Sunday Poster Session
Category: Stomach
P1643 - Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome: A Case Report
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
- IM
Ibrahim Mohammed, MD
Albany Medical Center
Albany, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Ibrahim Mohammed, MD, Ahmad Abulawi, MD, Khaled Elsokary, DO, Asra Batool, MD
Albany Medical Center, Albany, NY
Introduction: Gastric polyposis syndrome includes various disorders with multiple stomach polyps. These polyps can stem from conditions like familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, and juvenile polyposis syndrome. Though common in clinical practice, their links to systemic syndromes and genetic factors require thorough diagnosis and tailored management. This case report highlights a complex gastric polyposis syndrome, focusing on diagnostic challenges, histopathological features, and therapeutic strategies.
Case Description/Methods: This is a 40-year-old man with history of iron deficiency anemia and asthma who presented to the emergency department with hematemesis. He denied having diarrhea, constipation, bloody stools or black stools. On initial evaluation, he was found to be anemic with a heart rate of 140. The patient was adequately resuscitated and had an EGD which showed congested, friable, nodular mucosa in the esophagus, multiple gastric polyps, and few duodenal polyps. Biopsies were suggestive of a gastric adenoma with intestinal metaplasia and multiple hamartomatous polyps. He had a colonoscopy which showed normal mucosa in rectum and sigmoid colon. He also had a capsule endoscopy which showed gastric polyps, nodular mucosa with polyps in the proximal duodenum, a large pedunculated polyp in the small bowel, and multiple small polyps in the distal terminal ileum. He was assessed by the general surgery team for evaluation for gastrectomy. Eventually, the patient had a total gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y esophagojejunostomy, small bowel resection and placement of feeding jejunostomy tube.
Discussion: Gastric polyposis syndromes present a diagnostic challenge due to varied histologic findings, from hamartomatous to adenomatous polyps. In patients with nodular mucosa and multiple gastric polyps, considering an underlying polyposis syndrome is crucial. Specifically, multiple gastric hyperplastic-type polyps in the corpus and fundus may indicate gastric adenocarcinoma and proximal polyposis of the stomach (GAPPS). Diagnosing polyposis syndrome based solely on gastric polyps requires caution. These syndromes can appear in various gastrointestinal conditions, highlighting the need for thorough evaluation to distinguish and manage them appropriately. Understanding syndromes like juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is vital for personalized care and surveillance in patients with multiple gastric polyps.
Disclosures:
Ibrahim Mohammed, MD, Ahmad Abulawi, MD, Khaled Elsokary, DO, Asra Batool, MD. P1643 - Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome: A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Albany Medical Center, Albany, NY
Introduction: Gastric polyposis syndrome includes various disorders with multiple stomach polyps. These polyps can stem from conditions like familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, and juvenile polyposis syndrome. Though common in clinical practice, their links to systemic syndromes and genetic factors require thorough diagnosis and tailored management. This case report highlights a complex gastric polyposis syndrome, focusing on diagnostic challenges, histopathological features, and therapeutic strategies.
Case Description/Methods: This is a 40-year-old man with history of iron deficiency anemia and asthma who presented to the emergency department with hematemesis. He denied having diarrhea, constipation, bloody stools or black stools. On initial evaluation, he was found to be anemic with a heart rate of 140. The patient was adequately resuscitated and had an EGD which showed congested, friable, nodular mucosa in the esophagus, multiple gastric polyps, and few duodenal polyps. Biopsies were suggestive of a gastric adenoma with intestinal metaplasia and multiple hamartomatous polyps. He had a colonoscopy which showed normal mucosa in rectum and sigmoid colon. He also had a capsule endoscopy which showed gastric polyps, nodular mucosa with polyps in the proximal duodenum, a large pedunculated polyp in the small bowel, and multiple small polyps in the distal terminal ileum. He was assessed by the general surgery team for evaluation for gastrectomy. Eventually, the patient had a total gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y esophagojejunostomy, small bowel resection and placement of feeding jejunostomy tube.
Discussion: Gastric polyposis syndromes present a diagnostic challenge due to varied histologic findings, from hamartomatous to adenomatous polyps. In patients with nodular mucosa and multiple gastric polyps, considering an underlying polyposis syndrome is crucial. Specifically, multiple gastric hyperplastic-type polyps in the corpus and fundus may indicate gastric adenocarcinoma and proximal polyposis of the stomach (GAPPS). Diagnosing polyposis syndrome based solely on gastric polyps requires caution. These syndromes can appear in various gastrointestinal conditions, highlighting the need for thorough evaluation to distinguish and manage them appropriately. Understanding syndromes like juvenile polyposis syndrome (JPS) and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is vital for personalized care and surveillance in patients with multiple gastric polyps.

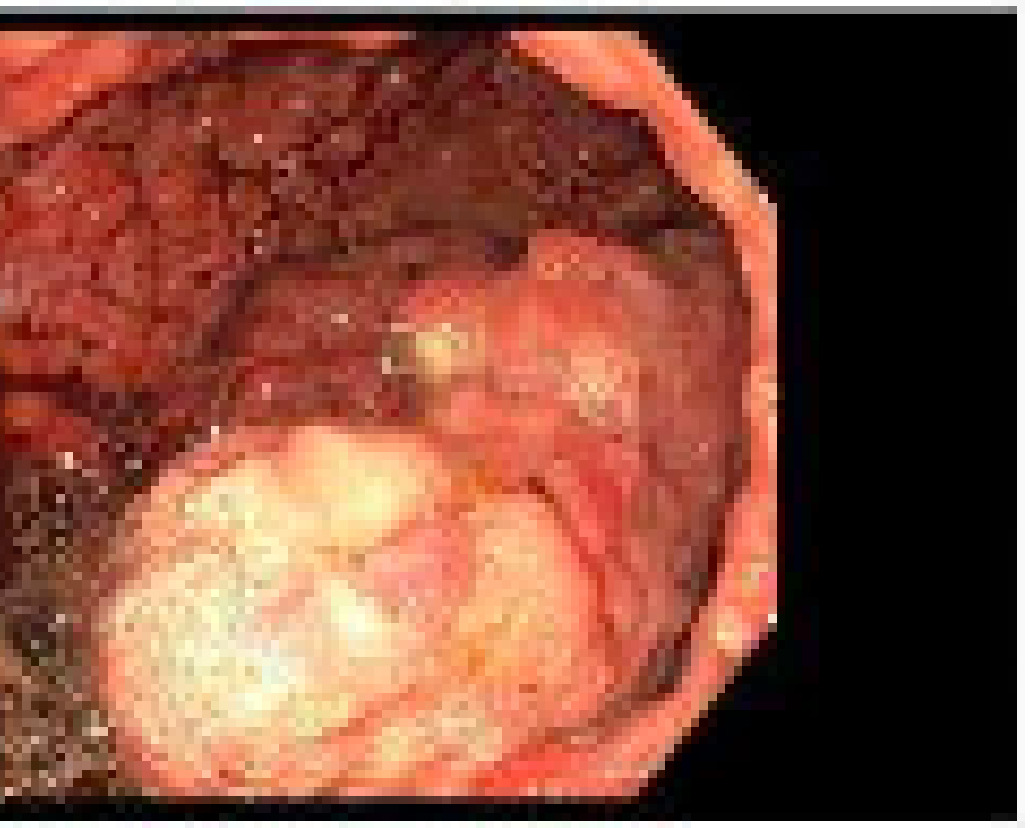
Figure: Figure 1. EGD findings showing multiple polyps in the stomach
Disclosures:
Ibrahim Mohammed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Abulawi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khaled Elsokary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asra Batool indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ibrahim Mohammed, MD, Ahmad Abulawi, MD, Khaled Elsokary, DO, Asra Batool, MD. P1643 - Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome: A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
