Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3080 - A Severe Case of Drug-Induced Liver Injury After Ingestion of Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
.jpg)
Priyam Doshi, MD, MPH
Western Reserve Hospital
Cuyahoga Falls, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Priyam Doshi, MD, MPH1, Suhita Chandrasekharuni, DO2, Nivedita Doshi, MD3, Corey Sievers, MD1
1Western Reserve Hospital, Cuyahoga Falls, OH; 2Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine, Cuyahoga Falls, OH; 3Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH
Introduction: The antibiotic AC is a combination drug consisting of Amoxicillin, a penicillin, and Clavulanic acid, a beta-lactamase inhibitor. DILI is an adverse drug reaction, known to have an estimated incidence of 14-19 patients per 100,000 out of which 22% are hospitalized. 1 in 100,000 of these develop acute liver failure with 57% of such patients needing liver transplantation.6–9
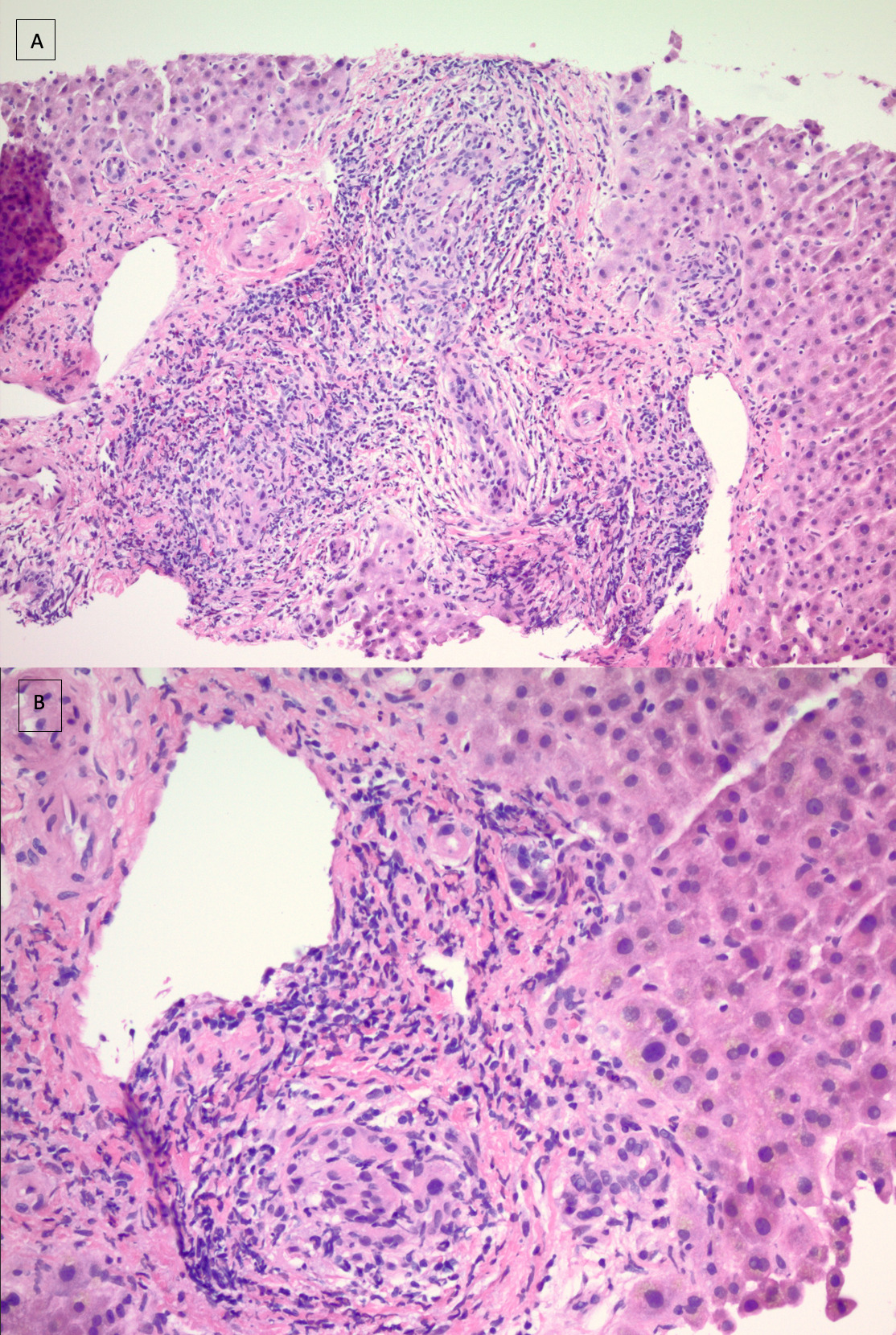
Case Description/Methods: 57-year-old man presented to the hospital with a 3-day history of dark urine and gray stools. He contracted an URTI after a recent travel on a Caribbean cruise 1 month ago, received a 3-day course of AC prescribed at an urgent care. Initial laboratory examination revealed T. Bil of 11.9, D. Bil 9, ALP 262, ALT 152, AST 80. CT abdomen was normal. CMV, EBV, AMA, ASMA, IgG were normal. The patient was started on fluids with trending of liver enzymes. T.Bil levels reached a high of 15 mg/dL. MRCP showed no have biliary dilation or choledocholithiasis, liver morphology was normal. Liver biopsy showed a cholestatic pattern of injury, raising concerns for an idiosyncratic DILI linked to recent AC use as in Figure 1. GI discharged patient on ursodeoxycholic acid for two weeks. During the follow-up appointments, levels of T. Bil and D. Bil continued to rise, peaking at 23mg/dL and 17.7mg/dL, respectively. It took approximately 6-8 weeks after discharge for the levels to return to normal.
Discussion: Based on our patient's clinical etiology, a case of DILI is very likely. Two distinct etiologies underlie these presentations— hepatic manifestations and immuno-allergic reactions. The onset of hepatotoxicity was noticed within 10 weeks after completing a course of AC.11–13. Histopathology consists mainly of a centrilobular and pan-lobular pattern of cholestasis, occasionally granulomatous.14–16 Younger patients and a shorter AC duration were associated with cytolytic damage, while older patients, aged above 55 years, and longer duration were linked to cholestatic/mixed damage.11 In most cases without a prior history of AC use, the onset of jaundice from the administration of AC had a median period longer than 17 days, with occurrence as early as 6 days in patients with prior drug use, reflecting possible pre-sensitization.12 Some patients with severe jaundice have benefited from corticosteroid and ursodeoxycholic acid therapy.13,18 It should be noted that even though re-exposure does not always lead to DILI, the consequences are serious with mortality as high as up to 13% of cases.10
Disclosures:
Priyam Doshi, MD, MPH1, Suhita Chandrasekharuni, DO2, Nivedita Doshi, MD3, Corey Sievers, MD1. P3080 - A Severe Case of Drug-Induced Liver Injury After Ingestion of Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Western Reserve Hospital, Cuyahoga Falls, OH; 2Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine, Cuyahoga Falls, OH; 3Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH
Introduction: The antibiotic AC is a combination drug consisting of Amoxicillin, a penicillin, and Clavulanic acid, a beta-lactamase inhibitor. DILI is an adverse drug reaction, known to have an estimated incidence of 14-19 patients per 100,000 out of which 22% are hospitalized. 1 in 100,000 of these develop acute liver failure with 57% of such patients needing liver transplantation.6–9
Case Description/Methods: 57-year-old man presented to the hospital with a 3-day history of dark urine and gray stools. He contracted an URTI after a recent travel on a Caribbean cruise 1 month ago, received a 3-day course of AC prescribed at an urgent care. Initial laboratory examination revealed T. Bil of 11.9, D. Bil 9, ALP 262, ALT 152, AST 80. CT abdomen was normal. CMV, EBV, AMA, ASMA, IgG were normal. The patient was started on fluids with trending of liver enzymes. T.Bil levels reached a high of 15 mg/dL. MRCP showed no have biliary dilation or choledocholithiasis, liver morphology was normal. Liver biopsy showed a cholestatic pattern of injury, raising concerns for an idiosyncratic DILI linked to recent AC use as in Figure 1. GI discharged patient on ursodeoxycholic acid for two weeks. During the follow-up appointments, levels of T. Bil and D. Bil continued to rise, peaking at 23mg/dL and 17.7mg/dL, respectively. It took approximately 6-8 weeks after discharge for the levels to return to normal.
Discussion: Based on our patient's clinical etiology, a case of DILI is very likely. Two distinct etiologies underlie these presentations— hepatic manifestations and immuno-allergic reactions. The onset of hepatotoxicity was noticed within 10 weeks after completing a course of AC.11–13. Histopathology consists mainly of a centrilobular and pan-lobular pattern of cholestasis, occasionally granulomatous.14–16 Younger patients and a shorter AC duration were associated with cytolytic damage, while older patients, aged above 55 years, and longer duration were linked to cholestatic/mixed damage.11 In most cases without a prior history of AC use, the onset of jaundice from the administration of AC had a median period longer than 17 days, with occurrence as early as 6 days in patients with prior drug use, reflecting possible pre-sensitization.12 Some patients with severe jaundice have benefited from corticosteroid and ursodeoxycholic acid therapy.13,18 It should be noted that even though re-exposure does not always lead to DILI, the consequences are serious with mortality as high as up to 13% of cases.10

Figure: Figure 1: (A) Liver biopsy shows damage of bile ducts and possible focal granulomatous inflammation (H&E 40x). (B) Involvement of portal areas by predominantly lymphocytic infiltrates with few neutrophils and eosinophils (H&E 200x). H&E, hematoxylin and eosin
Disclosures:
Priyam Doshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suhita Chandrasekharuni indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nivedita Doshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Corey Sievers indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Priyam Doshi, MD, MPH1, Suhita Chandrasekharuni, DO2, Nivedita Doshi, MD3, Corey Sievers, MD1. P3080 - A Severe Case of Drug-Induced Liver Injury After Ingestion of Amoxicillin-Clavulanic Acid, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
