Sunday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P1108 - Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Symptomatic Pancreatic Gastrinoma
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- AC
Ashleigh Chuah, MD
Emory University School of Medicine
Atlanta, GA
Presenting Author(s)
Ashleigh Chuah, MD, Field Willingham, MD, MPH
Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: Gastrinomas are neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) that oversecrete gastrin and can cause Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Management can include medication therapy and surgical resection. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (EUS-RFA), which uses thermal energy to induce cellular necrosis, has shown early promise in the management of pancreatic NETs.
Case Description/Methods: A 70-year-old male with history of parathyroid adenoma, hypertension presented with epigastric pain, diarrhea, melena, facial flushing, and 10-lb weight loss for 3 months. Laboratory evaluation revealed iron deficiency anemia, elevated urine 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) 8.3 mg/24hr, elevated serum chromogranin A 443 ng/mL, and normal gastrin 70 pg/mL. He underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy that demonstrated gastritis, gastric ulcers with positive H. pylori, and a 1.5 cm raised sessile polyp in the duodenal bulb with positive immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for chromogranin, consistent with NET. Dotatate positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) revealed a focus of radiotracer uptake in the pancreatic body. An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) revealed a 10 x 7 mm hypoechoic mass in the pancreatic body, and fine needle aspiration showed round eccentric hyperchromatic nuclei, with positive IHC staining for chromogranin, synaptophysin, and gastrin, consistent with gastrinoma. He was seen by surgical oncology and initially offered resection but was then referred for evaluation for endoscopic management. He underwent EUS with band ligation of the duodenal bulb lesion plus EUS guided RFA to the pancreatic gastrinoma with a 19 gauge 7 mm treatment zone trocar. 8 ablations were performed (29, 18, 10, 15, 13, 7, 6, 10 seconds). At 3 months, repeat EUS revealed a well-healed scar in the duodenal bulb and ablation-related changes in the pancreatic body. Biopsies of the bulb revealed scar and no neuroendocrine cells. He also reported resolution of flushing, diarrhea, and weight loss. Repeat labs revealed normalized urine 5-HIAA 6.0 mg/24hr and chromogranin A 236 ng/mL.
Discussion: Literature on EUS-RFA for symptomatic NETs has predominantly focused on insulinomas. To our knowledge, we describe the first case of EUS-RFA for symptomatic gastrinoma with resolution of symptoms, highlighting its potential as a minimally invasive alternative to surgery. Further research is needed to examine the long-term efficacy and safety and to compare outcomes between EUS-RFA and resection.
Disclosures:
Ashleigh Chuah, MD, Field Willingham, MD, MPH. P1108 - Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Symptomatic Pancreatic Gastrinoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA
Introduction: Gastrinomas are neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) that oversecrete gastrin and can cause Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Management can include medication therapy and surgical resection. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (EUS-RFA), which uses thermal energy to induce cellular necrosis, has shown early promise in the management of pancreatic NETs.
Case Description/Methods: A 70-year-old male with history of parathyroid adenoma, hypertension presented with epigastric pain, diarrhea, melena, facial flushing, and 10-lb weight loss for 3 months. Laboratory evaluation revealed iron deficiency anemia, elevated urine 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) 8.3 mg/24hr, elevated serum chromogranin A 443 ng/mL, and normal gastrin 70 pg/mL. He underwent esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy that demonstrated gastritis, gastric ulcers with positive H. pylori, and a 1.5 cm raised sessile polyp in the duodenal bulb with positive immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for chromogranin, consistent with NET. Dotatate positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) revealed a focus of radiotracer uptake in the pancreatic body. An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) revealed a 10 x 7 mm hypoechoic mass in the pancreatic body, and fine needle aspiration showed round eccentric hyperchromatic nuclei, with positive IHC staining for chromogranin, synaptophysin, and gastrin, consistent with gastrinoma. He was seen by surgical oncology and initially offered resection but was then referred for evaluation for endoscopic management. He underwent EUS with band ligation of the duodenal bulb lesion plus EUS guided RFA to the pancreatic gastrinoma with a 19 gauge 7 mm treatment zone trocar. 8 ablations were performed (29, 18, 10, 15, 13, 7, 6, 10 seconds). At 3 months, repeat EUS revealed a well-healed scar in the duodenal bulb and ablation-related changes in the pancreatic body. Biopsies of the bulb revealed scar and no neuroendocrine cells. He also reported resolution of flushing, diarrhea, and weight loss. Repeat labs revealed normalized urine 5-HIAA 6.0 mg/24hr and chromogranin A 236 ng/mL.
Discussion: Literature on EUS-RFA for symptomatic NETs has predominantly focused on insulinomas. To our knowledge, we describe the first case of EUS-RFA for symptomatic gastrinoma with resolution of symptoms, highlighting its potential as a minimally invasive alternative to surgery. Further research is needed to examine the long-term efficacy and safety and to compare outcomes between EUS-RFA and resection.

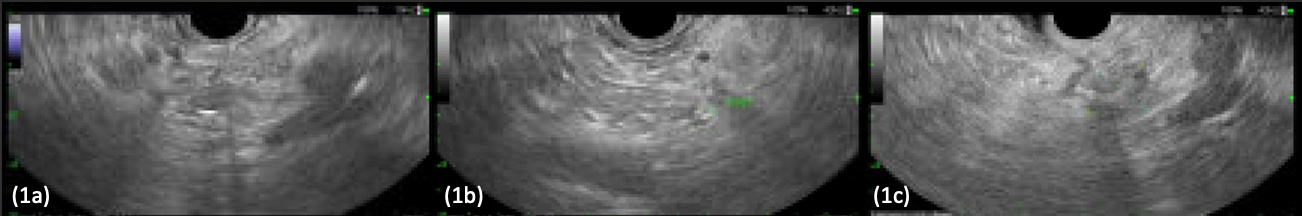
Figure: Figure 1. Endoscopic ultrasound showing the pancreatic gastrinoma measuring 10 mm x 7 mm, immediately before RFA (A), immediately after RFA (B), and at 3 month follow up. Ablation site measures 13 mm x 10 mm and endosonographically appears well-healed, with hypoechoic and heterogenous changes (C).
Disclosures:
Ashleigh Chuah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Field Willingham indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashleigh Chuah, MD, Field Willingham, MD, MPH. P1108 - Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Symptomatic Pancreatic Gastrinoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
