Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P2927 - Adequacy of Hepatitis C Testing in the Outpatient Setting in Accordance With the Latest USPSTF Guidelines: A Cross-Sectional Study and a Quality Improvement Project
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Usama Abu-Heija, MBBS
East Tennessee State University
Johnson City, TN
Presenting Author(s)
Usama Abu-heija, MBBS1, Asaiel Makahleh, MD1, Sagar Nagpal, MBBS1, Ahmad Abu-Heija, MBBS2, Maya Shatta, MBBS3, Rupal Shah, MD1
1East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN; 2Oak Ridge Gastroenterology Associates, Knoxville, TN; 3StatCare Hospitalist Group, Knoxville, TN
Introduction: Hepatitis C viral (HCV) infection is a very common communicable disease and is associated with a significant disease burden. In 2023 the reported prevalence of chronic HCV in the United States was between 2.7 – 3.9 million. In 2013, the USPSTF recommended HCV screening for high-risk individuals and adults born between 1945-1965. However, in 2020, they updated their guidelines to include all adults aged 18-79, and those outside this age range who were at high risk. Our Study is directed at evaluating the adequacy of hepatitis C screening in the outpatient setting as well as discussing tools to maximize screening.
Methods: We retrospectively collected data from the outpatient records of five primary care clinical practices in the East Tennessee area between March 2020 and March 2023. We analyzed records of patients aged 18-79 as well as patients younger than 18 and older than 79 that had a high risk of infection. We utilized our electronic medical records (EMR) to collect visit information for every patient that had an annual visit in this time period. We cross matched the collected records of visits with ordered tests ( HCV antibody, genotype and RNA). We excluded all patients that were previously tested for hepatitis C prior to March 2020.
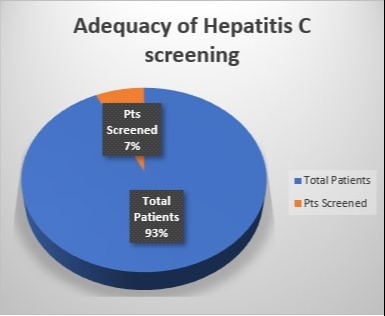
Results: Our analysis involved 9,936 patients who met the inclusion criteria. Among the studied population, 40% (3,967) were females, while 60% (5,969) were males. The predominant test ordered was the Hepatitis C Antibody with Reflex PCR, accounting for 88% (668) of the total tests performed. Only 7.56% (751) of patients underwent adequate testing within the three-year period following the publication of the new guidelines.
Discussion: Hepatitis C screening is a challenging project that has shown itself to be of great importance. Screening reduces the risks Hepatitis C developing into one of the many unfavorable outcomes associated with its course, such as cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. We aimed at highlighting how there is plenty of room when it comes to increasing the adequacy of hepatitis C screening in our community and very likely nationwide. Our quality improvement project will include multiple Systemic and educational interventions to increase appropriate screening for hepatitis C in the outpatient setting. Such as, tagging patient’s charts in the EMR to help in identifying patients who meet criteria for testing. As well as implementing dedicated didactics on this topic aimed at medical residents and primary care providers.
Disclosures:
Usama Abu-heija, MBBS1, Asaiel Makahleh, MD1, Sagar Nagpal, MBBS1, Ahmad Abu-Heija, MBBS2, Maya Shatta, MBBS3, Rupal Shah, MD1. P2927 - Adequacy of Hepatitis C Testing in the Outpatient Setting in Accordance With the Latest USPSTF Guidelines: A Cross-Sectional Study and a Quality Improvement Project, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1East Tennessee State University, Johnson City, TN; 2Oak Ridge Gastroenterology Associates, Knoxville, TN; 3StatCare Hospitalist Group, Knoxville, TN
Introduction: Hepatitis C viral (HCV) infection is a very common communicable disease and is associated with a significant disease burden. In 2023 the reported prevalence of chronic HCV in the United States was between 2.7 – 3.9 million. In 2013, the USPSTF recommended HCV screening for high-risk individuals and adults born between 1945-1965. However, in 2020, they updated their guidelines to include all adults aged 18-79, and those outside this age range who were at high risk. Our Study is directed at evaluating the adequacy of hepatitis C screening in the outpatient setting as well as discussing tools to maximize screening.
Methods: We retrospectively collected data from the outpatient records of five primary care clinical practices in the East Tennessee area between March 2020 and March 2023. We analyzed records of patients aged 18-79 as well as patients younger than 18 and older than 79 that had a high risk of infection. We utilized our electronic medical records (EMR) to collect visit information for every patient that had an annual visit in this time period. We cross matched the collected records of visits with ordered tests ( HCV antibody, genotype and RNA). We excluded all patients that were previously tested for hepatitis C prior to March 2020.
Results: Our analysis involved 9,936 patients who met the inclusion criteria. Among the studied population, 40% (3,967) were females, while 60% (5,969) were males. The predominant test ordered was the Hepatitis C Antibody with Reflex PCR, accounting for 88% (668) of the total tests performed. Only 7.56% (751) of patients underwent adequate testing within the three-year period following the publication of the new guidelines.
Discussion: Hepatitis C screening is a challenging project that has shown itself to be of great importance. Screening reduces the risks Hepatitis C developing into one of the many unfavorable outcomes associated with its course, such as cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. We aimed at highlighting how there is plenty of room when it comes to increasing the adequacy of hepatitis C screening in our community and very likely nationwide. Our quality improvement project will include multiple Systemic and educational interventions to increase appropriate screening for hepatitis C in the outpatient setting. Such as, tagging patient’s charts in the EMR to help in identifying patients who meet criteria for testing. As well as implementing dedicated didactics on this topic aimed at medical residents and primary care providers.

Figure: Adequacy of Hepatitis C screening
Disclosures:
Usama Abu-heija indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asaiel Makahleh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sagar Nagpal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Abu-Heija indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maya Shatta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rupal Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Usama Abu-heija, MBBS1, Asaiel Makahleh, MD1, Sagar Nagpal, MBBS1, Ahmad Abu-Heija, MBBS2, Maya Shatta, MBBS3, Rupal Shah, MD1. P2927 - Adequacy of Hepatitis C Testing in the Outpatient Setting in Accordance With the Latest USPSTF Guidelines: A Cross-Sectional Study and a Quality Improvement Project, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

