Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1419 - Concurrent Streptococcus Anginosus Liver Abscess and Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Rare Case Successfully Managed With Antibiotics and Anticoagulation
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- SA
Shamsuddin Anwar, MD
Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health
Staten Island, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Ali Haider, MD1, Shamsuddin Anwar, MD2, Mahreen Anwar, BS2, Samyak Dhruv, MD2
1Nishtar Medical University, Chicago, IL; 2Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY
Introduction: Streptococcus anginosus is a gram-positive cocci typically found in the oropharynx, gastrointestinal, and urogenital tracts. While it is a rare cause of liver abscesses, its association with portal vein thrombosis is even sparse. We present a case of pyogenic liver abscess caused by Streptococcus anginosus with concurrent portal vein thrombosis, successfully managed with intravenous antibiotics and therapeutic anticoagulation.
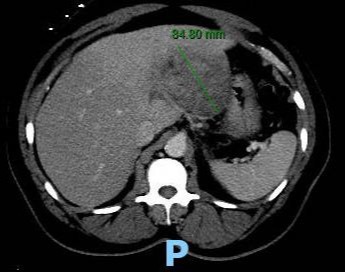
Case Description/Methods: A 64-year-old male with diabetes mellitus and hypertension presented with fever of 101.2 F, generalized malaise, right upper quadrant pain and sepsis on admission. He had no relevant travelling history. His bloodwork showed elevated liver enzymes and computed tomographic imaging revealed a large heterogeneous abscess up to 8.4 cm in the left hepatic lobe with central necrosis and left portal vein thrombosis.
The patient was initiated on intravenous fluids and antibiotics (ceftriaxone and metronidazole). Hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan yielded negative results for gallbladder and biliary tract disease and the blood cultures were positive for Streptococcus anginosus group (Streptococcus constellatus species). The patient at this point described that he had a root canal done approximately four weeks before his symptoms started. A transesophageal echocardiogram failed to reveal any valvular vegetations and repeat blood cultures were negative.
There was no good anatomic window available to drain the hepatic collection so patient was planned for prolonged course of intravenous antibiotics. Serial imaging studies were planned for the outpatient follow up. He was also initiated on full anticoagulation with apixaban for left portal vein thrombosis.
Discussion: Streptococcus anginosus is a group of uncommon organisms to cause serious infections in humans. A few cases of liver abscess with streptococcus anginosus (streptococcus constellatus) have been documented in the medical literature. In this case report, we present a huge liver abscess secondary to Streptococcus anginosus in an immunocompetent patient, the likely source of infection being odontogenic seeding. Portal vein thrombosis from streptococcus anginosus is rare phenomenon as described in our case. The pathology of portal vein thrombosis is likely due to severe inflammation from pyogenic liver abscess.
Based on this case report we suggest discussing risks versus benefits of utilizing prophylactic antibiotics before dental manipulation to prevent serious complications.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ali Haider, MD1, Shamsuddin Anwar, MD2, Mahreen Anwar, BS2, Samyak Dhruv, MD2. P1419 - Concurrent <i>Streptococcus Anginosus</i> Liver Abscess and Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Rare Case Successfully Managed With Antibiotics and Anticoagulation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Nishtar Medical University, Chicago, IL; 2Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY
Introduction: Streptococcus anginosus is a gram-positive cocci typically found in the oropharynx, gastrointestinal, and urogenital tracts. While it is a rare cause of liver abscesses, its association with portal vein thrombosis is even sparse. We present a case of pyogenic liver abscess caused by Streptococcus anginosus with concurrent portal vein thrombosis, successfully managed with intravenous antibiotics and therapeutic anticoagulation.
Case Description/Methods: A 64-year-old male with diabetes mellitus and hypertension presented with fever of 101.2 F, generalized malaise, right upper quadrant pain and sepsis on admission. He had no relevant travelling history. His bloodwork showed elevated liver enzymes and computed tomographic imaging revealed a large heterogeneous abscess up to 8.4 cm in the left hepatic lobe with central necrosis and left portal vein thrombosis.
The patient was initiated on intravenous fluids and antibiotics (ceftriaxone and metronidazole). Hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan yielded negative results for gallbladder and biliary tract disease and the blood cultures were positive for Streptococcus anginosus group (Streptococcus constellatus species). The patient at this point described that he had a root canal done approximately four weeks before his symptoms started. A transesophageal echocardiogram failed to reveal any valvular vegetations and repeat blood cultures were negative.
There was no good anatomic window available to drain the hepatic collection so patient was planned for prolonged course of intravenous antibiotics. Serial imaging studies were planned for the outpatient follow up. He was also initiated on full anticoagulation with apixaban for left portal vein thrombosis.
Discussion: Streptococcus anginosus is a group of uncommon organisms to cause serious infections in humans. A few cases of liver abscess with streptococcus anginosus (streptococcus constellatus) have been documented in the medical literature. In this case report, we present a huge liver abscess secondary to Streptococcus anginosus in an immunocompetent patient, the likely source of infection being odontogenic seeding. Portal vein thrombosis from streptococcus anginosus is rare phenomenon as described in our case. The pathology of portal vein thrombosis is likely due to severe inflammation from pyogenic liver abscess.
Based on this case report we suggest discussing risks versus benefits of utilizing prophylactic antibiotics before dental manipulation to prevent serious complications.

Figure: CT Scan showing 8.4 cm abscess in the left hepatic lobe.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ali Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shamsuddin Anwar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahreen Anwar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Samyak Dhruv indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Haider, MD1, Shamsuddin Anwar, MD2, Mahreen Anwar, BS2, Samyak Dhruv, MD2. P1419 - Concurrent <i>Streptococcus Anginosus</i> Liver Abscess and Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Rare Case Successfully Managed With Antibiotics and Anticoagulation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
