Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1251 - Clinical and Socio-Demographic Predictors of 30-Day Readmissions in Patients With Non-Malignant Portal Vein Thrombosis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Medha Rajamanuri, MBBS
Southern Illinois University
springfield, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Medha Rajamanuri, MBBS1, Sai Shanmukha Sreeram Pannala, MD2, Sophia dar, MD1, Muhammad YN. Chaudhary, MBChB3, Nadeem Anwar, MD4
1Southern Illinois University, Springfield, IL; 2Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY; 3Indiana University Southwest, Evansville, IN; 4West Virginia University Charleston Area Medical Center, Charleston, WV
Introduction: Non-malignant portal vein thrombosis (PVT) occurs in individuals with cirrhosis, inflammatory abdominal diseases like sepsis or pancreatitis, or hematologic disorders. Identifying factors contributing to 30-day readmissions in these patients is essential. This study aims to identify these predictors to prevent readmissions.
Methods: This retrospective study used the National Readmission Database (2016-2020) to identify patients with non-malignant PVT using ICD-10 codes. Socio-demographic predictors and clinical predictors, including comorbidities like alcohol use, obesity, hyperlipidemia (HLD), diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2), coronary artery disease (CAD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), hypertension (HTN), cirrhosis, hepatic encephalopathy (HE), ascites, variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding (VUGIB), spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), liver transplantation (LT), pancreatitis, sepsis, and coagulation disorders, were analyzed. Hazard ratios (HRs) and p-values were calculated using the Cox regression model.
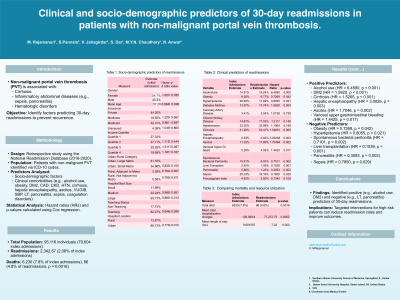
Results: The total population included 95,116 individuals, with 79,604 index admissions. There were 2,342.57 readmissions, 2.06% of index admissions. Deaths were 6,230 (7.8%) for index admissions and 86 (4.8%) for readmissions (p = 0.0016). Positive predictors included alcohol use (HR = 6.4590, p = 0.000), DM2 (HR = 1.5920, p = 0.000), cirrhosis (HR = 1.5265, p = 0.000), HE (HR = 3.0026, p = 0.003), ascites (HR = 1.7046, p = 0.002), and VUGIB (HR = 1.4425, p = 0.017). Negative predictors included obesity (HR= 0.7268, p = 0.042), HLD (HR = 0.8055, p = 0.021), SBP (HR= 0.7101, p = 0.002), LT (HR = 0.1039, p = 0.001), pancreatitis (HR = 0.3093, p = 0.002), and sepsis (HR = 0.7850, p = 0.029).
Discussion: This study highlights several positive predictors of 30-day readmissions in non-malignant PVT patients, including alcohol use, DM2, and cirrhosis. Negative predictors include LT, HLD, pancreatitis during the initial admission, and SBP. Healthcare providers can use this knowledge to identify high-risk patients and implement targeted interventions to reduce readmission rates and improve outcomes.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Medha Rajamanuri, MBBS1, Sai Shanmukha Sreeram Pannala, MD2, Sophia dar, MD1, Muhammad YN. Chaudhary, MBChB3, Nadeem Anwar, MD4. P1251 - Clinical and Socio-Demographic Predictors of 30-Day Readmissions in Patients With Non-Malignant Portal Vein Thrombosis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Southern Illinois University, Springfield, IL; 2Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY; 3Indiana University Southwest, Evansville, IN; 4West Virginia University Charleston Area Medical Center, Charleston, WV
Introduction: Non-malignant portal vein thrombosis (PVT) occurs in individuals with cirrhosis, inflammatory abdominal diseases like sepsis or pancreatitis, or hematologic disorders. Identifying factors contributing to 30-day readmissions in these patients is essential. This study aims to identify these predictors to prevent readmissions.
Methods: This retrospective study used the National Readmission Database (2016-2020) to identify patients with non-malignant PVT using ICD-10 codes. Socio-demographic predictors and clinical predictors, including comorbidities like alcohol use, obesity, hyperlipidemia (HLD), diabetes mellitus type 2 (DM2), coronary artery disease (CAD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), hypertension (HTN), cirrhosis, hepatic encephalopathy (HE), ascites, variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding (VUGIB), spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), liver transplantation (LT), pancreatitis, sepsis, and coagulation disorders, were analyzed. Hazard ratios (HRs) and p-values were calculated using the Cox regression model.
Results: The total population included 95,116 individuals, with 79,604 index admissions. There were 2,342.57 readmissions, 2.06% of index admissions. Deaths were 6,230 (7.8%) for index admissions and 86 (4.8%) for readmissions (p = 0.0016). Positive predictors included alcohol use (HR = 6.4590, p = 0.000), DM2 (HR = 1.5920, p = 0.000), cirrhosis (HR = 1.5265, p = 0.000), HE (HR = 3.0026, p = 0.003), ascites (HR = 1.7046, p = 0.002), and VUGIB (HR = 1.4425, p = 0.017). Negative predictors included obesity (HR= 0.7268, p = 0.042), HLD (HR = 0.8055, p = 0.021), SBP (HR= 0.7101, p = 0.002), LT (HR = 0.1039, p = 0.001), pancreatitis (HR = 0.3093, p = 0.002), and sepsis (HR = 0.7850, p = 0.029).
Discussion: This study highlights several positive predictors of 30-day readmissions in non-malignant PVT patients, including alcohol use, DM2, and cirrhosis. Negative predictors include LT, HLD, pancreatitis during the initial admission, and SBP. Healthcare providers can use this knowledge to identify high-risk patients and implement targeted interventions to reduce readmission rates and improve outcomes.

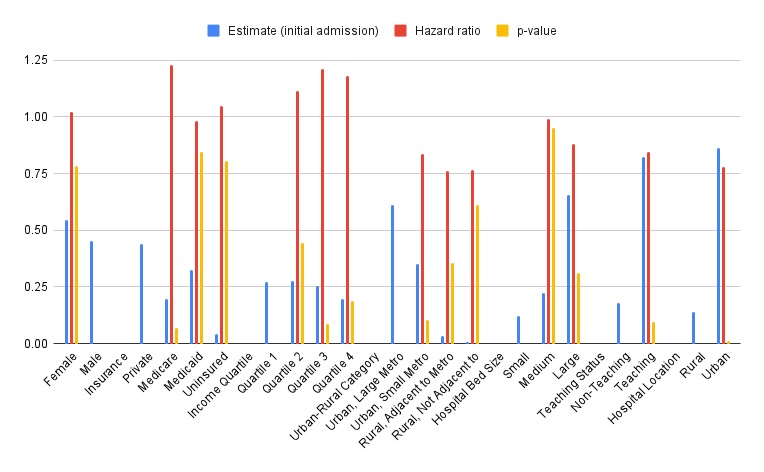
Figure: Socio-demographic predictors of readmissions
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Medha Rajamanuri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Shanmukha Sreeram Pannala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sophia dar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Chaudhary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nadeem Anwar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Medha Rajamanuri, MBBS1, Sai Shanmukha Sreeram Pannala, MD2, Sophia dar, MD1, Muhammad YN. Chaudhary, MBChB3, Nadeem Anwar, MD4. P1251 - Clinical and Socio-Demographic Predictors of 30-Day Readmissions in Patients With Non-Malignant Portal Vein Thrombosis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
