaju Adeniran, MBBS
West Virginia University School of Medicine
Morgantown, WV
Presenting Author(s)
Olanrewaju Adeniran, MBBS1, Ayowumi Adekolu, MD1, Joshua Kirkpatrick, MD1, Ethan M.. Cohen, MD2, Kanith Farah, MD1, Hilary Elom, MD3, Luis M.. Nieto, MD4, Ifeoma P. Kwentoh, MD5, Farirai Marwizi, MD6, Sharon Narvaez, MD7, Do Han Kim, MD8, Donghyun Ko, MD9, Swapna Gayam, MD2, Justin T.. Kupec, MD2
1West Virginia University School of Medicine, Morgantown, WV; 2West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 3West Virginia University School of Medicine, Columbia, MO; 4Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA; 5Harlem Hospital Center, New York, NY; 6St. John's Medical College and Hospital, Rockaway Park, NY; 7Universidad de Guayaquil, School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA; 8Mount Sinai Morningside and West, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 9Yale-New Haven Health/Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT
Introduction: Inconsistent data exist on the use of PPI in IBD patients. Some studies suggest that PPIs increase the risk of IBD complications. Others believe there is no increased IBD risk with PPI use after eliminating protopathic bias. This ongoing debate necessitates further research. While most studies focus on new IBD diagnoses or complications in patients already on PPIs, limited studies have assessed the risk of starting PPI in patients with IBD on biologics or immunomodulators. We aim to evaluate the risk of IBD complications, such as flares, bleeding, abscesses, fistulas, and intestinal obstruction, in this group of patients.
Methods: We conducted a population-based, nationwide retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX platform. Adult patients aged ≥18 years with IBD on biologics or immunomodulators, not on PPI, served as controls. In the intervention cohort, participants were started on PPI. IBD-related complications before and up to 1 month after the initiation of PPI were excluded. Patients with IBD on biologics or immunomodulators not on PPI were matched with those started on PPI using a 1:1 Propensity Score Matching (PSM) according to demographics, steroid use, long-term NSAID use, and nicotine use.
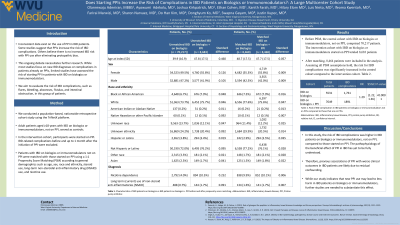
Results: Before PSM, the control cohort with IBD on biologics or immunomodulators, not on PPI, comprised 70,217 patients. The intervention cohort with IBD on biologics or immunomodulators started on PPI totaled 8,683 patients. After matching, 8,464 patients were included in the analysis. Assuming all PSM assumptions hold, the risk for IBD complications was significantly increased in the control cohort (RR 1.288; 95% CI 1.22, 1.36) compared to the intervention cohort (Table 1).
Discussion: In this study, the risk of IBD complications was higher in IBD patients on biologics or immunomodulators, not on PPI, compared to those started on PPI. The pathophysiology of the beneficial effect of PPI in IBD has yet to be fully understood. A proposed mechanism relates its chemical structure to that of metronidazole, which is effective in treating colitis. Others state that PPI may reduce oxidative stress and nitric oxide levels. Therefore, previous associations of PPI with worse clinical outcomes in IBD patients are likely due to residual confounding. While our study indicates that new PPI use may lead to less harm in IBD patients on biologics or immunomodulators, further studies are needed to substantiate this effect.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Olanrewaju Adeniran, MBBS1, Ayowumi Adekolu, MD1, Joshua Kirkpatrick, MD1, Ethan M.. Cohen, MD2, Kanith Farah, MD1, Hilary Elom, MD3, Luis M.. Nieto, MD4, Ifeoma P. Kwentoh, MD5, Farirai Marwizi, MD6, Sharon Narvaez, MD7, Do Han Kim, MD8, Donghyun Ko, MD9, Swapna Gayam, MD2, Justin T.. Kupec, MD2. P0824 - Does Starting PPIs Increase the Risk of Complications in IBD Patients on Biologics or Immunomodulators?: A Large Multicenter Cohort Study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1West Virginia University School of Medicine, Morgantown, WV; 2West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 3West Virginia University School of Medicine, Columbia, MO; 4Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA; 5Harlem Hospital Center, New York, NY; 6St. John's Medical College and Hospital, Rockaway Park, NY; 7Universidad de Guayaquil, School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA; 8Mount Sinai Morningside and West, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY; 9Yale-New Haven Health/Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT
Introduction: Inconsistent data exist on the use of PPI in IBD patients. Some studies suggest that PPIs increase the risk of IBD complications. Others believe there is no increased IBD risk with PPI use after eliminating protopathic bias. This ongoing debate necessitates further research. While most studies focus on new IBD diagnoses or complications in patients already on PPIs, limited studies have assessed the risk of starting PPI in patients with IBD on biologics or immunomodulators. We aim to evaluate the risk of IBD complications, such as flares, bleeding, abscesses, fistulas, and intestinal obstruction, in this group of patients.
Methods: We conducted a population-based, nationwide retrospective cohort study using the TriNetX platform. Adult patients aged ≥18 years with IBD on biologics or immunomodulators, not on PPI, served as controls. In the intervention cohort, participants were started on PPI. IBD-related complications before and up to 1 month after the initiation of PPI were excluded. Patients with IBD on biologics or immunomodulators not on PPI were matched with those started on PPI using a 1:1 Propensity Score Matching (PSM) according to demographics, steroid use, long-term NSAID use, and nicotine use.
Results: Before PSM, the control cohort with IBD on biologics or immunomodulators, not on PPI, comprised 70,217 patients. The intervention cohort with IBD on biologics or immunomodulators started on PPI totaled 8,683 patients. After matching, 8,464 patients were included in the analysis. Assuming all PSM assumptions hold, the risk for IBD complications was significantly increased in the control cohort (RR 1.288; 95% CI 1.22, 1.36) compared to the intervention cohort (Table 1).
Discussion: In this study, the risk of IBD complications was higher in IBD patients on biologics or immunomodulators, not on PPI, compared to those started on PPI. The pathophysiology of the beneficial effect of PPI in IBD has yet to be fully understood. A proposed mechanism relates its chemical structure to that of metronidazole, which is effective in treating colitis. Others state that PPI may reduce oxidative stress and nitric oxide levels. Therefore, previous associations of PPI with worse clinical outcomes in IBD patients are likely due to residual confounding. While our study indicates that new PPI use may lead to less harm in IBD patients on biologics or immunomodulators, further studies are needed to substantiate this effect.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Olanrewaju Adeniran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayowumi Adekolu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joshua Kirkpatrick indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ethan Cohen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kanith Farah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hilary Elom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Luis Nieto indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ifeoma Kwentoh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Farirai Marwizi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sharon Narvaez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Do Han Kim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Donghyun Ko indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swapna Gayam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Justin Kupec indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Olanrewaju Adeniran, MBBS1, Ayowumi Adekolu, MD1, Joshua Kirkpatrick, MD1, Ethan M.. Cohen, MD2, Kanith Farah, MD1, Hilary Elom, MD3, Luis M.. Nieto, MD4, Ifeoma P. Kwentoh, MD5, Farirai Marwizi, MD6, Sharon Narvaez, MD7, Do Han Kim, MD8, Donghyun Ko, MD9, Swapna Gayam, MD2, Justin T.. Kupec, MD2. P0824 - Does Starting PPIs Increase the Risk of Complications in IBD Patients on Biologics or Immunomodulators?: A Large Multicenter Cohort Study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
