Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
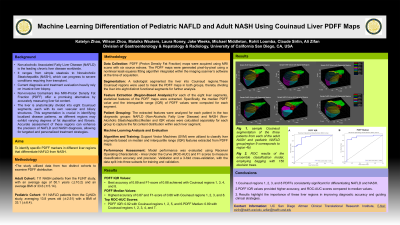
P1188 - Machine Learning Differentiation of Pediatric NAFLD and Adult NASH Using Couinaud Liver PDFF Maps
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- KZ
Katelyn Zhao
UC San Diego
La Jolla, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Katelyn Zhao, 1, Wilson Zhu, 1, Malaika Wauters, 1, Laura Roney, 1, Jake Weeks, BS1, Michael Middleton, PhD1, Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc2, Claude Sirlin, MD1, Ali Zifan, PhD1
1UC San Diego, La Jolla, CA; 2University of California San Diego School of Medicine, La Jolla, CA
Introduction: Non-alcoholic Associated Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the leading chronic liver disease worldwide, spanning from simple steatosis to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to severe liver conditions requiring transplant. Current diagnosis and treatment evaluation heavily rely on invasive liver biopsy, limiting widespread use. Non-invasive biomarkers like MRI-Proton Density Fat Fraction (PDFF) offer a promising alternative by accurately measuring liver fat content, potentially transforming NASH management and clinical trials. The goal of this study is to pinpoint specific PDFF markers in different liver regions that reliably differentiate between NAFLD and NASH.
Methods: Data from two cohorts: 111 adult patients from the FLINT study (age:50.1 ±10.2; BMI:33.6±5.14) diagnosed with NASH, and 111 pediatric NAFLD patients from the CyNCh study (age:13.8 ±2.51; BMI:33.1±6.4). Radiologist segmented Couinaud regions, were used to mask PDFF maps into eight functional segments. PDFF maps were derived using six source echoes. These were computed pixel-by-pixel using software on the scanner at the time of acquisition using a nonlinear least-squares fit. For each of the 8 regions, median and interquartile ranges (IQR) of PDFF values were extracted for each patient in each of the 2 groups. Machine learning algorithms, specifically Support Vector Machines (SVM), were trained using these median and IQR features to identify which liver segments or combinations best discriminated between pediatric NAFLD and Adult NASH. Model performance was evaluated using ROC-AUC and F1 scores using 3-fold cross-validation.
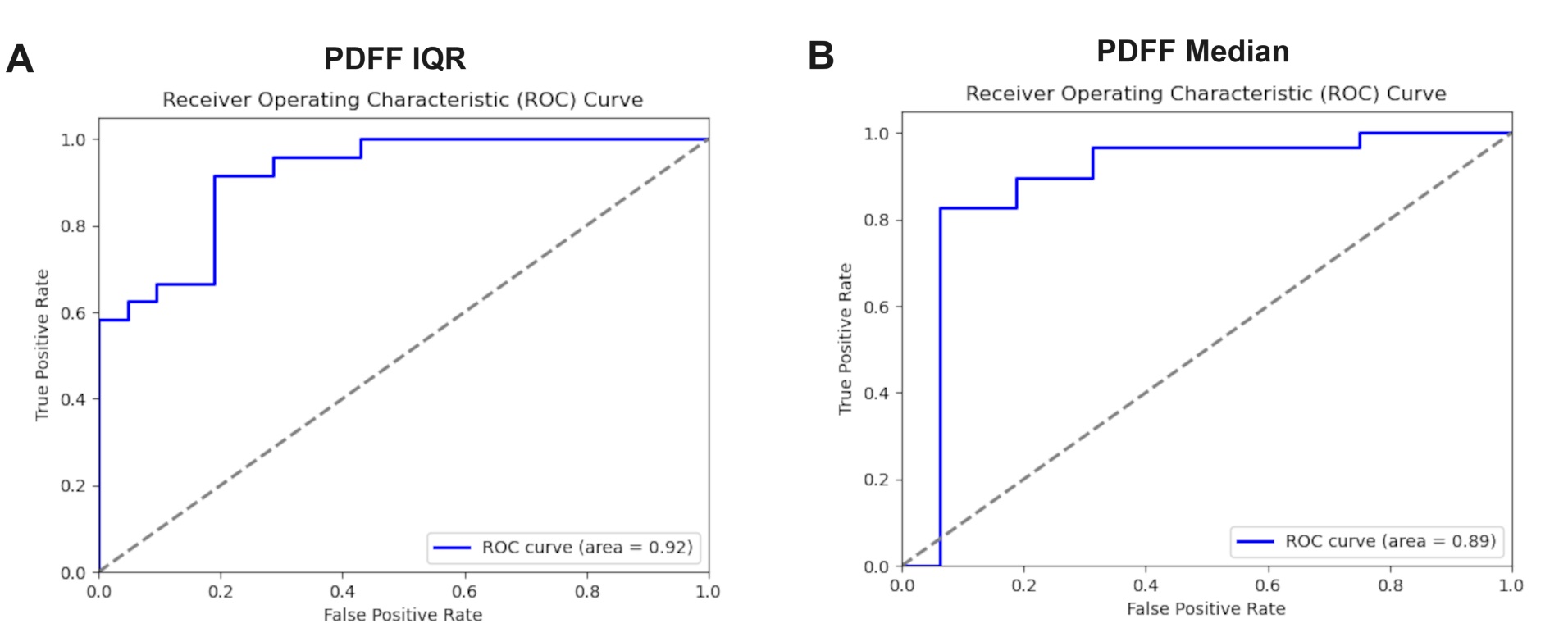
Results: Using regional PDFF IQR values produced the best results, particularly Couinaud regions 1, 3, 4, and 8 achieving the highest accuracy of 0.89 and an F1-score of 0.88. In comparison, for PDFF Median values, Couinaud regions 1, 2, 3, and 8 yielded the highest accuracy of 0.87 and an F1-score of 0.86. The top ROC-AUC score for PDFF IQR values was 0.92 with Couinaud regions 1, 2, 5, and 6, while for Median values, the highest ROC-AUC was 0.89 with Couinaud regions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 7.
Discussion: Couinaud regions 1, 2, 3, and 8 PDFFs demonstrate consistent significance in the differentiation of NAFLD and NASH, with PDFF IQR values achieving higher accuracy and ROC-AUC scores. These findings underscore the critical role of these specific liver regions in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and guiding effective clinical strategies for liver disease.
Disclosures:
Katelyn Zhao, 1, Wilson Zhu, 1, Malaika Wauters, 1, Laura Roney, 1, Jake Weeks, BS1, Michael Middleton, PhD1, Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc2, Claude Sirlin, MD1, Ali Zifan, PhD1. P1188 - Machine Learning Differentiation of Pediatric NAFLD and Adult NASH Using Couinaud Liver PDFF Maps, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1UC San Diego, La Jolla, CA; 2University of California San Diego School of Medicine, La Jolla, CA
Introduction: Non-alcoholic Associated Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the leading chronic liver disease worldwide, spanning from simple steatosis to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), which can progress to severe liver conditions requiring transplant. Current diagnosis and treatment evaluation heavily rely on invasive liver biopsy, limiting widespread use. Non-invasive biomarkers like MRI-Proton Density Fat Fraction (PDFF) offer a promising alternative by accurately measuring liver fat content, potentially transforming NASH management and clinical trials. The goal of this study is to pinpoint specific PDFF markers in different liver regions that reliably differentiate between NAFLD and NASH.
Methods: Data from two cohorts: 111 adult patients from the FLINT study (age:50.1 ±10.2; BMI:33.6±5.14) diagnosed with NASH, and 111 pediatric NAFLD patients from the CyNCh study (age:13.8 ±2.51; BMI:33.1±6.4). Radiologist segmented Couinaud regions, were used to mask PDFF maps into eight functional segments. PDFF maps were derived using six source echoes. These were computed pixel-by-pixel using software on the scanner at the time of acquisition using a nonlinear least-squares fit. For each of the 8 regions, median and interquartile ranges (IQR) of PDFF values were extracted for each patient in each of the 2 groups. Machine learning algorithms, specifically Support Vector Machines (SVM), were trained using these median and IQR features to identify which liver segments or combinations best discriminated between pediatric NAFLD and Adult NASH. Model performance was evaluated using ROC-AUC and F1 scores using 3-fold cross-validation.
Results: Using regional PDFF IQR values produced the best results, particularly Couinaud regions 1, 3, 4, and 8 achieving the highest accuracy of 0.89 and an F1-score of 0.88. In comparison, for PDFF Median values, Couinaud regions 1, 2, 3, and 8 yielded the highest accuracy of 0.87 and an F1-score of 0.86. The top ROC-AUC score for PDFF IQR values was 0.92 with Couinaud regions 1, 2, 5, and 6, while for Median values, the highest ROC-AUC was 0.89 with Couinaud regions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 7.
Discussion: Couinaud regions 1, 2, 3, and 8 PDFFs demonstrate consistent significance in the differentiation of NAFLD and NASH, with PDFF IQR values achieving higher accuracy and ROC-AUC scores. These findings underscore the critical role of these specific liver regions in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and guiding effective clinical strategies for liver disease.

Figure: Figure 1. ROC-AUC curves od using median and IQR values of the Couinaud Liver regions.
Disclosures:
Katelyn Zhao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wilson Zhu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Malaika Wauters indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laura Roney indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jake Weeks indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Middleton indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rohit Loomba: 89BIO – Consultant. Aardvark – Consultant. Altimmune – Consultant. Madrigal Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Merck – Consultant. Novo Nordisk – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Terns – Consultant. Viking – Consultant.
Claude Sirlin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Zifan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Katelyn Zhao, 1, Wilson Zhu, 1, Malaika Wauters, 1, Laura Roney, 1, Jake Weeks, BS1, Michael Middleton, PhD1, Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc2, Claude Sirlin, MD1, Ali Zifan, PhD1. P1188 - Machine Learning Differentiation of Pediatric NAFLD and Adult NASH Using Couinaud Liver PDFF Maps, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
