Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1215 - Bedside Assessment of Sarcopenia in Hospitalised Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ramesh Kumar, MBBS, MD, DM
All India Institute of Medical Sciences
Patna, Bihar, India
Presenting Author(s)
Ramesh Kumar, MBBS, MD, DM, Sabbu S Prakash, MBBS, MD, Rajeev N Priyadarshi, MBBS, MD, Sudhir Kumar, MBBS, MD, DM
All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, Bihar, India
Introduction: Sarcopenia is associated with many adverse outcomes in patients with cirrhosis. The tools currently in use for assessing sarcopenia have numerous flaws. We evaluated the utility of portable ultrasonography and a dynamometer for the bedside assessment of sarcopenia and its implications in hospitalised cirrhosis patients.
Methods: A dynamometer was used to test the hand grip strength (HGS), and ultrasound was used to measure the thickness of the forearm and quadriceps muscles. HGS value < 27 kg for men and < 16 kg for women was taken as significant according to the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People (EWGSOP2) criteria. Arm and quadriceps muscles indices were derived as sum of corresponding muscle thickness of right and left side in cm divied by height2 (m2). The lower normal limit of muscle mass (5th percentile) was determined on 100 matched healthy controls.
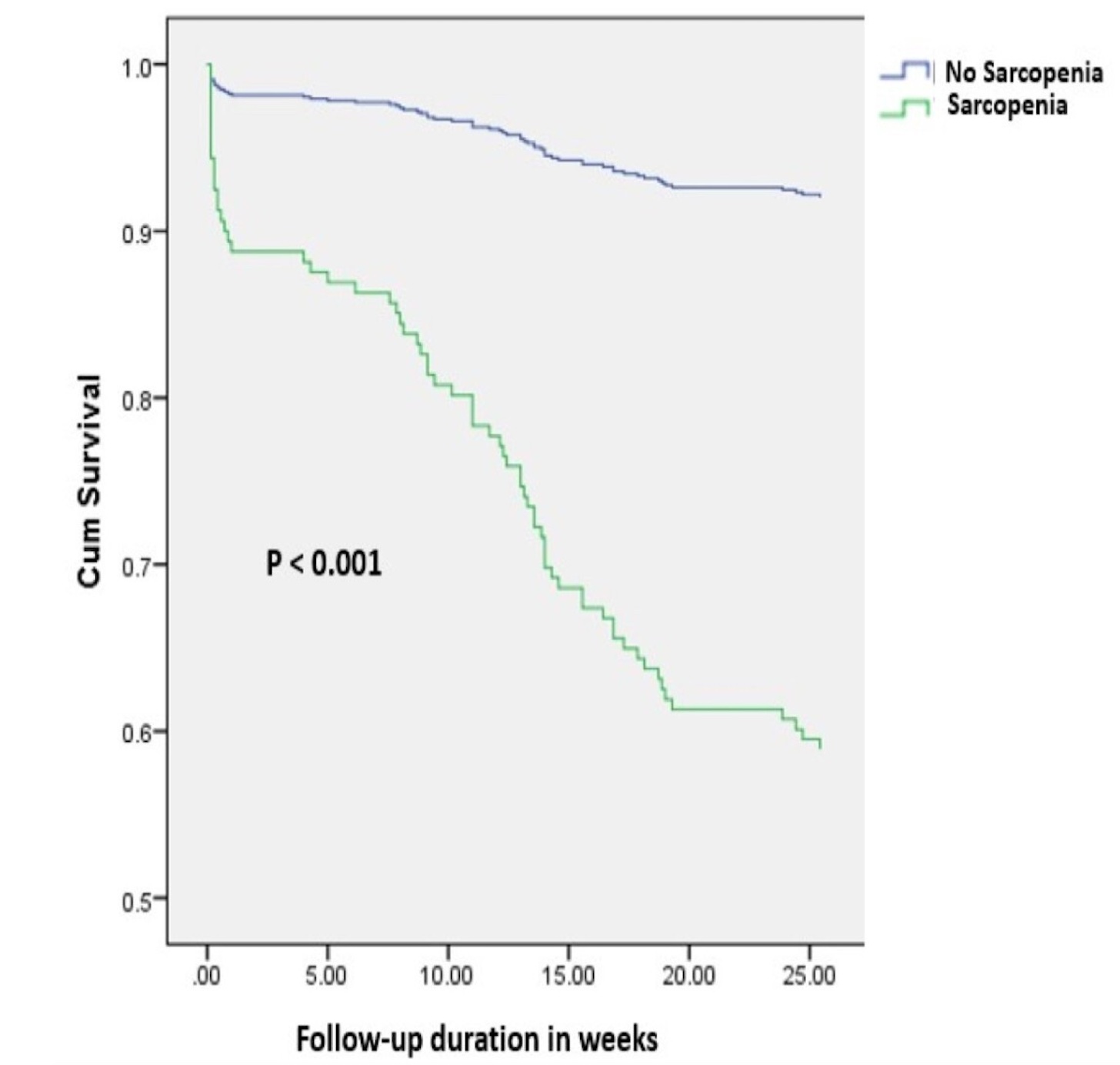
Results: According to the EWGSOP2 criteria and HGS values, the prevalence of sarcopenia and probable sarcopenia among 300 cirrhosis patients were 56% and 62.3%, respectively. HGS alone identified sarcopenia in 88.9% of patients, while overestimated it in 6.3% of cases. The prevalence rate of sarcopenic obesity was 11%. Compared to patients without sarcopenia, sarcopenic patients had more complications of cirrhosis, such as ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, sepsis, hepatorenal syndrome, and refractory ascites. In-hospital (p=0.037), 3-month (p< 0.001), and 6-month (p< 0.001) mortality rates were all higher among sarcopenic patients. On cox-regression survival analysis, overall 6-months mortality was significantly higher in sarcopenic patients compared to patients without sarcopenia (hazard ratio: 6.37, 95% confidence interval: 3.15 – 12.8, p< 0.001).
Discussion: Bedside assessment of sarcopenia using a portable ultrasound machine and a dynamometer detected liver cirrhosis patients with higher risk of complications and mortality. Sarcopenia was detected in a considerable proportion of hospitalized cirrhosis patients using this simple, convenient and safe method. Additionally, it offers the advantage of repeated assessments, which can assist clinicians in both diagnosis and monitoring the effectiveness of targeted therapies.
Disclosures:
Ramesh Kumar, MBBS, MD, DM, Sabbu S Prakash, MBBS, MD, Rajeev N Priyadarshi, MBBS, MD, Sudhir Kumar, MBBS, MD, DM. P1215 - Bedside Assessment of Sarcopenia in Hospitalised Patients with Liver Cirrhosis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, Bihar, India
Introduction: Sarcopenia is associated with many adverse outcomes in patients with cirrhosis. The tools currently in use for assessing sarcopenia have numerous flaws. We evaluated the utility of portable ultrasonography and a dynamometer for the bedside assessment of sarcopenia and its implications in hospitalised cirrhosis patients.
Methods: A dynamometer was used to test the hand grip strength (HGS), and ultrasound was used to measure the thickness of the forearm and quadriceps muscles. HGS value < 27 kg for men and < 16 kg for women was taken as significant according to the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People (EWGSOP2) criteria. Arm and quadriceps muscles indices were derived as sum of corresponding muscle thickness of right and left side in cm divied by height2 (m2). The lower normal limit of muscle mass (5th percentile) was determined on 100 matched healthy controls.
Results: According to the EWGSOP2 criteria and HGS values, the prevalence of sarcopenia and probable sarcopenia among 300 cirrhosis patients were 56% and 62.3%, respectively. HGS alone identified sarcopenia in 88.9% of patients, while overestimated it in 6.3% of cases. The prevalence rate of sarcopenic obesity was 11%. Compared to patients without sarcopenia, sarcopenic patients had more complications of cirrhosis, such as ascites, variceal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, sepsis, hepatorenal syndrome, and refractory ascites. In-hospital (p=0.037), 3-month (p< 0.001), and 6-month (p< 0.001) mortality rates were all higher among sarcopenic patients. On cox-regression survival analysis, overall 6-months mortality was significantly higher in sarcopenic patients compared to patients without sarcopenia (hazard ratio: 6.37, 95% confidence interval: 3.15 – 12.8, p< 0.001).
Discussion: Bedside assessment of sarcopenia using a portable ultrasound machine and a dynamometer detected liver cirrhosis patients with higher risk of complications and mortality. Sarcopenia was detected in a considerable proportion of hospitalized cirrhosis patients using this simple, convenient and safe method. Additionally, it offers the advantage of repeated assessments, which can assist clinicians in both diagnosis and monitoring the effectiveness of targeted therapies.

Figure: Cox regression survival curves for 6-month overall survival of liver cirrhosis patients stratified by the presence or absence of sarcopenia.
Disclosures:
Ramesh Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sabbu S Prakash indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajeev N Priyadarshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sudhir Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ramesh Kumar, MBBS, MD, DM, Sabbu S Prakash, MBBS, MD, Rajeev N Priyadarshi, MBBS, MD, Sudhir Kumar, MBBS, MD, DM. P1215 - Bedside Assessment of Sarcopenia in Hospitalised Patients with Liver Cirrhosis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
