Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P4078 - What Happens in Vagus: A Case Series of Three Pain-Predominant DGBI Managed With Transauricular Vagal Nerve Stimulation
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E


Saad Javed, MD
Allegheny Health Network
Pittsburgh, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Saad Javed, MD
Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA
Introduction: Transcutaneous auricular vagal nerve stimulation (taVNS) has been explored in both scientific research and various clinical settings. While noninvasive devices including transcutaneous stimulation of auricular VN or carotid VN are undergoing clinical trials, we share our real-life experience of three cases - with varying neurogastroenterology and motility manifestations.
Case Description/Methods: Case 1:
32 year old woman with Ehler Danlos Syndrome and POTS presented with an eight-month history of early satiety, nausea, vomiting, weight loss and epigastric pain. Gastric emptying scan did not show delayed gastric emptying. Endoscopic evaluation was normal. Dietary modification, metoclopramide, mirtazapine, cyproheptadine, pyridostigmine and omeprazole only led to partial improvement in symptoms of nausea and early satiety. Notably, she continued to struggle with epigastric pain. TaVNS was initiated.
Case 2:
26 year old woman with anxiety, contracted COVID-19 infection where anosmia and respiratory symptoms lasted for two weeks. Despite resolution of initial symptoms, over the next year, she started experiencing recurrent, progressively worsening episodes of generalized abdominal pain without change in bowel habits or association with food intake. Endoscopic evaluation, cross-sectional imaging and GES were normal. She responded partially to duloxetine, pregabalin and CBT therapy. Eventually, after several months of recurring symptoms and multiple ER visits, she was advised taVNS.
Case 3:
47 year old man presented with severe constipation associated with abdominal pain and bloating. While his pain improved after defecation, he rarely felt completely evacuated. Sitzmarks® Study revealed delayed colonic transit. Colonoscopy, CT enterography and anorectal manometry were normal. He had tried linaclotide, plecanatide, lubriprostone and prucalopride. Tenapanor was started, leading to improvement in constipation but abdominal pain persisted. Adjunct pharmacological neuromodulators like nortriptyline, duloxetine and gabapentin were not helpful. Adjunct taVNS was initiated
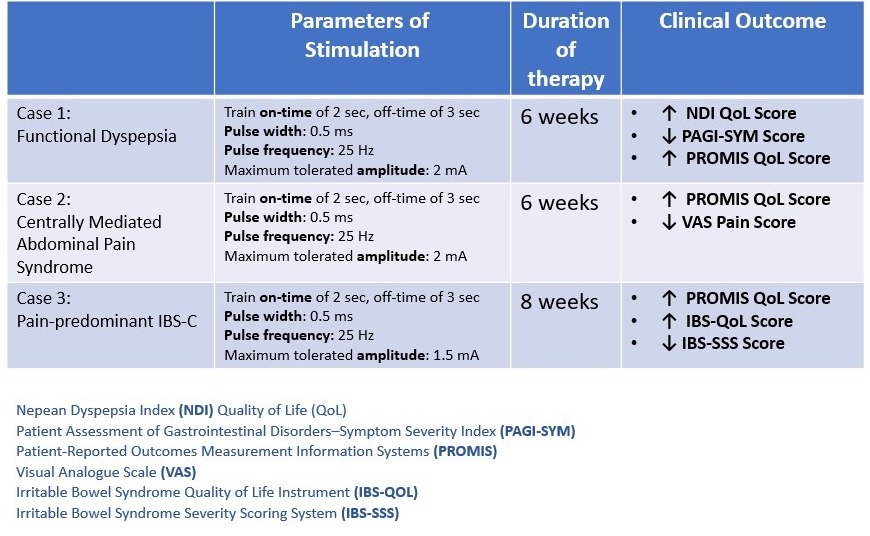
Discussion: Vagal nerve stimulation (VNS) is emerging as a nonpharmacologic therapeutic strategy for disorders of gut–brain interaction. The current conceptual framework implicates anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects VNS. We share our stimulation parameters and outcomes (Table 1) in management of three pain-predominant DGBIs, including functional dyspepsia, centrally mediated abdominal pain syndrome, and pain-predominant IBS-C.
Disclosures:
Saad Javed, MD. P4078 - What Happens in Vagus: A Case Series of Three Pain-Predominant DGBI Managed With Transauricular Vagal Nerve Stimulation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA
Introduction: Transcutaneous auricular vagal nerve stimulation (taVNS) has been explored in both scientific research and various clinical settings. While noninvasive devices including transcutaneous stimulation of auricular VN or carotid VN are undergoing clinical trials, we share our real-life experience of three cases - with varying neurogastroenterology and motility manifestations.
Case Description/Methods: Case 1:
32 year old woman with Ehler Danlos Syndrome and POTS presented with an eight-month history of early satiety, nausea, vomiting, weight loss and epigastric pain. Gastric emptying scan did not show delayed gastric emptying. Endoscopic evaluation was normal. Dietary modification, metoclopramide, mirtazapine, cyproheptadine, pyridostigmine and omeprazole only led to partial improvement in symptoms of nausea and early satiety. Notably, she continued to struggle with epigastric pain. TaVNS was initiated.
Case 2:
26 year old woman with anxiety, contracted COVID-19 infection where anosmia and respiratory symptoms lasted for two weeks. Despite resolution of initial symptoms, over the next year, she started experiencing recurrent, progressively worsening episodes of generalized abdominal pain without change in bowel habits or association with food intake. Endoscopic evaluation, cross-sectional imaging and GES were normal. She responded partially to duloxetine, pregabalin and CBT therapy. Eventually, after several months of recurring symptoms and multiple ER visits, she was advised taVNS.
Case 3:
47 year old man presented with severe constipation associated with abdominal pain and bloating. While his pain improved after defecation, he rarely felt completely evacuated. Sitzmarks® Study revealed delayed colonic transit. Colonoscopy, CT enterography and anorectal manometry were normal. He had tried linaclotide, plecanatide, lubriprostone and prucalopride. Tenapanor was started, leading to improvement in constipation but abdominal pain persisted. Adjunct pharmacological neuromodulators like nortriptyline, duloxetine and gabapentin were not helpful. Adjunct taVNS was initiated
Discussion: Vagal nerve stimulation (VNS) is emerging as a nonpharmacologic therapeutic strategy for disorders of gut–brain interaction. The current conceptual framework implicates anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects VNS. We share our stimulation parameters and outcomes (Table 1) in management of three pain-predominant DGBIs, including functional dyspepsia, centrally mediated abdominal pain syndrome, and pain-predominant IBS-C.

Figure: Table 1: taVNS in DGBI - Parameters of Stimulation and Outcomes
Disclosures:
Saad Javed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saad Javed, MD. P4078 - What Happens in Vagus: A Case Series of Three Pain-Predominant DGBI Managed With Transauricular Vagal Nerve Stimulation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
