Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P2924 - Assessing the Efficacy of Farnesoid X Receptor Agonists in the Management of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
- JK
Jai Kumar, MD
Wayne State University School of Medicine / Ascension Providence Rochester Hospital
Troy, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Jai Kumar, MD1, Tripti Nagar, MD2, Misha Hasan, MBBS3, Sana Mohsin, MBBS3, Sarwan Kumar, MD1
1Wayne State University School of Medicine / Ascension Providence Rochester Hospital, Troy, MI; 2Wayne State University School of Medicine / Ascension Providence Rochester Hospital, Rochester, MI; 3Ziauddin University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
Introduction: Several randomized clinical trials have been conducted assessing the potential efficacy of Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonists in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). A comprehensive review and analysis were needed to evaluate the findings of these trials. Hence, this systematic review and meta-analysis aim to study the association between FXR agonists and hepatic outcomes in patients with MASLD.
Methods: Systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy of FXR agonists in 1,227 patients assigned to the FXR intervention group compared to 650 patients in the placebo group. Changes in liver enzymes and hepatic steatosis assessed by MRI-PDFF were evaluated.
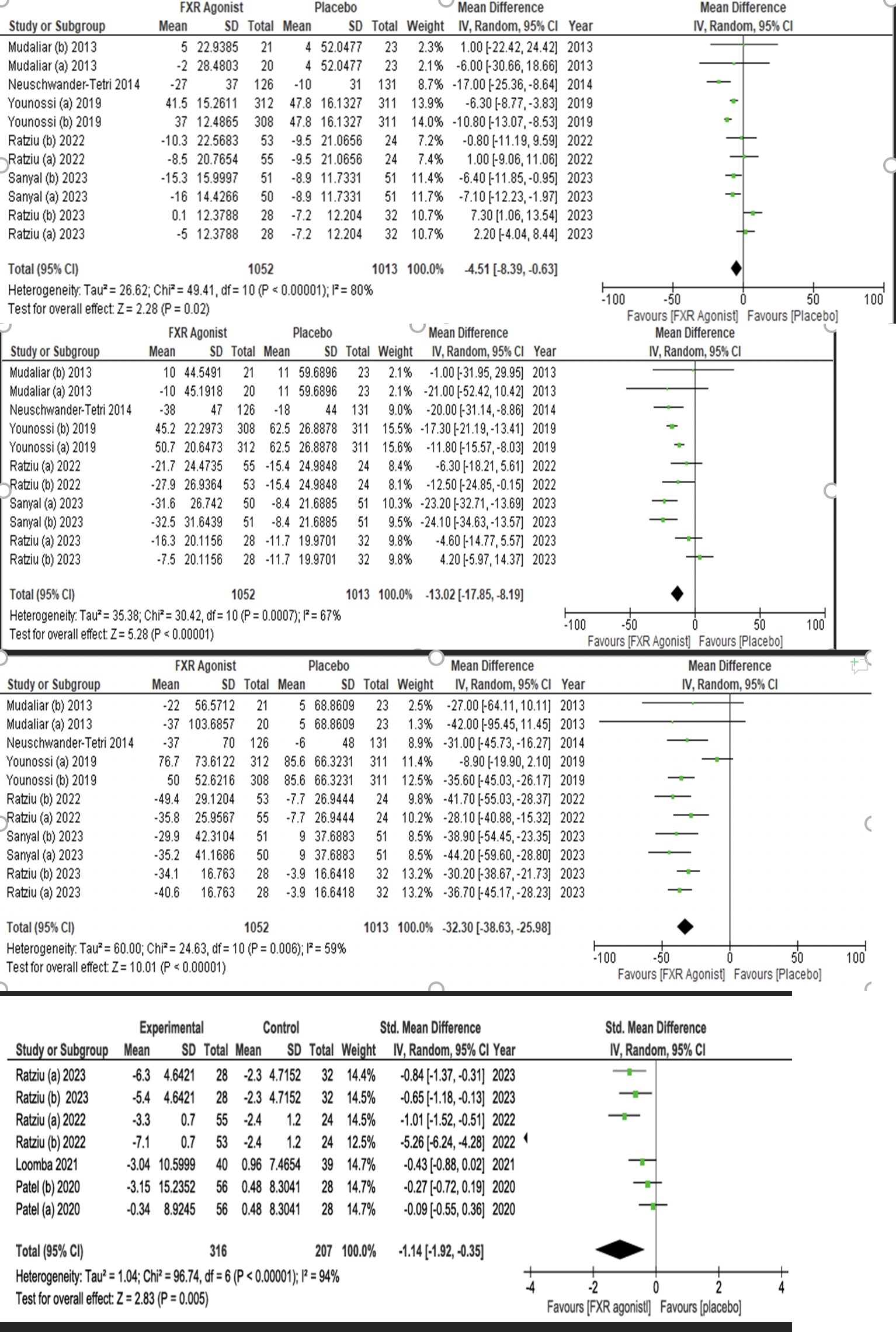
Results: FXR agonist use was associated with a significant reduction in levels of AST, (WMD= -4.51, 95% CI=[-8.39,-0.63], P=0.02); ALT (WMD= -13.02, 95% CI=[-17.85,-8.19], P< 0.00001); GGT (WMD= -32.20, 95% CI=[-38.63,-25.98], P< 0.00001); MRI-PDFF, (SMD= -1.14, 95% CI=[-1.92,-0.35], P=0.005). FXR agonists did not significantly affect ALP levels, (WMD= 25.04, 95% CI=[19.22,30.87], P< 0.00001]
Discussion: MASLD, characterized by the accumulation of fat in over 5% of hepatocytes without significant alcohol intake, is closely linked to insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Recent studies reveal that MASLD involves a complex interplay of metabolic abnormalities and inflammation. FXR agonists, including obeticholic acid, have shown promise in improving insulin sensitivity, reducing liver enzyme levels, and improving histological changes in patients with MASLD and MASH.
Our meta-analysis demonstrated that FXR agonist therapy leads to significant decreases in hepatic steatosis and liver enzymes, highlighting their potential as effective treatments. Despite some limitations, such as short trial durations and variations in dosages, the findings underscore the potential of FXR agonists in managing and treating MASLD and MASH. These results not only offer valuable clinical insights but also pave the way for future studies on FXR agonists as viable pharmacological options for these conditions.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Jai Kumar, MD1, Tripti Nagar, MD2, Misha Hasan, MBBS3, Sana Mohsin, MBBS3, Sarwan Kumar, MD1. P2924 - Assessing the Efficacy of Farnesoid X Receptor Agonists in the Management of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Wayne State University School of Medicine / Ascension Providence Rochester Hospital, Troy, MI; 2Wayne State University School of Medicine / Ascension Providence Rochester Hospital, Rochester, MI; 3Ziauddin University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan
Introduction: Several randomized clinical trials have been conducted assessing the potential efficacy of Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonists in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). A comprehensive review and analysis were needed to evaluate the findings of these trials. Hence, this systematic review and meta-analysis aim to study the association between FXR agonists and hepatic outcomes in patients with MASLD.
Methods: Systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy of FXR agonists in 1,227 patients assigned to the FXR intervention group compared to 650 patients in the placebo group. Changes in liver enzymes and hepatic steatosis assessed by MRI-PDFF were evaluated.
Results: FXR agonist use was associated with a significant reduction in levels of AST, (WMD= -4.51, 95% CI=[-8.39,-0.63], P=0.02); ALT (WMD= -13.02, 95% CI=[-17.85,-8.19], P< 0.00001); GGT (WMD= -32.20, 95% CI=[-38.63,-25.98], P< 0.00001); MRI-PDFF, (SMD= -1.14, 95% CI=[-1.92,-0.35], P=0.005). FXR agonists did not significantly affect ALP levels, (WMD= 25.04, 95% CI=[19.22,30.87], P< 0.00001]
Discussion: MASLD, characterized by the accumulation of fat in over 5% of hepatocytes without significant alcohol intake, is closely linked to insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Recent studies reveal that MASLD involves a complex interplay of metabolic abnormalities and inflammation. FXR agonists, including obeticholic acid, have shown promise in improving insulin sensitivity, reducing liver enzyme levels, and improving histological changes in patients with MASLD and MASH.
Our meta-analysis demonstrated that FXR agonist therapy leads to significant decreases in hepatic steatosis and liver enzymes, highlighting their potential as effective treatments. Despite some limitations, such as short trial durations and variations in dosages, the findings underscore the potential of FXR agonists in managing and treating MASLD and MASH. These results not only offer valuable clinical insights but also pave the way for future studies on FXR agonists as viable pharmacological options for these conditions.

Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Jai Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tripti Nagar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Misha Hasan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sana Mohsin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sarwan Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jai Kumar, MD1, Tripti Nagar, MD2, Misha Hasan, MBBS3, Sana Mohsin, MBBS3, Sarwan Kumar, MD1. P2924 - Assessing the Efficacy of Farnesoid X Receptor Agonists in the Management of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
