Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1218 - Trends in Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma From 2000 to 2020: A SEER-Based Analysis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Urmimala Chaudhuri, DO
Wright State University
Centerville, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Urmimala Chaudhuri, DO1, Chase Thornton, MD2, Drew Triplett, DO2
1Wright State University, Centerville, OH; 2Wright State University, Dayton, OH
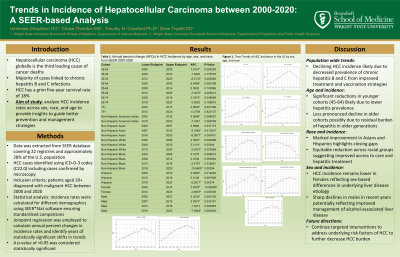
Introduction: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a significant global health concern ranking as the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. The risk factors for HCC include chronic hepatitis B and C, alcohol-associated liver disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The aim of this study is to understand the recent trends in incidence of HCC utilizing the SEER database from 2000 to 2020.
Methods: Incidence rates of HCC per 100,000 population (age-adjusted) from 2000 to 2020 were calculated utilizing a population-based cancer registry, SEER*Stat (version 8.4.3). HCC was identified by ICD-O-3 code and by malignant type confirmed by histopathology only. We utilized Joinpoint Regression Program version 5.0.1 to report time-trends as annual percentage change (APC). Statistical significance was set at P value less than 0.05.
Results: There were a total of 240,433 cases of HCC recorded from 2000 to 2020. Since 2015, the incidence of HCC has been consistently declining. This trend is evident across all age groups, particularly among 45-54 year olds (APC -8.2172, P-value < 0.0005) and 55-64 year olds (APC -7.0275, P-value < 0.0005). Decline in HCC incidence was observed across all racial demographics. Notably, Blacks have had a significant decrease in HCC incidence, especially from 2018 to 2020 (APC -10.6409, P-value < 0.05). Similarly, the APC decreased in Hispanics from 2018 to 2020 (APC -8.2517, P-value < 0.005). The incidence of HCC among Asians decreased significantly from 2016 to 2020 (APC -8.0577, P-value < 0.0005). Furthermore, the incidence of HCC among both sexes has declined. The APC was -2.8378 from 2014 to 2020 for females and -7.2848 for males from 2018 to 2020.
Discussion: The decline in HCC incidence suggests improvement in managing etiologies of HCC including chronic hepatitis. However, disparities exist among demographic groups as highlighted in the results. This indicates a need for targeted interventions that address the underlying risk factors of HCC including focusing on obesity and alcohol use disorder. With continued efforts focused on prevention, early detection, and treatment, the burden of HCC will continue to decline.
Disclosures:
Urmimala Chaudhuri, DO1, Chase Thornton, MD2, Drew Triplett, DO2. P1218 - Trends in Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma From 2000 to 2020: A SEER-Based Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Urmimala Chaudhuri, DO1, Chase Thornton, MD2, Drew Triplett, DO2
1Wright State University, Centerville, OH; 2Wright State University, Dayton, OH
Introduction: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a significant global health concern ranking as the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. The risk factors for HCC include chronic hepatitis B and C, alcohol-associated liver disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The aim of this study is to understand the recent trends in incidence of HCC utilizing the SEER database from 2000 to 2020.
Methods: Incidence rates of HCC per 100,000 population (age-adjusted) from 2000 to 2020 were calculated utilizing a population-based cancer registry, SEER*Stat (version 8.4.3). HCC was identified by ICD-O-3 code and by malignant type confirmed by histopathology only. We utilized Joinpoint Regression Program version 5.0.1 to report time-trends as annual percentage change (APC). Statistical significance was set at P value less than 0.05.
Results: There were a total of 240,433 cases of HCC recorded from 2000 to 2020. Since 2015, the incidence of HCC has been consistently declining. This trend is evident across all age groups, particularly among 45-54 year olds (APC -8.2172, P-value < 0.0005) and 55-64 year olds (APC -7.0275, P-value < 0.0005). Decline in HCC incidence was observed across all racial demographics. Notably, Blacks have had a significant decrease in HCC incidence, especially from 2018 to 2020 (APC -10.6409, P-value < 0.05). Similarly, the APC decreased in Hispanics from 2018 to 2020 (APC -8.2517, P-value < 0.005). The incidence of HCC among Asians decreased significantly from 2016 to 2020 (APC -8.0577, P-value < 0.0005). Furthermore, the incidence of HCC among both sexes has declined. The APC was -2.8378 from 2014 to 2020 for females and -7.2848 for males from 2018 to 2020.
Discussion: The decline in HCC incidence suggests improvement in managing etiologies of HCC including chronic hepatitis. However, disparities exist among demographic groups as highlighted in the results. This indicates a need for targeted interventions that address the underlying risk factors of HCC including focusing on obesity and alcohol use disorder. With continued efforts focused on prevention, early detection, and treatment, the burden of HCC will continue to decline.
Disclosures:
Urmimala Chaudhuri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chase Thornton indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Drew Triplett indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Urmimala Chaudhuri, DO1, Chase Thornton, MD2, Drew Triplett, DO2. P1218 - Trends in Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma From 2000 to 2020: A SEER-Based Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.


