Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1253 - Rifaxmin and Lactulose vs Rifaximin and Miralax Therapy in Preventing Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Comparitive Analysis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Mohamad-Noor Abu-Hammour, MD
Cleveland Clinic Fairview
Cleveland, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Mohamad-Noor Abu-Hammour, MD1, Rashid Abdel-Razeq, MD2, Aravinthan Vignarajah, MD3, Gianina Flocco, MD4, Thabet Qapaja, MD2, Kamal Hassan, MD5, Barish Eren, MD3, Islam B Mohamed, MD3
1Cleveland Clinic Fairview, Cleveland, OH; 2Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 3Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 4Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Fairview Park, OH; 5New York-Presbyterian/Queens, New York, NY
Introduction: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a major complication of cirrhosis, characterized by cognitive dysfunction due to the accumulation of neurotoxins like ammonia. Traditional management includes lactulose, which reduces ammonia absorption, and rifaximin, which decreases intestinal ammonia-producing bacteria. Recent evidence suggests that Miralax, an osmotic laxative, is noninferior to lactulose for managing HE. This study aims to evaluate whether the combination of rifaximin and Miralax is associated with preventing HE episodes, reducing hospitalizations, and improving overall survival.
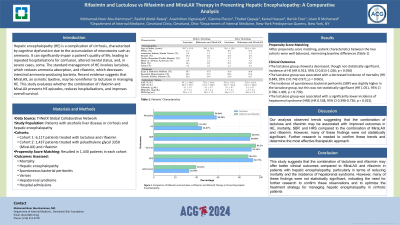
Methods: We identified two cohorts using the TriNetX health research database. The first cohort included 6,117 cirrhotic patients prescribed lactulose and rifaximin. The second cohort consisted of 1,437 cirrhotic patients on Miralax and rifaximin. Propensity score matching adjusted for key characteristics, resulting in 1,430 matched pairs. Outcomes included incidence of all-cause mortality, hepatic encephalopathy (HE), spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), variceal development, hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), and all-cause hospitalizations.
Results: The analysis revealed that the lactulose group was associated with a decreased incidence of HE (HR 0.913, 95% CI 0.813-1.026; p = 0.950), though this was not statistically significant. The lactulose group was also associated with a decreased incidence of mortality (HR 0.849, 95% CI 0.742-0.971; p = 0.065), incidence of SBP (HR 1.051, 95% CI 0.786-1.405; p = 0.739), and incidence of HRS (HR 0.538, 95% CI 0.398-0.726; p = 0.022).
Discussion: Our analysis observed trends suggesting that the combination of lactulose and rifaximin may be associated with better outcomes in terms of HE, mortality, SBP, and HRS compared to Miralax and Rifaximin. However, many of these findings were not statistically significant. Further research is necessary to confirm these trends and to determine the most effective therapeutic approach.
Disclosures:
Mohamad-Noor Abu-Hammour, MD1, Rashid Abdel-Razeq, MD2, Aravinthan Vignarajah, MD3, Gianina Flocco, MD4, Thabet Qapaja, MD2, Kamal Hassan, MD5, Barish Eren, MD3, Islam B Mohamed, MD3. P1253 - Rifaxmin and Lactulose vs Rifaximin and Miralax Therapy in Preventing Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Comparitive Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cleveland Clinic Fairview, Cleveland, OH; 2Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 3Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 4Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Fairview Park, OH; 5New York-Presbyterian/Queens, New York, NY
Introduction: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a major complication of cirrhosis, characterized by cognitive dysfunction due to the accumulation of neurotoxins like ammonia. Traditional management includes lactulose, which reduces ammonia absorption, and rifaximin, which decreases intestinal ammonia-producing bacteria. Recent evidence suggests that Miralax, an osmotic laxative, is noninferior to lactulose for managing HE. This study aims to evaluate whether the combination of rifaximin and Miralax is associated with preventing HE episodes, reducing hospitalizations, and improving overall survival.
Methods: We identified two cohorts using the TriNetX health research database. The first cohort included 6,117 cirrhotic patients prescribed lactulose and rifaximin. The second cohort consisted of 1,437 cirrhotic patients on Miralax and rifaximin. Propensity score matching adjusted for key characteristics, resulting in 1,430 matched pairs. Outcomes included incidence of all-cause mortality, hepatic encephalopathy (HE), spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), variceal development, hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), and all-cause hospitalizations.
Results: The analysis revealed that the lactulose group was associated with a decreased incidence of HE (HR 0.913, 95% CI 0.813-1.026; p = 0.950), though this was not statistically significant. The lactulose group was also associated with a decreased incidence of mortality (HR 0.849, 95% CI 0.742-0.971; p = 0.065), incidence of SBP (HR 1.051, 95% CI 0.786-1.405; p = 0.739), and incidence of HRS (HR 0.538, 95% CI 0.398-0.726; p = 0.022).
Discussion: Our analysis observed trends suggesting that the combination of lactulose and rifaximin may be associated with better outcomes in terms of HE, mortality, SBP, and HRS compared to Miralax and Rifaximin. However, many of these findings were not statistically significant. Further research is necessary to confirm these trends and to determine the most effective therapeutic approach.
Disclosures:
Mohamad-Noor Abu-Hammour indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rashid Abdel-Razeq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aravinthan Vignarajah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gianina Flocco indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thabet Qapaja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kamal Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Barish Eren indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Islam B Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamad-Noor Abu-Hammour, MD1, Rashid Abdel-Razeq, MD2, Aravinthan Vignarajah, MD3, Gianina Flocco, MD4, Thabet Qapaja, MD2, Kamal Hassan, MD5, Barish Eren, MD3, Islam B Mohamed, MD3. P1253 - Rifaxmin and Lactulose vs Rifaximin and Miralax Therapy in Preventing Hepatic Encephalopathy: A Comparitive Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
