Sunday Poster Session
Category: Practice Management
P1489 - Sentiment Shifts: Mapping the AI Adoption Curve in Gastroenterology
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

- RR
Rajmohan Rammohan, MD
Nassau University Medical Center
East Meadow, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: This study investigates the changing public and patient perceptions of artificial intelligence (AI) in gastroenterology. As AI technology becomes more integrated into healthcare, understanding its acceptance among users, especially in handling patient queries, is crucial. Our analysis highlights the growing positive sentiment towards AI's role in improving gastroenterological care, reflecting its potential to enhance diagnostic and treatment processes. This increasing acceptance suggests a significant shift in how patients view the integration of AI into their healthcare journey.
Methods: We utilized Twitter API, PHP, and RAI to gather responses from Twitter, YouTube, Reddit, and Facebook. Sentiment analysis on tweets was conducted using VADER, and descriptive statistics summarized the data. Independent t-tests compared sentiments, and correlation analysis explored sentiment trends over three years. SPSS was used for data analysis.
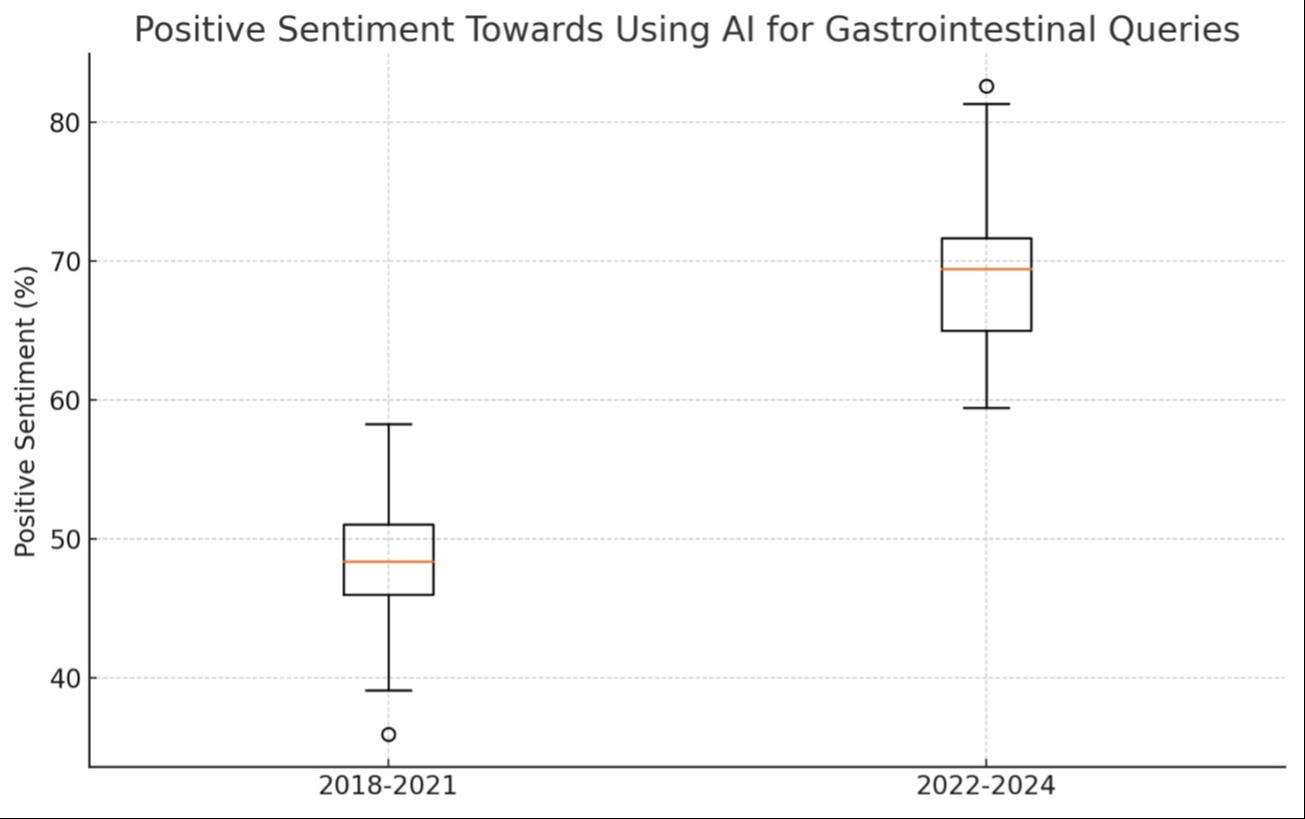
Results: From December 2017 to November 2022, we recorded 7,651,350 responses, with 3,520,673 from December 2018 to November 2021 and 4,130,677 from January 2022 to April 2024. There was a significant improvement in positive sentiment towards using artificial intelligence for gastrointestinal queries from 2022 to 2024 compared to 2018-2022, with positive responses increasing from 49% to 69% (P=0.022, 95% CI).
Discussion: The marked rise in positive sentiment toward AI in gastroenterology from 2018 to 2024 underscores a pivotal shift in patient and public attitudes. This trend may reflect greater awareness and trust in AI's ability to enhance healthcare outcomes. However, it also raises questions about integrating such technology in clinical settings, potential privacy concerns, and the need for robust AI systems that are accessible and understandable to both practitioners and patients. Further exploring these factors is essential to fully harness AI's capabilities in improving gastroenterological care.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P1489 - Sentiment Shifts: Mapping the AI Adoption Curve in Gastroenterology, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: This study investigates the changing public and patient perceptions of artificial intelligence (AI) in gastroenterology. As AI technology becomes more integrated into healthcare, understanding its acceptance among users, especially in handling patient queries, is crucial. Our analysis highlights the growing positive sentiment towards AI's role in improving gastroenterological care, reflecting its potential to enhance diagnostic and treatment processes. This increasing acceptance suggests a significant shift in how patients view the integration of AI into their healthcare journey.
Methods: We utilized Twitter API, PHP, and RAI to gather responses from Twitter, YouTube, Reddit, and Facebook. Sentiment analysis on tweets was conducted using VADER, and descriptive statistics summarized the data. Independent t-tests compared sentiments, and correlation analysis explored sentiment trends over three years. SPSS was used for data analysis.
Results: From December 2017 to November 2022, we recorded 7,651,350 responses, with 3,520,673 from December 2018 to November 2021 and 4,130,677 from January 2022 to April 2024. There was a significant improvement in positive sentiment towards using artificial intelligence for gastrointestinal queries from 2022 to 2024 compared to 2018-2022, with positive responses increasing from 49% to 69% (P=0.022, 95% CI).
Discussion: The marked rise in positive sentiment toward AI in gastroenterology from 2018 to 2024 underscores a pivotal shift in patient and public attitudes. This trend may reflect greater awareness and trust in AI's ability to enhance healthcare outcomes. However, it also raises questions about integrating such technology in clinical settings, potential privacy concerns, and the need for robust AI systems that are accessible and understandable to both practitioners and patients. Further exploring these factors is essential to fully harness AI's capabilities in improving gastroenterological care.

Figure: Sentiment analysis overtime
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Reshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Greeshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Melvin Joy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dilman Natt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leeza Pannikodu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhishek Tadikonda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Winghang Lau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jiten Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishnaiyer Subramani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Mustacchia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P1489 - Sentiment Shifts: Mapping the AI Adoption Curve in Gastroenterology, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
