Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P0943 - Interleukin-12/23 vs Interleukin-23 Inhibitors in Moderate to Severe Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ravi Teja Pasam, MBBS, MPH
Wentworth-Douglass Hospital
Portsmouth, NH
Presenting Author(s)
Ravi Teja Pasam, MBBS, MPH1, Misha Gautam, MD2, Sruthi Venugopalan, MD3, Babu Mohan, MD4, Udaykumar Navaneethan, MD5
1Wentworth-Douglass Hospital, Portsmouth, NH; 2University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 3University of Nevada Reno School of Medicine, Reno, NV; 4Orlando Gastroenterology PA, Orlando, FL; 5Orlando Health, Digestive Health Institute, Orlando, FL
Introduction: Existing literature shows significantly better outcomes with interleukin-23 (IL-23) inhibitors compared to interleukin-12,23 (IL-12,23) inhibitors for plaque psoriasis. However, it is not clear if this is true in patients with moderate to severe Crohn's disease (CD) as well. A systematic review and network meta-analysis (NMA) was performed to compare the outcomes of IL-23 inhibitors to IL-12,23 inhibitors in patients with CD.
Methods: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing IL-12,23 inhibitors or IL-23 inhibitors to placebo or to each other in patients with moderate to severe CD were included. The primary outcomes of interest were clinical response and remission in the induction phase. Secondary outcomes were corticosteroid-free remission, endoscopic response, endoscopic remission, mucosal healing and safety outcomes in the induction and maintenance phases. Random effects NMA was conducted using the netmeta package in R.
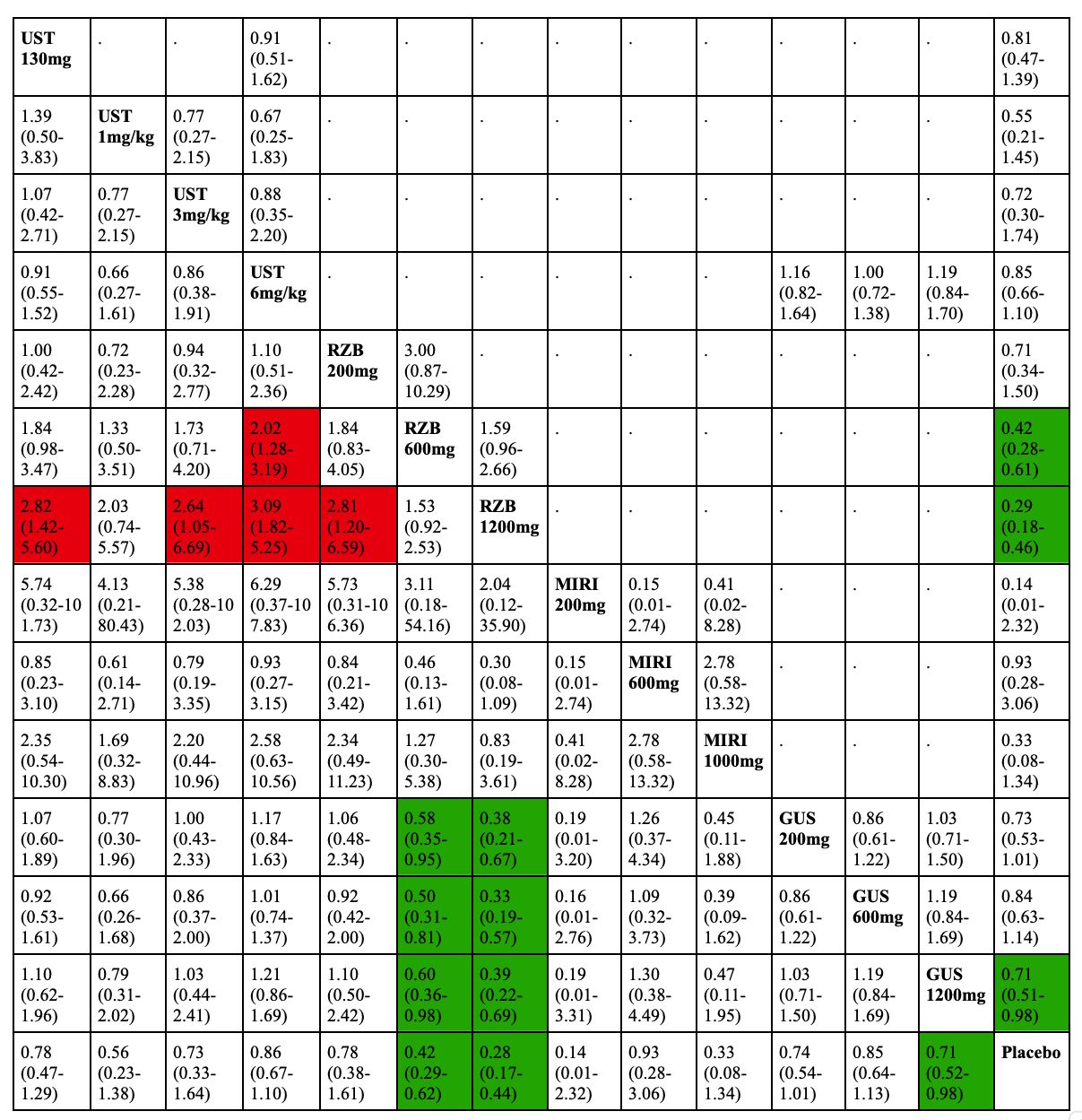
Results: Data from 12 RCTs (6,577 patients) were included in the final analysis. There were no significant differences between Ustekinumab and IL-23 inhibitors (Risankizumab, Mirkiziumab and Guselkumab) in terms of the clinical and endoscopic outcomes in the induction and maintenance phases. Ustekinumab 6 mg/kg induction dose was associated with a significantly higher rate of serious adverse events (SAE) compared to Risankizumab 600 mg every four weeks [Risk ratio (RR): 2.02, 95% Confidence interval (95% CI): 1.28 - 3.19] and 1200 mg every four weeks (RR: 3.09 95% CI: 1.82-5.25) induction doses. There were no significant differences between IL-12,23 inhibitors and IL-23 inhibitors with regard to the rest of the safety outcomes.
Discussion: There were no significant differences between IL-12,23 inhibitors and IL-23 inhibitors in terms of efficacy outcomes in patients with moderate to severe CD. However, Risankizumab can be considered over Ustekinumab in view of a better safety profile. Head to head trials are required to assess the relative efficacy of these groups of medications.
Disclosures:
Ravi Teja Pasam, MBBS, MPH1, Misha Gautam, MD2, Sruthi Venugopalan, MD3, Babu Mohan, MD4, Udaykumar Navaneethan, MD5. P0943 - Interleukin-12/23 vs Interleukin-23 Inhibitors in Moderate to Severe Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Wentworth-Douglass Hospital, Portsmouth, NH; 2University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 3University of Nevada Reno School of Medicine, Reno, NV; 4Orlando Gastroenterology PA, Orlando, FL; 5Orlando Health, Digestive Health Institute, Orlando, FL
Introduction: Existing literature shows significantly better outcomes with interleukin-23 (IL-23) inhibitors compared to interleukin-12,23 (IL-12,23) inhibitors for plaque psoriasis. However, it is not clear if this is true in patients with moderate to severe Crohn's disease (CD) as well. A systematic review and network meta-analysis (NMA) was performed to compare the outcomes of IL-23 inhibitors to IL-12,23 inhibitors in patients with CD.
Methods: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing IL-12,23 inhibitors or IL-23 inhibitors to placebo or to each other in patients with moderate to severe CD were included. The primary outcomes of interest were clinical response and remission in the induction phase. Secondary outcomes were corticosteroid-free remission, endoscopic response, endoscopic remission, mucosal healing and safety outcomes in the induction and maintenance phases. Random effects NMA was conducted using the netmeta package in R.
Results: Data from 12 RCTs (6,577 patients) were included in the final analysis. There were no significant differences between Ustekinumab and IL-23 inhibitors (Risankizumab, Mirkiziumab and Guselkumab) in terms of the clinical and endoscopic outcomes in the induction and maintenance phases. Ustekinumab 6 mg/kg induction dose was associated with a significantly higher rate of serious adverse events (SAE) compared to Risankizumab 600 mg every four weeks [Risk ratio (RR): 2.02, 95% Confidence interval (95% CI): 1.28 - 3.19] and 1200 mg every four weeks (RR: 3.09 95% CI: 1.82-5.25) induction doses. There were no significant differences between IL-12,23 inhibitors and IL-23 inhibitors with regard to the rest of the safety outcomes.
Discussion: There were no significant differences between IL-12,23 inhibitors and IL-23 inhibitors in terms of efficacy outcomes in patients with moderate to severe CD. However, Risankizumab can be considered over Ustekinumab in view of a better safety profile. Head to head trials are required to assess the relative efficacy of these groups of medications.

Figure: League table comparing serious adverse events associated with interleukin-12,23 inhibitors compared to interleukin-23 inhibitors in patients with moderate to severe Crohn's disease. Risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals were used. Comparisons should be read from left (active agent) to right (control arm). Risk ratios above the diagonal represent direct pairwise meta-analysis. Risk ratios below the diagonal represent network meta-analysis. Risk ratios highlighted in green indicate favorable outcomes. Risk ratios highlighted in red indicate unfavorable outcome. UST - Ustekinumab; RZB - Risankizumab; MIRI - Mirikizumab; GUS - Guselkumab.
Disclosures:
Ravi Teja Pasam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Misha Gautam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sruthi Venugopalan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Babu Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Udaykumar Navaneethan: AbbVie – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. BMS – Speakers Bureau. Janssen – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Lily – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Speakers Bureau.
Ravi Teja Pasam, MBBS, MPH1, Misha Gautam, MD2, Sruthi Venugopalan, MD3, Babu Mohan, MD4, Udaykumar Navaneethan, MD5. P0943 - Interleukin-12/23 vs Interleukin-23 Inhibitors in Moderate to Severe Crohn’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
