Sunday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P1062 - The Efficacy and Safety of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Peri-Appendiceal Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
.jpg)
Hazem Abosheaishaa, MD
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Queens, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Hazem Abosheaishaa, MD1, Abdellatif Ismail, MD2, Mohanad Awadalla, MD3, Shaikhoon Mohammed, MD4, Monzer Abdalla, MD5, Ayman Elawad, MD6, Chukwunonso Ezeani, MBBS7, Jenson Phung, MD8, Mohamed Abdallah, MD9, Neil Nero, 9, Amit Bhatt, MD10, Madhusudhan R. Sanaka, MD11, Mohammad Bilal, MD12
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens, NY; 2University of Maryland Medical Center, Baltimore, MD; 3Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA; 4Macon Medical Group PC, Atlanta, GA; 5Ascension Saint Francis Hospital, Evanston, IL; 6Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA; 7Baton Rouge General Medical Center, Baton Rouge, LA; 8University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN; 9Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 10Digestive Disease Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 11Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 12University of Minnesota and Minneapolis VA Health Care System, Minneapolis, MN
Introduction: Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has emerged as a promising technique for managing early-stage gastrointestinal neoplastic lesions. However, its application to peri-appendiceal lesions presents unique challenges due to anatomical complexities and the theoretical risk of causing appendicitis or bowel perforation associated with endoscopic resections. Therefore, surgical resection is often used to manage these lesions. This systematic review and meta-analysis aim to evaluate the safety and efficacy of ESD in managing peri-appendiceal lesions.
Methods: A systematic search across multiple databases was conducted, adhering to PRISMA guidelines. Eligible studies focused on adult populations undergoing ESD for peri-appendiceal lesions. The primary outcome was technical success and secondary outcomes included R0 resection, en-bloc resection, adverse events (AEs), and the need for surgery. Data was reported using confidence interval (CI) and heterogeneity (I2).
Results: Six studies comprising 298 patients were included. Technical success was achieved in 98% [95% CI [97 -100 %]; I:4.63%], with R0 resection and en-bloc resection rates of 84% [95% CI [77%-91%]; I:61.86%] and 92%, [95% CI [86%-97%]; I:66.11%], respectively. The overall rates of polyp recurrence, appendicitis, and bleeding were 0.1% [95% CI [0%-2%]; I :0 %], 3% [95% CI [0%-4%]; I :0 %], and 1% [95% CI [0%-3%]; I :0 %], respectively with, and respectively. The incidence of perforation was 11% [95% CI [3%-19%]; I:84.55%], and the need for surgical intervention was 6% [95% CI [1%-10%]; I:74.12%].
Discussion: Our study showed that ESD is an effective alternative to surgical resection for managing periappendiceal lesions. The high rates of technical success (98%), en-bloc resection (92%), and R0 resection (84%) indicate that ESD can achieve thorough and precise removal of these lesions. However, the relatively high incidence of perforation (11%) and the need for surgical intervention in some cases (6%) highlight the necessity for careful patient selection and skilled execution of the procedure.
Disclosures:
Hazem Abosheaishaa, MD1, Abdellatif Ismail, MD2, Mohanad Awadalla, MD3, Shaikhoon Mohammed, MD4, Monzer Abdalla, MD5, Ayman Elawad, MD6, Chukwunonso Ezeani, MBBS7, Jenson Phung, MD8, Mohamed Abdallah, MD9, Neil Nero, 9, Amit Bhatt, MD10, Madhusudhan R. Sanaka, MD11, Mohammad Bilal, MD12. P1062 - The Efficacy and Safety of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Peri-Appendiceal Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens, NY; 2University of Maryland Medical Center, Baltimore, MD; 3Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA; 4Macon Medical Group PC, Atlanta, GA; 5Ascension Saint Francis Hospital, Evanston, IL; 6Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA; 7Baton Rouge General Medical Center, Baton Rouge, LA; 8University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN; 9Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 10Digestive Disease Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 11Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 12University of Minnesota and Minneapolis VA Health Care System, Minneapolis, MN
Introduction: Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has emerged as a promising technique for managing early-stage gastrointestinal neoplastic lesions. However, its application to peri-appendiceal lesions presents unique challenges due to anatomical complexities and the theoretical risk of causing appendicitis or bowel perforation associated with endoscopic resections. Therefore, surgical resection is often used to manage these lesions. This systematic review and meta-analysis aim to evaluate the safety and efficacy of ESD in managing peri-appendiceal lesions.
Methods: A systematic search across multiple databases was conducted, adhering to PRISMA guidelines. Eligible studies focused on adult populations undergoing ESD for peri-appendiceal lesions. The primary outcome was technical success and secondary outcomes included R0 resection, en-bloc resection, adverse events (AEs), and the need for surgery. Data was reported using confidence interval (CI) and heterogeneity (I2).
Results: Six studies comprising 298 patients were included. Technical success was achieved in 98% [95% CI [97 -100 %]; I:4.63%], with R0 resection and en-bloc resection rates of 84% [95% CI [77%-91%]; I:61.86%] and 92%, [95% CI [86%-97%]; I:66.11%], respectively. The overall rates of polyp recurrence, appendicitis, and bleeding were 0.1% [95% CI [0%-2%]; I :0 %], 3% [95% CI [0%-4%]; I :0 %], and 1% [95% CI [0%-3%]; I :0 %], respectively with, and respectively. The incidence of perforation was 11% [95% CI [3%-19%]; I:84.55%], and the need for surgical intervention was 6% [95% CI [1%-10%]; I:74.12%].
Discussion: Our study showed that ESD is an effective alternative to surgical resection for managing periappendiceal lesions. The high rates of technical success (98%), en-bloc resection (92%), and R0 resection (84%) indicate that ESD can achieve thorough and precise removal of these lesions. However, the relatively high incidence of perforation (11%) and the need for surgical intervention in some cases (6%) highlight the necessity for careful patient selection and skilled execution of the procedure.

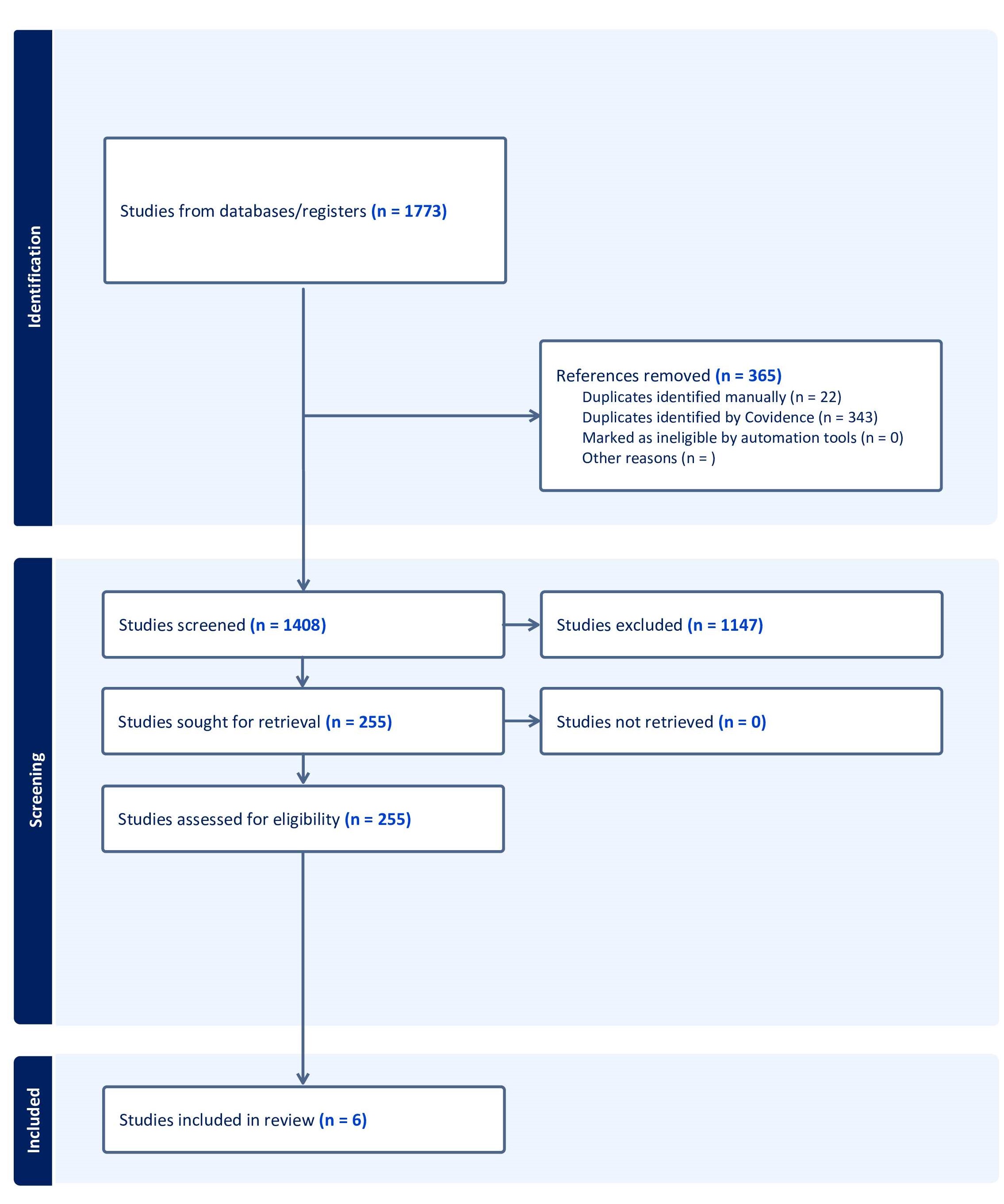
Figure: Figure 1: PRISMA flow diagram of our search.
Disclosures:
Hazem Abosheaishaa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdellatif Ismail indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohanad Awadalla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shaikhoon Mohammed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Monzer Abdalla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayman Elawad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chukwunonso Ezeani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jenson Phung indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Abdallah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neil Nero indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amit Bhatt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhusudhan R. Sanaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammad Bilal: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Cook endoscopy – Speakers Bureau.
Hazem Abosheaishaa, MD1, Abdellatif Ismail, MD2, Mohanad Awadalla, MD3, Shaikhoon Mohammed, MD4, Monzer Abdalla, MD5, Ayman Elawad, MD6, Chukwunonso Ezeani, MBBS7, Jenson Phung, MD8, Mohamed Abdallah, MD9, Neil Nero, 9, Amit Bhatt, MD10, Madhusudhan R. Sanaka, MD11, Mohammad Bilal, MD12. P1062 - The Efficacy and Safety of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Peri-Appendiceal Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
