Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0268 - Unusual Discovery Within a Rectal Polyp
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Layth Alzubaidy, MD
University of Texas Health Science Center
Tyler, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Layth Alzubaidy, MD1, Muhammad Majeed, MD1, Tony E. Yusuf, MD2
1University of Texas Health Science Center, Tyler, TX; 2University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX
Introduction: Schistosomiasis is the second most common tropical disease worldwide. Its life cycle involves snails as intermediate hosts. The parasites penetrate human skin, mature, and release eggs that trigger a strong immune response, leading to granuloma formation. Chronic inflammation from these eggs can distort the colonic mucosa, contributing to the development of colonic polyps.
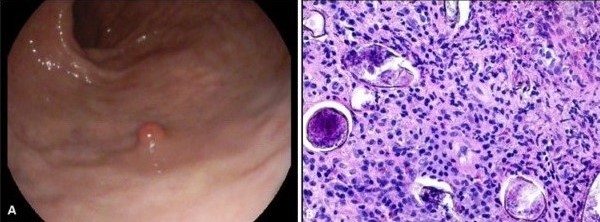
Case Description/Methods: We present a case of a 40-year-old male with a history of diarrhea alternating with constipation for several months presented in the gastroenterology clinic. The patient had no known chronic medical issues and maintained excellent health. The patient relocated from Guinea around 15 years before his evaluation and has remained in the United States since. The physical examination was unremarkable. Laboratory tests including a complete metabolic panel, complete blood count, and thyroid panel were insignificant, except for eosinophilia (11.2%). A stool analysis for ova & parasite was unremarkable and he was referred for a diagnostic colonoscopy. The ileocolonoscopy was unremarkable except for a sessile polyp in the rectum (Figure A). Histopathological examination revealed glandular and smooth muscle proliferation as well as oocytes surrounded by inflammation, along with eggs characterized by a refractile shell and spine (Figure B), Schistosoma haematobium. The patient was subsequently treated with Praziquantel with improvement of symptoms.
Discussion: The histopathological examination of the above polyp revealed hyperplastic changes, including eggs containing terminal spines, which suggested Schistosoma haematobium. Praziquantel (40-60 mg/kg) is the preferred drug for treating schistosomiasis. Praziquantel is highly effective at eliminating adult schistosomes. After treatment, eosinophilia typically normalizes within a few weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the infection and the individual's immune response. Monitoring eosinophil counts is advisable to assess the continued reduction of eosinophilia and the effectiveness of therapy. This case underscores the significance of a thorough evaluation and the value of histopathological examination in diagnosing and managing parasitic infections. Schistosomiasis should be considered as a potential diagnosis in patients with gastrointestinal symptoms in the appropriate context such as migration from an endemic area. Early recognition and treatment can prevent complications and improve patient outcomes.
Disclosures:
Layth Alzubaidy, MD1, Muhammad Majeed, MD1, Tony E. Yusuf, MD2. P0268 - Unusual Discovery Within a Rectal Polyp, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Texas Health Science Center, Tyler, TX; 2University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX
Introduction: Schistosomiasis is the second most common tropical disease worldwide. Its life cycle involves snails as intermediate hosts. The parasites penetrate human skin, mature, and release eggs that trigger a strong immune response, leading to granuloma formation. Chronic inflammation from these eggs can distort the colonic mucosa, contributing to the development of colonic polyps.
Case Description/Methods: We present a case of a 40-year-old male with a history of diarrhea alternating with constipation for several months presented in the gastroenterology clinic. The patient had no known chronic medical issues and maintained excellent health. The patient relocated from Guinea around 15 years before his evaluation and has remained in the United States since. The physical examination was unremarkable. Laboratory tests including a complete metabolic panel, complete blood count, and thyroid panel were insignificant, except for eosinophilia (11.2%). A stool analysis for ova & parasite was unremarkable and he was referred for a diagnostic colonoscopy. The ileocolonoscopy was unremarkable except for a sessile polyp in the rectum (Figure A). Histopathological examination revealed glandular and smooth muscle proliferation as well as oocytes surrounded by inflammation, along with eggs characterized by a refractile shell and spine (Figure B), Schistosoma haematobium. The patient was subsequently treated with Praziquantel with improvement of symptoms.
Discussion: The histopathological examination of the above polyp revealed hyperplastic changes, including eggs containing terminal spines, which suggested Schistosoma haematobium. Praziquantel (40-60 mg/kg) is the preferred drug for treating schistosomiasis. Praziquantel is highly effective at eliminating adult schistosomes. After treatment, eosinophilia typically normalizes within a few weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the infection and the individual's immune response. Monitoring eosinophil counts is advisable to assess the continued reduction of eosinophilia and the effectiveness of therapy. This case underscores the significance of a thorough evaluation and the value of histopathological examination in diagnosing and managing parasitic infections. Schistosomiasis should be considered as a potential diagnosis in patients with gastrointestinal symptoms in the appropriate context such as migration from an endemic area. Early recognition and treatment can prevent complications and improve patient outcomes.

Figure: Figure A: Endoscopic image of the rectal polyp. Figure B: Microscopic view showing the parasite egg (Hematoxylin and Eosin 400x magnification).
Disclosures:
Layth Alzubaidy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Majeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tony E. Yusuf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Layth Alzubaidy, MD1, Muhammad Majeed, MD1, Tony E. Yusuf, MD2. P0268 - Unusual Discovery Within a Rectal Polyp, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
