Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P2994 - Hidden Perils: Delayed Pyogenic Liver Abscess Diagnosis Leading to Severe Endogenous Endophthalmitis
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Lawrence Zhou, MD
The University of Kansas School of Medicine
Wichita, KS
Presenting Author(s)
Lawrence Zhou, MD1, Aastha V. Bharwad, MD2, Kevin Singh, MD2, Nathan Tofteland, MD2
1The University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS; 2University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS
Introduction: Klebsiella species are gram-negative, encapsulated, anaerobic bacteria that are part of normal mucosal and gastrointestinal flora. It is known to cause pneumonia and urinary tract infection, but is also an emerging pathogen in the West for pyogenic liver abscess (PLA) and meningitis. The highest incidence of PLA is in Asia and can occur in otherwise healthy adults with an observed mortality rate of 8-14%. Endogenous endophthalmitis (EE) is the most common septic complication of PLA, occurring via hematogenous spread. Here we present an older male with delayed diagnosis leading to development of EE.
Case Description/Methods: A 71 year-old male with history of gastroesophageal reflux, diabetes, and incarcerated >25 years presented for right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain. Labs were significant for bilirubin 1.9 mg/dL which peaked at 5.1 mg/dL, and AST 55 Units/L and ALT 70 Units/L which later normalized. Imaging showed small volume fluid adjacent to the greater curvature of the stomach suggesting gastritis, nonspecific lesions in the left hepatic (2 x 2.6 cm) and caudate lobe (4.9 x 3.6 cm), cholelithiasis, and delayed gallbladder filling. The patient left against medical advice before magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) could be performed.
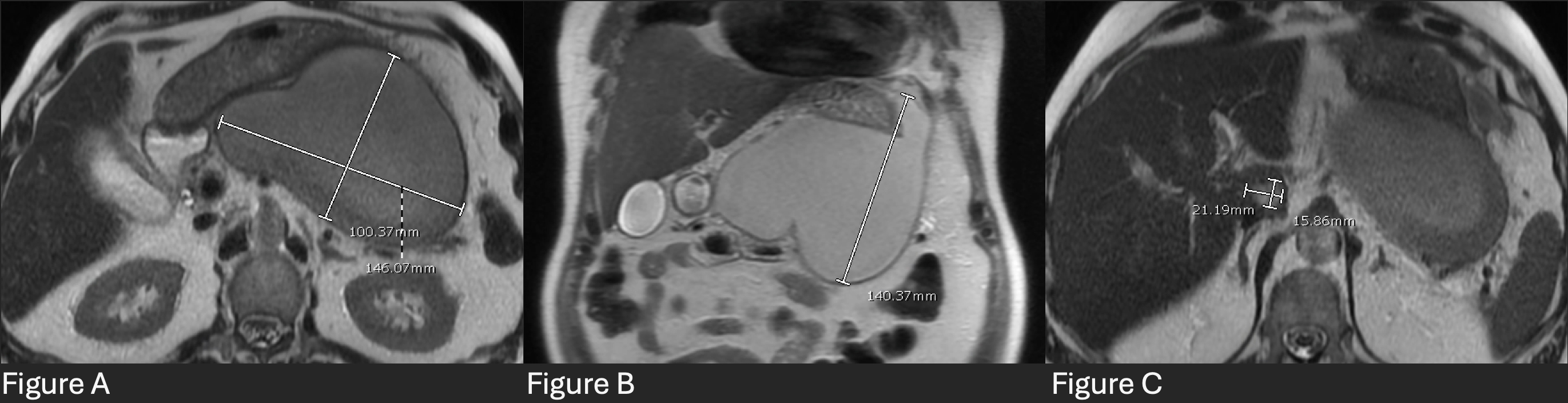
One month later, he was re-admitted for left eye pain and diagnosed with pre and post-septal cellulitis. Labs were significant for WBC 22.1k/mm3 and vitreous culture grew Klebsiella pneumoniae. He continued to complain of abdominal pain, nausea, and early satiety. Abdominal MRI/MRCP showed a peripheral enhancing collection in the caudate lobe (2.1 x 1.7 x 1.5 cm), and large peri-pancreatic lobulated collection (16.1 x 10.1 x 14 cm) in the lesser sac resulting in mass effect upon the stomach and pancreas (Figure A-C). Robotic-assisted laparoscopic cyst-gastrostomy was performed which drained 750 ml of purulent fluid. He was eventually discharged on antibiotics pending resolution of the abscess.
Discussion: This patient’s initial hospitalization for abdominal pain revealed multiple lesions within the liver. However, his labs did not indicate an infectious process and he was afebrile. His second admission was due to eye complaints, which appear to be a common theme per previous case reports. PLA due to Klebsiella species is an emerging pathogen in the West, and when untreated increases the risk of septic complications via hematogenous spread. It is important to keep it as a differential in patients presenting with RUQ pain to prevent catastrophic complications.
Disclosures:
Lawrence Zhou, MD1, Aastha V. Bharwad, MD2, Kevin Singh, MD2, Nathan Tofteland, MD2. P2994 - Hidden Perils: Delayed Pyogenic Liver Abscess Diagnosis Leading to Severe Endogenous Endophthalmitis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS; 2University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita, KS
Introduction: Klebsiella species are gram-negative, encapsulated, anaerobic bacteria that are part of normal mucosal and gastrointestinal flora. It is known to cause pneumonia and urinary tract infection, but is also an emerging pathogen in the West for pyogenic liver abscess (PLA) and meningitis. The highest incidence of PLA is in Asia and can occur in otherwise healthy adults with an observed mortality rate of 8-14%. Endogenous endophthalmitis (EE) is the most common septic complication of PLA, occurring via hematogenous spread. Here we present an older male with delayed diagnosis leading to development of EE.
Case Description/Methods: A 71 year-old male with history of gastroesophageal reflux, diabetes, and incarcerated >25 years presented for right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain. Labs were significant for bilirubin 1.9 mg/dL which peaked at 5.1 mg/dL, and AST 55 Units/L and ALT 70 Units/L which later normalized. Imaging showed small volume fluid adjacent to the greater curvature of the stomach suggesting gastritis, nonspecific lesions in the left hepatic (2 x 2.6 cm) and caudate lobe (4.9 x 3.6 cm), cholelithiasis, and delayed gallbladder filling. The patient left against medical advice before magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) could be performed.
One month later, he was re-admitted for left eye pain and diagnosed with pre and post-septal cellulitis. Labs were significant for WBC 22.1k/mm3 and vitreous culture grew Klebsiella pneumoniae. He continued to complain of abdominal pain, nausea, and early satiety. Abdominal MRI/MRCP showed a peripheral enhancing collection in the caudate lobe (2.1 x 1.7 x 1.5 cm), and large peri-pancreatic lobulated collection (16.1 x 10.1 x 14 cm) in the lesser sac resulting in mass effect upon the stomach and pancreas (Figure A-C). Robotic-assisted laparoscopic cyst-gastrostomy was performed which drained 750 ml of purulent fluid. He was eventually discharged on antibiotics pending resolution of the abscess.
Discussion: This patient’s initial hospitalization for abdominal pain revealed multiple lesions within the liver. However, his labs did not indicate an infectious process and he was afebrile. His second admission was due to eye complaints, which appear to be a common theme per previous case reports. PLA due to Klebsiella species is an emerging pathogen in the West, and when untreated increases the risk of septic complications via hematogenous spread. It is important to keep it as a differential in patients presenting with RUQ pain to prevent catastrophic complications.

Figure: Figure A - Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) of the abdomen, view #1. Figure B - MRCP of the abdomen, view #2. Figure C - MRCP of the abdomen, view #3.
Disclosures:
Lawrence Zhou indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aastha Bharwad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nathan Tofteland indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lawrence Zhou, MD1, Aastha V. Bharwad, MD2, Kevin Singh, MD2, Nathan Tofteland, MD2. P2994 - Hidden Perils: Delayed Pyogenic Liver Abscess Diagnosis Leading to Severe Endogenous Endophthalmitis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
