Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0104 - The Successful Use of a High-Dose Immunosuppression Combination Regimen for the Management of Refractory IgG4 Sclerosing Cholangitis With Progressive Multisystemic Involvement: A Case Report
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ujwala Pamidimukkala, MD
Indiana University School of Medicine
Indianapolis, IN
Presenting Author(s)
Ujwala Pamidimukkala, MD1, Gabriella Aitcheson, MD1, Michael Rosenheck, MD1, Hala Fatima, MD2, Itegbemie Obaitan, MD, MPH1
1Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 2Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN
Introduction: IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis is an immunologic fibroinflammatory disease of the biliary tree. Glucocorticoids are used as first-line treatment, with Rituximab recommended as second-line. We present a refractory progressive case requiring a novel immunosuppressant combination regimen to achieve control.
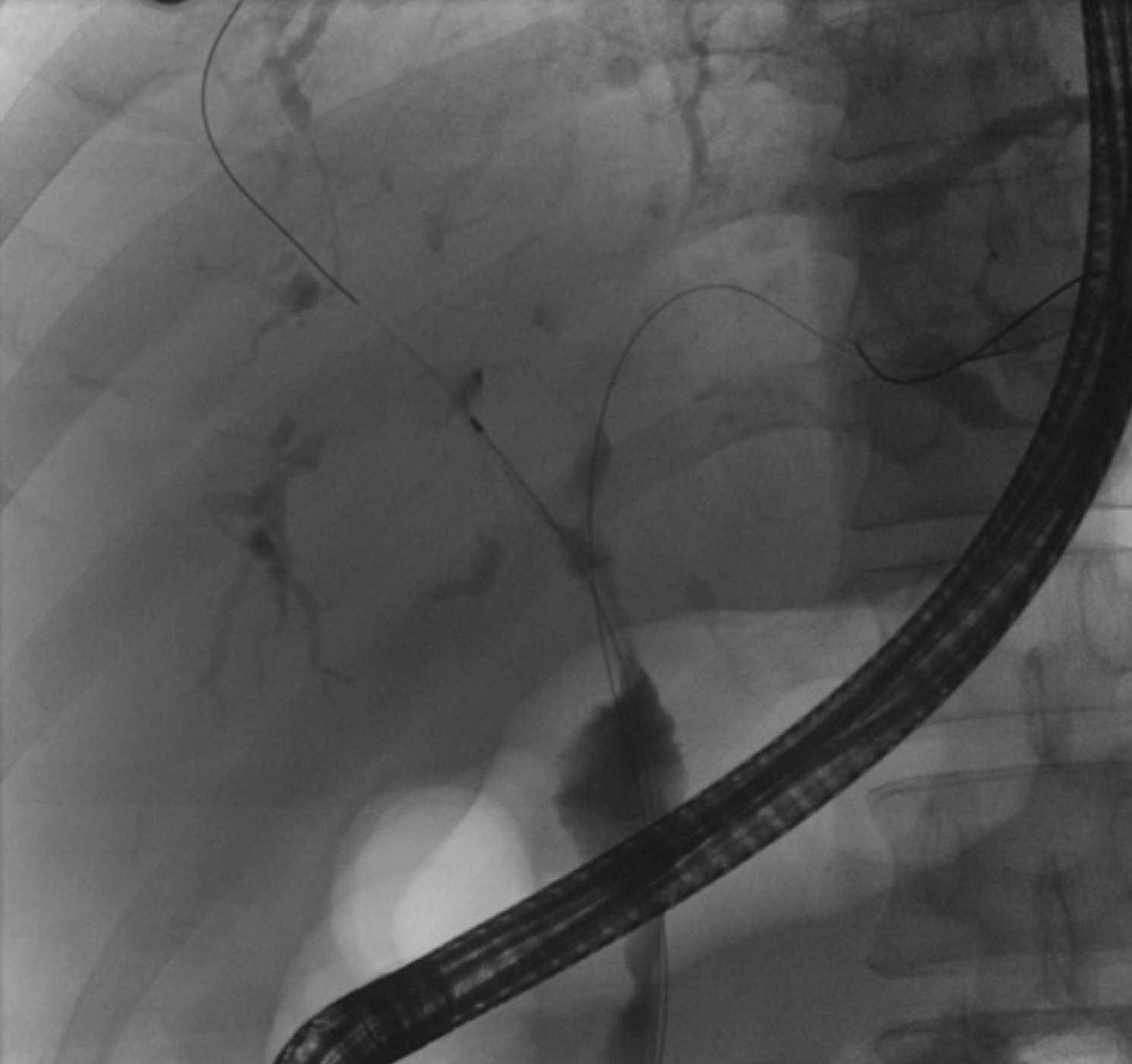
Case Description/Methods: This is a 53-year-old man who had an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) for obstructive jaundice, with multiple extrahepatic strictures requiring treatment. Serum IgG4 was 1030 mg/dL with ampullary biopsies positive for IgG4 so an initial diagnosis of Type III IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis was made. High-dose Prednisone was started but discontinued due to steroid-induced central serous chorioretinopathy. Azathioprine therapy led to myelosuppression. Rituximab 375mg/m2 q3 months was started and escalated over time to q1month dosing due to worsening biliary disease. Rituximab was complicated by lobular capillary hemangioma of the forehead and mild infusion reactions treated with Benadryl, but continued. Despite improvement in serum IgG4 levels over the next few months, he had relapsing clinical symptoms and developed diffuse intrahepatic duct involvement. Over the next three years, he had one episode of ascending cholangitis, developed chronic autoimmune pancreatitis with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, IgG4-related enlargement of orbital and lacrimal glands and IgG4-related Stage 3b chronic kidney disease with nephrotic range proteinuria. A trial of 1000mg BID Mycophenolate mofetil was initiated in addition to Rituximab, with resolution of biliary strictures, transaminase elevation, renal function and other associated symptoms. The immunosuppressive regimen is now being slowly tapered without disease recurrence.
Discussion: The first-line treatment for IgG4-related disease is daily prednisone for 4-6 weeks with a gradual taper. Rituximab is next-line with a high success rate and Azathioprine and Mycophenolate mofetil are alternatives. Our patient could not tolerate a prolonged course of glucocorticoids, Azathioprine and had disease progression to other organ systems on Rituximab monotherapy. There are currently no guidelines on effective non-glucocorticoid immunosuppression combination regimens for Rituximab refractory patients, so our documented success with the Rituximab and high-dose Mycophenolate Mofetil combination may be helpful for similar patients. Further studies on the efficacy and safety of this combination regimen are needed.
Disclosures:
Ujwala Pamidimukkala, MD1, Gabriella Aitcheson, MD1, Michael Rosenheck, MD1, Hala Fatima, MD2, Itegbemie Obaitan, MD, MPH1. P0104 - The Successful Use of a High-Dose Immunosuppression Combination Regimen for the Management of Refractory IgG4 Sclerosing Cholangitis With Progressive Multisystemic Involvement: A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 2Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN
Introduction: IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis is an immunologic fibroinflammatory disease of the biliary tree. Glucocorticoids are used as first-line treatment, with Rituximab recommended as second-line. We present a refractory progressive case requiring a novel immunosuppressant combination regimen to achieve control.
Case Description/Methods: This is a 53-year-old man who had an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) for obstructive jaundice, with multiple extrahepatic strictures requiring treatment. Serum IgG4 was 1030 mg/dL with ampullary biopsies positive for IgG4 so an initial diagnosis of Type III IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis was made. High-dose Prednisone was started but discontinued due to steroid-induced central serous chorioretinopathy. Azathioprine therapy led to myelosuppression. Rituximab 375mg/m2 q3 months was started and escalated over time to q1month dosing due to worsening biliary disease. Rituximab was complicated by lobular capillary hemangioma of the forehead and mild infusion reactions treated with Benadryl, but continued. Despite improvement in serum IgG4 levels over the next few months, he had relapsing clinical symptoms and developed diffuse intrahepatic duct involvement. Over the next three years, he had one episode of ascending cholangitis, developed chronic autoimmune pancreatitis with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, IgG4-related enlargement of orbital and lacrimal glands and IgG4-related Stage 3b chronic kidney disease with nephrotic range proteinuria. A trial of 1000mg BID Mycophenolate mofetil was initiated in addition to Rituximab, with resolution of biliary strictures, transaminase elevation, renal function and other associated symptoms. The immunosuppressive regimen is now being slowly tapered without disease recurrence.
Discussion: The first-line treatment for IgG4-related disease is daily prednisone for 4-6 weeks with a gradual taper. Rituximab is next-line with a high success rate and Azathioprine and Mycophenolate mofetil are alternatives. Our patient could not tolerate a prolonged course of glucocorticoids, Azathioprine and had disease progression to other organ systems on Rituximab monotherapy. There are currently no guidelines on effective non-glucocorticoid immunosuppression combination regimens for Rituximab refractory patients, so our documented success with the Rituximab and high-dose Mycophenolate Mofetil combination may be helpful for similar patients. Further studies on the efficacy and safety of this combination regimen are needed.

Figure: IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis progression on Rituximab monotherapy
Disclosures:
Ujwala Pamidimukkala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gabriella Aitcheson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Rosenheck indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hala Fatima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Itegbemie Obaitan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ujwala Pamidimukkala, MD1, Gabriella Aitcheson, MD1, Michael Rosenheck, MD1, Hala Fatima, MD2, Itegbemie Obaitan, MD, MPH1. P0104 - The Successful Use of a High-Dose Immunosuppression Combination Regimen for the Management of Refractory IgG4 Sclerosing Cholangitis With Progressive Multisystemic Involvement: A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
