Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1242 - Improving the Screening and Management of Underserved Patients With Risk Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in the Primary Care Setting
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Danzhu Zhao, DO
University of Connecticut Health Center
WEST HARTFORD, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Danzhu Zhao, DO1, Ruchir Damjibhai. Paladiya, MBBS2, Amanda Frondella, MD2, Nicole Bambara, MD1, Neil Khoury, MD3, Cunegundo Vergara, MD4
1University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, CT; 2University of Connecticut Health Center, Hartford, CT; 3UConn Health, Hartford, CT; 4Hartford HealthCare, Hartford, CT
Introduction: The prevalence of MASLD is rising globally along with its associated cardiometabolic risk factors, increasing the risk for liver fibrosis and all-cause mortality. The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) recommends using the FIB-4 index to guide management in patients with risk factors for MASLD. Hartford Hospital Adult Primary Care Clinic (HH APC) provides care to an underserved population with a high prevalence of cardiometabolic risk factors for MASLD, but lacks clear guidelines for screening and management.
Methods: Data was collected from the HH APC medical record database. We included patients ages >35 years with at least one of the following: hypertension, obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, obstructive sleep apnea, and/or hyperlipidemia. We excluded patients ages < 35 years with viral hepatitis, alcohol use >20g/d charted in women or >30g/d charted in men. Pre-intervention data was collected from 4/20/2023. Post-intervention data was collected 1 year later, 4/20/2024.
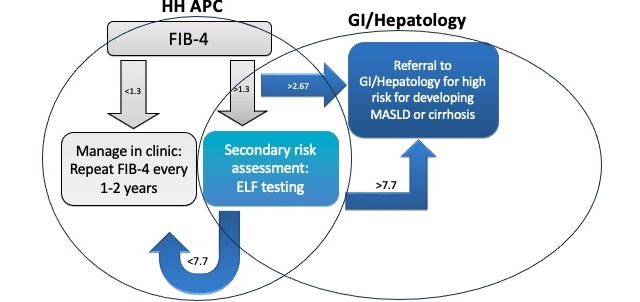
The primary aim was to improve MASLD screening by increasing the rate of FIB-4 index calculation from baseline 2.1% to 50% within 1 year. Primary intervention was calculating FIB-4 index with ".fib-4" smart-phrase on Epic for patients meeting inclusion criteria. We used the FIB-4 index to risk-stratify patients per AASLD guidelines in our second intervention (Table 1 and Figure 1).
Results: Out of 597 HH APC charts reviewed, 63 were excluded for age. FIB-4 index could not be calculated in 291 patients whose CBC/CMP/hepatic function panel were outdated ( >1 year), or who met exclusion criteria. We calculated the FIB-4 index for 45.5% eligible patients compared to approximately 2.1% prior. We identified 50 patients who qualified for ELF testing compared to 0 patients previously. 13 qualified for GI referral compared to 4 who had previously been referred.
Discussion: The FIB-4 index, though underutilized, is easily implementable. We increased FIB-4 index screening by 43.4%, identifying 50 patients retrospectively eligible for ELF testing and 9 for GI referral. Barriers included outdated laboratory results, inadequate alcohol use documentation, and time constraints within visits due to the complexity of care in our underserved patient population. Future interventions include advocating for routine CBC/CMP/hepatic function panel in high-risk patients with FIB-4 index calculation, and integrating our clinic’s medical assistants in helping obtain alcohol use history when rooming patients.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Danzhu Zhao, DO1, Ruchir Damjibhai. Paladiya, MBBS2, Amanda Frondella, MD2, Nicole Bambara, MD1, Neil Khoury, MD3, Cunegundo Vergara, MD4. P1242 - Improving the Screening and Management of Underserved Patients With Risk Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in the Primary Care Setting, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, CT; 2University of Connecticut Health Center, Hartford, CT; 3UConn Health, Hartford, CT; 4Hartford HealthCare, Hartford, CT
Introduction: The prevalence of MASLD is rising globally along with its associated cardiometabolic risk factors, increasing the risk for liver fibrosis and all-cause mortality. The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) recommends using the FIB-4 index to guide management in patients with risk factors for MASLD. Hartford Hospital Adult Primary Care Clinic (HH APC) provides care to an underserved population with a high prevalence of cardiometabolic risk factors for MASLD, but lacks clear guidelines for screening and management.
Methods: Data was collected from the HH APC medical record database. We included patients ages >35 years with at least one of the following: hypertension, obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, obstructive sleep apnea, and/or hyperlipidemia. We excluded patients ages < 35 years with viral hepatitis, alcohol use >20g/d charted in women or >30g/d charted in men. Pre-intervention data was collected from 4/20/2023. Post-intervention data was collected 1 year later, 4/20/2024.
The primary aim was to improve MASLD screening by increasing the rate of FIB-4 index calculation from baseline 2.1% to 50% within 1 year. Primary intervention was calculating FIB-4 index with ".fib-4" smart-phrase on Epic for patients meeting inclusion criteria. We used the FIB-4 index to risk-stratify patients per AASLD guidelines in our second intervention (Table 1 and Figure 1).
Results: Out of 597 HH APC charts reviewed, 63 were excluded for age. FIB-4 index could not be calculated in 291 patients whose CBC/CMP/hepatic function panel were outdated ( >1 year), or who met exclusion criteria. We calculated the FIB-4 index for 45.5% eligible patients compared to approximately 2.1% prior. We identified 50 patients who qualified for ELF testing compared to 0 patients previously. 13 qualified for GI referral compared to 4 who had previously been referred.
Discussion: The FIB-4 index, though underutilized, is easily implementable. We increased FIB-4 index screening by 43.4%, identifying 50 patients retrospectively eligible for ELF testing and 9 for GI referral. Barriers included outdated laboratory results, inadequate alcohol use documentation, and time constraints within visits due to the complexity of care in our underserved patient population. Future interventions include advocating for routine CBC/CMP/hepatic function panel in high-risk patients with FIB-4 index calculation, and integrating our clinic’s medical assistants in helping obtain alcohol use history when rooming patients.

Figure: Figure 1. Algorithm for managing patients ages >35 years but <65 years at risk for MASLD.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Danzhu Zhao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ruchir Paladiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amanda Frondella indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nicole Bambara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neil Khoury indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cunegundo Vergara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danzhu Zhao, DO1, Ruchir Damjibhai. Paladiya, MBBS2, Amanda Frondella, MD2, Nicole Bambara, MD1, Neil Khoury, MD3, Cunegundo Vergara, MD4. P1242 - Improving the Screening and Management of Underserved Patients With Risk Factors for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in the Primary Care Setting, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
