Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1177 - Evaluating the Impact of Melatonin Administration in Patients With Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Avneet Singh, DO
Cooper University Hospital
Camden, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Avneet Singh, DO1, Alexander Garcia, DO1, Fariha Hasan, MD2, Fatima Laique, MBBS3, Muhammad Haris, MBBS3, Mubashir Mohiuddin, MBBS3, Zehara Abidi, BS, MS4, Queenzy Jover, BSN, RN5, Mehak Bassi, MD6, Kunal Dalal, MD1
1Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 2Cooper University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 3Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 4Touro College of Osteopathic Medicine, New York, NY; 5Virtua Health System, Camden, NJ; 6St. Peter's University Hospital, New Brunswick, NJ
Introduction: Melatonin, a hormone the pineal gland produces, is known for its role in circadian rhythms and antioxidant properties. Recently, its potential therapeutic benefits have shown promising effects in managing Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). This systematic review and meta-analysis aims to assess the efficacy of melatonin in MASLD management.
Methods: We systematically reviewed PubMed, Cochrane Library, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) up to May 2024, identifying 173 initial results. Two reviewers independently extracted and analyzed data. Primary outcomes were mean differences (MD) in ALT, AST, GGT, Cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, and LDL levels. Secondary outcomes included ALP, total bilirubin, blood pressure, fasting blood sugar, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-a, waist circumference, weight, hs-CRP, and steatosis grade.
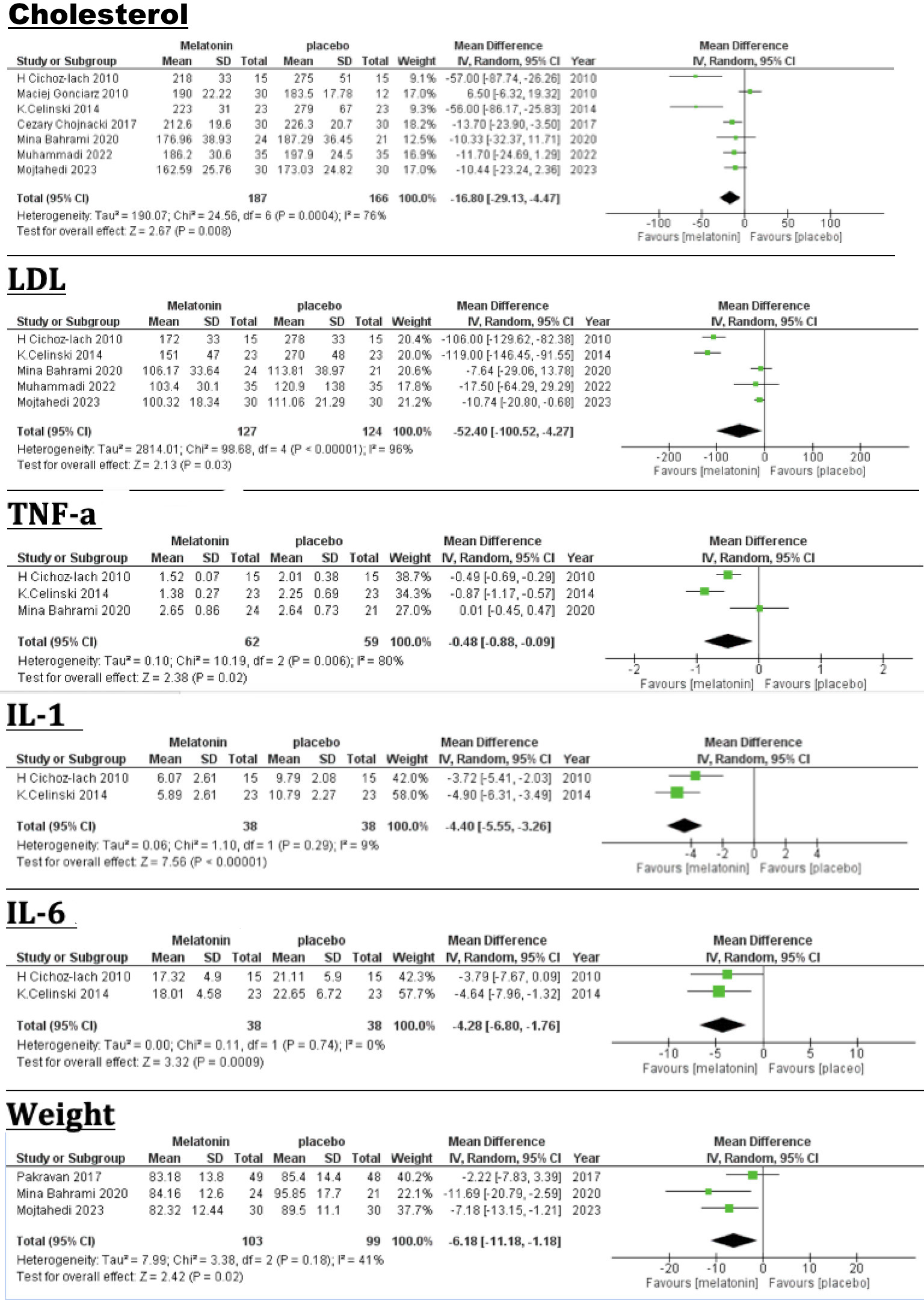
Results: Eleven trials, including 568 participants, met inclusion criteria with a mean age of 41.57 ± 9.10 years. A significant reduction was depicted in the MD values of Cholesterol [-16.80 mg/dL (95% CI: -29.13 to -4.47, p = 0.008)] and LDL [-52.4 mg/dL (95% CI: -100.52 to -4.27, p = 0.03)]. HDL levels exhibited an increase in MD of 1.71 mg/dL, although not statistically significant (95% CI: -1.66 to 5.07, p =0.32). Regarding anthropometric results, the MD values of waist [-5.30 cm (95% CI: -9.95 to -0.65, p = 0.03)] and weight [-6.18 kg (95% CI: -11.18 to -1.18, p = 0.02)] showed significant decreases. In addition, inflammatory markers such as IL-1 [-4.40 pg/ml (95% CI: -5.55 to -3.26, p < 0.00001)], IL-6 [-4.28 pg/ml (95% CI: -6.80 to -1.76, p = 0.0009)] and TNF-a [-0.48 pg/ml (95% CI: -0.88 to -0.09, p = 0.02)] had significant reductions. However, the MD in triglycerides [-22.03 mg/dL (95%CI: -47.68 to 3.63, p = 0.09)], GGT [-25.94 U/L (95% CI: -58.00 to 6.12, p = 0.11), ALT [-7.97 U/L(95% CI: -17.43 to 1.49, p = 0.10)], and AST [ -5.23 U/L (95% CI: -14.12 to 3.67, p = 0.25)] indicated no significant reductions.
Discussion: This meta-analysis highlights melatonin as a promising intervention for MASLD. Melatonin positively impacts lipid metabolism, anti-inflammatory makers, and anthropometric measures when used in MASLD patients. However, the variation in study methodologies and melatonin dosages necessitates careful consideration of these findings. Additional standardized RCTs are necessary to validate these findings for future guidelines.
Disclosures:
Avneet Singh, DO1, Alexander Garcia, DO1, Fariha Hasan, MD2, Fatima Laique, MBBS3, Muhammad Haris, MBBS3, Mubashir Mohiuddin, MBBS3, Zehara Abidi, BS, MS4, Queenzy Jover, BSN, RN5, Mehak Bassi, MD6, Kunal Dalal, MD1. P1177 - Evaluating the Impact of Melatonin Administration in Patients With Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cooper University Hospital, Camden, NJ; 2Cooper University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 3Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 4Touro College of Osteopathic Medicine, New York, NY; 5Virtua Health System, Camden, NJ; 6St. Peter's University Hospital, New Brunswick, NJ
Introduction: Melatonin, a hormone the pineal gland produces, is known for its role in circadian rhythms and antioxidant properties. Recently, its potential therapeutic benefits have shown promising effects in managing Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). This systematic review and meta-analysis aims to assess the efficacy of melatonin in MASLD management.
Methods: We systematically reviewed PubMed, Cochrane Library, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) up to May 2024, identifying 173 initial results. Two reviewers independently extracted and analyzed data. Primary outcomes were mean differences (MD) in ALT, AST, GGT, Cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, and LDL levels. Secondary outcomes included ALP, total bilirubin, blood pressure, fasting blood sugar, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-a, waist circumference, weight, hs-CRP, and steatosis grade.
Results: Eleven trials, including 568 participants, met inclusion criteria with a mean age of 41.57 ± 9.10 years. A significant reduction was depicted in the MD values of Cholesterol [-16.80 mg/dL (95% CI: -29.13 to -4.47, p = 0.008)] and LDL [-52.4 mg/dL (95% CI: -100.52 to -4.27, p = 0.03)]. HDL levels exhibited an increase in MD of 1.71 mg/dL, although not statistically significant (95% CI: -1.66 to 5.07, p =0.32). Regarding anthropometric results, the MD values of waist [-5.30 cm (95% CI: -9.95 to -0.65, p = 0.03)] and weight [-6.18 kg (95% CI: -11.18 to -1.18, p = 0.02)] showed significant decreases. In addition, inflammatory markers such as IL-1 [-4.40 pg/ml (95% CI: -5.55 to -3.26, p < 0.00001)], IL-6 [-4.28 pg/ml (95% CI: -6.80 to -1.76, p = 0.0009)] and TNF-a [-0.48 pg/ml (95% CI: -0.88 to -0.09, p = 0.02)] had significant reductions. However, the MD in triglycerides [-22.03 mg/dL (95%CI: -47.68 to 3.63, p = 0.09)], GGT [-25.94 U/L (95% CI: -58.00 to 6.12, p = 0.11), ALT [-7.97 U/L(95% CI: -17.43 to 1.49, p = 0.10)], and AST [ -5.23 U/L (95% CI: -14.12 to 3.67, p = 0.25)] indicated no significant reductions.
Discussion: This meta-analysis highlights melatonin as a promising intervention for MASLD. Melatonin positively impacts lipid metabolism, anti-inflammatory makers, and anthropometric measures when used in MASLD patients. However, the variation in study methodologies and melatonin dosages necessitates careful consideration of these findings. Additional standardized RCTs are necessary to validate these findings for future guidelines.

Figure: Figure 1: Forest plot of Cholesterol, LDL, TNF-a, IL-1, IL-6, and Weight
Disclosures:
Avneet Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Garcia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fariha Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fatima Laique indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Haris indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mubashir Mohiuddin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zehara Abidi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Queenzy Jover indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mehak Bassi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kunal Dalal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Avneet Singh, DO1, Alexander Garcia, DO1, Fariha Hasan, MD2, Fatima Laique, MBBS3, Muhammad Haris, MBBS3, Mubashir Mohiuddin, MBBS3, Zehara Abidi, BS, MS4, Queenzy Jover, BSN, RN5, Mehak Bassi, MD6, Kunal Dalal, MD1. P1177 - Evaluating the Impact of Melatonin Administration in Patients With Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
