Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0115 - Endoscopic Management of Complex Colonic Fistula Following Distal Pancreatectomy
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

WonKyung J. Cho, MD, MPH
Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Forest Hills - Northwell Health
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
WonKyung Cho, MD, MPH1, Henry Jen, MD2
1Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Forest Hills - Northwell Health, New York, NY; 2Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Forest Hills - Northwell Health, Forest Hills, NY
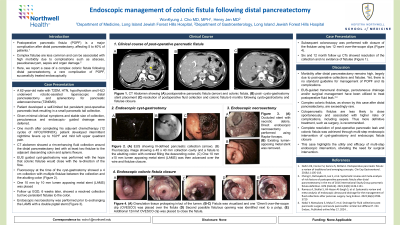
Introduction: Postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) is a major complication after distal pancreatectomy, affecting 5 to 40% of patients. Complex fistulae are less common and can be associated with higher morbidity including sepsis and organ damage. Here, we report a case of a complex colonic fistula following distal pancreatectomy, a rare complication of POPF, successfully treated endoscopically.
Case Description/Methods: A 62-year-old male with past medical history of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (T2N0) underwent robotic-assisted laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy complicated by a self-limited post-operative pancreatic leak resulting in a small pancreatic tail collection. Percutaneous and endoscopic-guided drainage was deferred as the patient was asymptomatic and the collection was stable on repeat imaging. Eight months following initiating adjuvant chemotherapy, the patient developed nighttime fevers
and mild left upper quadrant pain. CT abdomen showed a rim-enhancing fluid collection around the distal pancreatectomy bed with at least two fistulae to the adjacent descending colon and splenic flexure. The decision was made to endoscopically drain the collection with EUS guided cyst-gastrostomy with the hope that the colonic fistulae would close with redirection of flow. Fluoroscopy at the time of the cyst-gastrostomy showed a 4 cm collection with multiple fistulae between the collection and the abutting colon. One
10 mm by 10 mm lumen apposing metal stent (LAMS) was placed. Repeat EGD 6 weeks later showed a resolved collection but
two persistent fistulae to the colon.The LAMS was exchanged for a double pigtail stent.Subsequent colonoscopy was performed with closure of the fistulae using two 12 mm/t over-the-scope clips. Six and 12 month follow up CTs showed resolution of the collection and no evidence of fistulae.
Discussion: Morbidity from post-operative collections and fistulae is high. Yet, there is no standard guideline for management of POPF and its complications. Moreover, complex colonic fistulas, as shown by this case after distal pancreatectomy, are exceedingly rare. Here, we demonstrate the complete resolution of POPF and colonic fistula using a multi-step endoscopic intervention of cyst-gastrostomy and endoscopic fistula closure.
Disclosures:
WonKyung Cho, MD, MPH1, Henry Jen, MD2. P0115 - Endoscopic Management of Complex Colonic Fistula Following Distal Pancreatectomy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Forest Hills - Northwell Health, New York, NY; 2Long Island Jewish Medical Center, Forest Hills - Northwell Health, Forest Hills, NY
Introduction: Postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) is a major complication after distal pancreatectomy, affecting 5 to 40% of patients. Complex fistulae are less common and can be associated with higher morbidity including sepsis and organ damage. Here, we report a case of a complex colonic fistula following distal pancreatectomy, a rare complication of POPF, successfully treated endoscopically.
Case Description/Methods: A 62-year-old male with past medical history of pancreatic adenocarcinoma (T2N0) underwent robotic-assisted laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy complicated by a self-limited post-operative pancreatic leak resulting in a small pancreatic tail collection. Percutaneous and endoscopic-guided drainage was deferred as the patient was asymptomatic and the collection was stable on repeat imaging. Eight months following initiating adjuvant chemotherapy, the patient developed nighttime fevers
and mild left upper quadrant pain. CT abdomen showed a rim-enhancing fluid collection around the distal pancreatectomy bed with at least two fistulae to the adjacent descending colon and splenic flexure. The decision was made to endoscopically drain the collection with EUS guided cyst-gastrostomy with the hope that the colonic fistulae would close with redirection of flow. Fluoroscopy at the time of the cyst-gastrostomy showed a 4 cm collection with multiple fistulae between the collection and the abutting colon. One
10 mm by 10 mm lumen apposing metal stent (LAMS) was placed. Repeat EGD 6 weeks later showed a resolved collection but
two persistent fistulae to the colon.The LAMS was exchanged for a double pigtail stent.Subsequent colonoscopy was performed with closure of the fistulae using two 12 mm/t over-the-scope clips. Six and 12 month follow up CTs showed resolution of the collection and no evidence of fistulae.
Discussion: Morbidity from post-operative collections and fistulae is high. Yet, there is no standard guideline for management of POPF and its complications. Moreover, complex colonic fistulas, as shown by this case after distal pancreatectomy, are exceedingly rare. Here, we demonstrate the complete resolution of POPF and colonic fistula using a multi-step endoscopic intervention of cyst-gastrostomy and endoscopic fistula closure.

Figure:
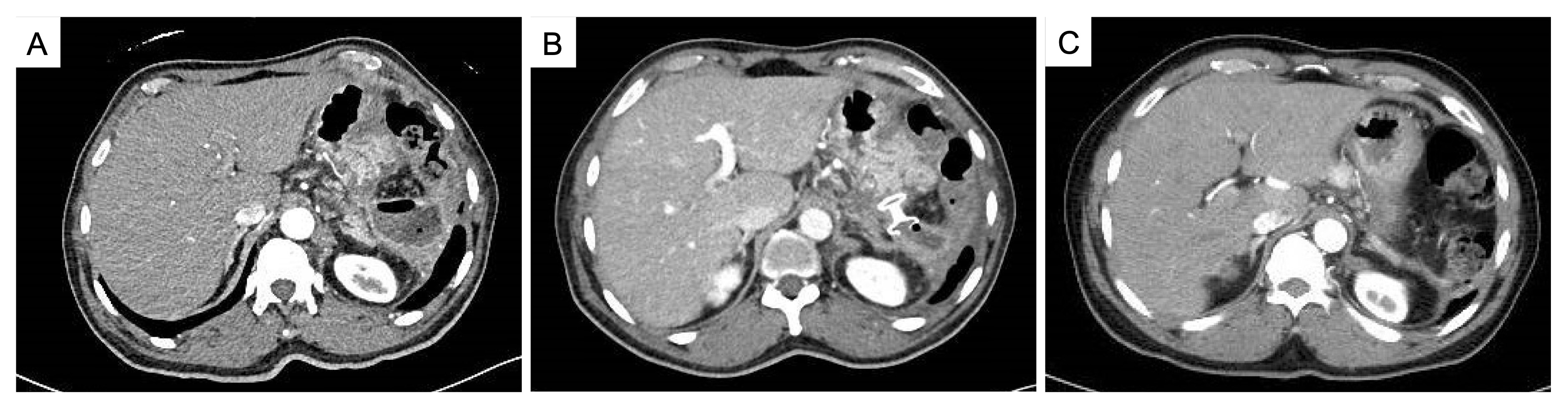
Figure. CT Abdomen showing (A) postoperative pancreatic fistula and colonic fistula, (B) post- cysto-gastrostomy stent placement (C) resolution of postoperative pancreatic fistula and colonic fistula following stent removal and clip closure of fistula.
Figure. CT Abdomen showing (A) postoperative pancreatic fistula and colonic fistula, (B) post- cysto-gastrostomy stent placement (C) resolution of postoperative pancreatic fistula and colonic fistula following stent removal and clip closure of fistula.
Disclosures:
WonKyung Cho indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Henry Jen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
WonKyung Cho, MD, MPH1, Henry Jen, MD2. P0115 - Endoscopic Management of Complex Colonic Fistula Following Distal Pancreatectomy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
