Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1431 - Drug-Induced Liver Injury: A Case of Amoxicillin-Clavulanate-Induced Liver Injury
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- AA
Amira Al-Nabolsi, DO
Corewell Health Farmington Hills
Dearborn, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Amira Al-Nabolsi, DO1, Barbara Senger, DO2, Hassan Eidy, DO3, Rami Dali, 4, Mohamed Musheinesh, DO2, Ashbita Pokharel, MD3
1Corewell Health Farmington Hills, Dearborn, MI; 2Beaumont Hospital, Farmington Hills, MI; 3Beaumont Hospital, Farmington HIlls, MI; 4Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, Rochester, MI
Introduction: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is the most common cause of acute liver failure, commonly caused by antibiotics and supplements, with symptom relief after several months. Diagnosis of DILI is one of exclusion, not requiring liver biopsy. Management includes immediate cessation of the offending agent with supportive care with n-acetylcysteine (NAC) and ursodiol, although there is little evidence to support their use. This is a unique case of amoxicillin-clavulanate induced DILI supported by liver biopsy.
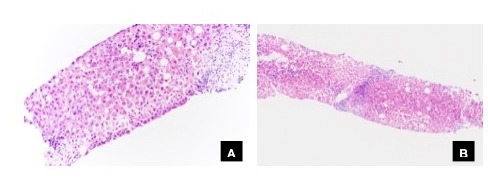
Case Description/Methods: A 59-year-old male with ulcerative colitis on balsalazide presented with nausea, vomiting, fatigue, jaundice, scleral icterus, and pruritis. Social history revealed alcohol use disorder (24 beers/week). Five days prior to arrival, he used prophylactic amoxicillin-clavulanate 875mg/125mg over 3 days for a root canal. Labs were notable for an INR 1.2, total bilirubin of 7.9 U/L, direct bilirubin 6.1 mg/dL, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 42 U/L, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 63 U/L, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) 196 U/L. Serology ruled out other etiologies of liver injury. Imaging showed hepatic steatosis, ruling out ductal stricture, choledocholithiasis, biliary ductal dilatation, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and portal vein thrombosis. He was discharged and advised to stop both amoxicillin-clavulanate and alcohol. He returned to the Emergency Department six days later with a total bilirubin of 17.2 mg/dL and worsening jaundice. He was admitted and treated with ursodiol 300mg three times daily. His total bilirubin peaked at 20.3 mg/dL, remaining atypically elevated, leading to the pursuit of a liver biopsy, consistent with drug-induced bile metabolism (Table 1, Figure 1A, B). Alcohol involvement may have contributed to the elevated bilirubin, supported by an elevated phosphatidylethanol level of 31 ng/mL and hepatic steatosis. Following ursodiol 300mg three times daily, he had complete symptom resolution and total bilirubin decreased to 1.6 mg/dL after eight weeks.
Discussion: This is a case of drug-induced liver injury secondary to amoxicillin-clavulanate with a component of alcohol use. Despite cessation of the offending agent, the patient's atypically rising bilirubin necessitated liver biopsy for diagnosis confirmation and to rule out other causes. While the utilization of ursodiol is not well studied in DILI management, this case highlights its successful use, as well as the importance of liver biopsy in atypical cases to confirm and rule out other etiologies.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Amira Al-Nabolsi, DO1, Barbara Senger, DO2, Hassan Eidy, DO3, Rami Dali, 4, Mohamed Musheinesh, DO2, Ashbita Pokharel, MD3. P1431 - Drug-Induced Liver Injury: A Case of Amoxicillin-Clavulanate-Induced Liver Injury, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Corewell Health Farmington Hills, Dearborn, MI; 2Beaumont Hospital, Farmington Hills, MI; 3Beaumont Hospital, Farmington HIlls, MI; 4Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, Rochester, MI
Introduction: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is the most common cause of acute liver failure, commonly caused by antibiotics and supplements, with symptom relief after several months. Diagnosis of DILI is one of exclusion, not requiring liver biopsy. Management includes immediate cessation of the offending agent with supportive care with n-acetylcysteine (NAC) and ursodiol, although there is little evidence to support their use. This is a unique case of amoxicillin-clavulanate induced DILI supported by liver biopsy.
Case Description/Methods: A 59-year-old male with ulcerative colitis on balsalazide presented with nausea, vomiting, fatigue, jaundice, scleral icterus, and pruritis. Social history revealed alcohol use disorder (24 beers/week). Five days prior to arrival, he used prophylactic amoxicillin-clavulanate 875mg/125mg over 3 days for a root canal. Labs were notable for an INR 1.2, total bilirubin of 7.9 U/L, direct bilirubin 6.1 mg/dL, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 42 U/L, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 63 U/L, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) 196 U/L. Serology ruled out other etiologies of liver injury. Imaging showed hepatic steatosis, ruling out ductal stricture, choledocholithiasis, biliary ductal dilatation, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and portal vein thrombosis. He was discharged and advised to stop both amoxicillin-clavulanate and alcohol. He returned to the Emergency Department six days later with a total bilirubin of 17.2 mg/dL and worsening jaundice. He was admitted and treated with ursodiol 300mg three times daily. His total bilirubin peaked at 20.3 mg/dL, remaining atypically elevated, leading to the pursuit of a liver biopsy, consistent with drug-induced bile metabolism (Table 1, Figure 1A, B). Alcohol involvement may have contributed to the elevated bilirubin, supported by an elevated phosphatidylethanol level of 31 ng/mL and hepatic steatosis. Following ursodiol 300mg three times daily, he had complete symptom resolution and total bilirubin decreased to 1.6 mg/dL after eight weeks.
Discussion: This is a case of drug-induced liver injury secondary to amoxicillin-clavulanate with a component of alcohol use. Despite cessation of the offending agent, the patient's atypically rising bilirubin necessitated liver biopsy for diagnosis confirmation and to rule out other causes. While the utilization of ursodiol is not well studied in DILI management, this case highlights its successful use, as well as the importance of liver biopsy in atypical cases to confirm and rule out other etiologies.

Figure: Cholestatic hepatitis with canalicular cholestasis, associated with hepatocellular degeneration and mild portal inflammatory infiltrates, consistent with drug-induced bile metabolism.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Amira Al-Nabolsi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Barbara Senger indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hassan Eidy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rami Dali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Musheinesh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashbita Pokharel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amira Al-Nabolsi, DO1, Barbara Senger, DO2, Hassan Eidy, DO3, Rami Dali, 4, Mohamed Musheinesh, DO2, Ashbita Pokharel, MD3. P1431 - Drug-Induced Liver Injury: A Case of Amoxicillin-Clavulanate-Induced Liver Injury, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
