Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3108 - Simultaneous Liver and Kidney Transplant After Over-the-Counter Aspirin Overuse
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Faris Shweikeh, MD
Cleveland Clinic Akron General
Akron, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Neha Sharma, MD1, Naga Venkata Rama Krishna Vura, MD2, Faris Shweikeh, MD3, Anamay N. Sharma, MD4, Raja Chandra Chakinala, MD5, Courtney Thomas, DO2, Carmen Landaverde, MD6
1University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX; 2University of Texas Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX; 3Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH; 4Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, OH; 5Guthrie Robert Packer Hospital, Sayre, PA; 6Texas Liver Institute, Austin, TX
Introduction: Aspirin is one of the most used analgesic and antipyretic medications worldwide after modifying salicylic acid to re-create acetylsalicylic acid in 1897 by German chemist Felix Hoffman. We report a case of a patient receiving a simultaneous liver and kidney (SLK) transplant after consuming excessive amounts of over-the-counter (OTC) Aspirin. There have been no documented cases of patients receiving SLK transplants after an aspirin overdose.
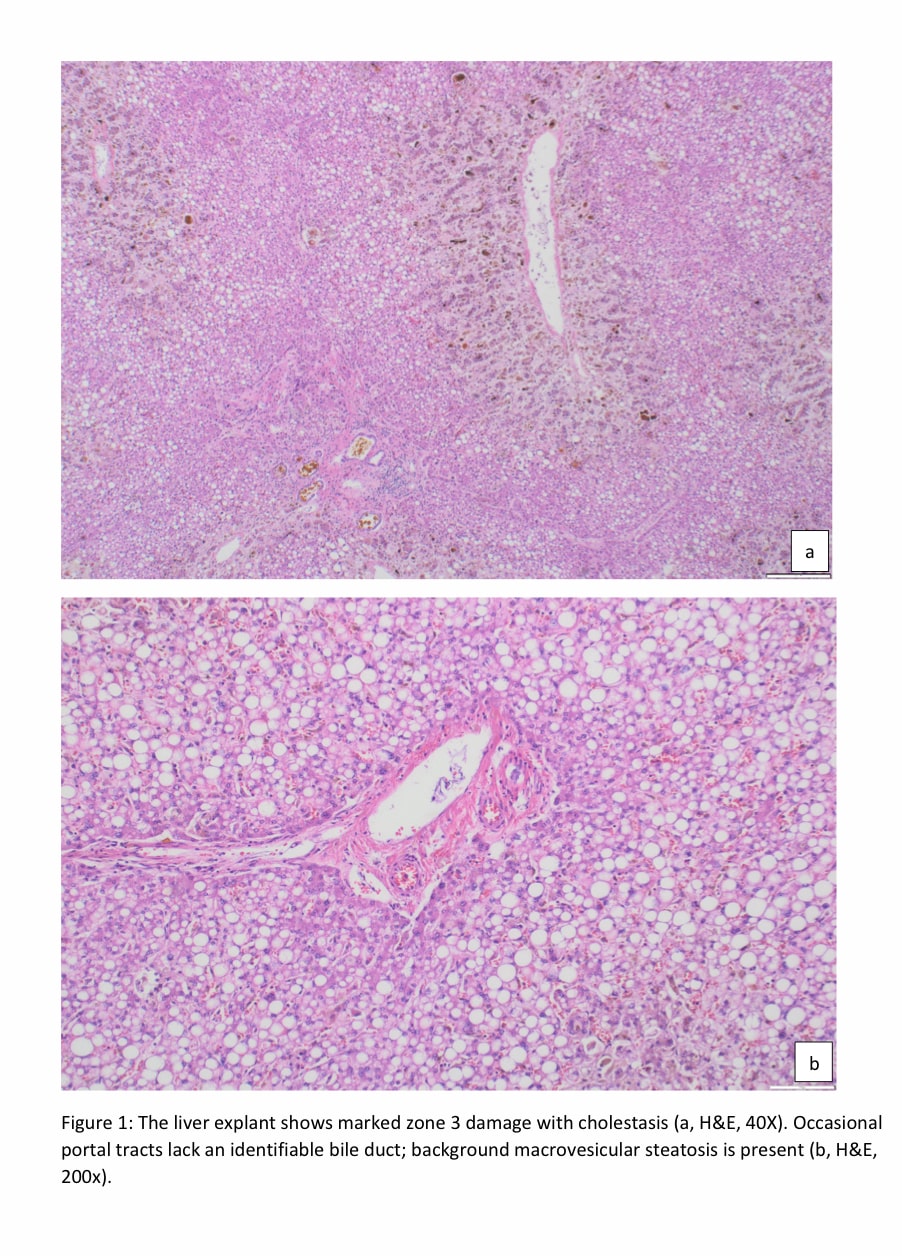
Case Description/Methods: A 27-year-old woman who tested positive for infectious mononucleosis was started on OTC analgesics for pain relief. Over three weeks, she took more than 3 grams of aspirin (500 mg tablets) daily. She developed nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, and bloody stools. Lab tests showed a significant rise in liver enzymes and Creatinine. She was started on hemodialysis (HD), and the workup for viral hepatitis, Wilson's disease, and other autoimmune conditions was negative. Her liver enzymes remained stable and improved for a month, then started to worsen. A liver biopsy showed cholestatic injury, more prominent in zone 3, with marked macrovesicular steatosis. No periductal inflammation, florid duct lesions, granulomas, onion skinning fibrosis, or fibro-obliterative lesions were identified. Marked cholestatic hepatitis in this patient, with a history of NSAID use, is consistent with drug-induced liver injury. She underwent expedited liver/kidney transplant evaluation and eventually received DDLT for subacute liver failure from DILI and DDKT for anuric biopsy-proven ATN requiring HD.
Discussion: The incidence of hepatotoxicity associated with non-narcotic analgesics is low, with an incidence of < 0.1%, but results in 2.2 hospitalizations per 100,000 population per year. OTC analgesics increase the risk of hepatotoxicity and renal toxicity, increasing medical and economic costs. Aspirin causes dose-dependent toxicity and is an intrinsic hepatotoxin. Hepatotoxicity occurs with 1,800 to 3,200 mg daily ( >100mg/kg) and salicylate levels greater than 25 mg/dL. Severe acute toxicity occurs at a dose of 300mg/kg, and a dose of 500 mg/kg is potentially lethal. Hepatocellular injury is the most common, but cholestatic and mixed injury with steatosis and granulomatous changes were reported. Adult Liver transplant candidates who meet the criteria of CKD, AKI, and metabolic disease are eligible for SLK transplant per the Organ Procurement and Transplant Network/United Network for Organ Sharing OPTN/UNOS policy implemented in August 2017.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Neha Sharma, MD1, Naga Venkata Rama Krishna Vura, MD2, Faris Shweikeh, MD3, Anamay N. Sharma, MD4, Raja Chandra Chakinala, MD5, Courtney Thomas, DO2, Carmen Landaverde, MD6. P3108 - Simultaneous Liver and Kidney Transplant After Over-the-Counter Aspirin Overuse, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX; 2University of Texas Health San Antonio, San Antonio, TX; 3Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH; 4Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, OH; 5Guthrie Robert Packer Hospital, Sayre, PA; 6Texas Liver Institute, Austin, TX
Introduction: Aspirin is one of the most used analgesic and antipyretic medications worldwide after modifying salicylic acid to re-create acetylsalicylic acid in 1897 by German chemist Felix Hoffman. We report a case of a patient receiving a simultaneous liver and kidney (SLK) transplant after consuming excessive amounts of over-the-counter (OTC) Aspirin. There have been no documented cases of patients receiving SLK transplants after an aspirin overdose.
Case Description/Methods: A 27-year-old woman who tested positive for infectious mononucleosis was started on OTC analgesics for pain relief. Over three weeks, she took more than 3 grams of aspirin (500 mg tablets) daily. She developed nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, and bloody stools. Lab tests showed a significant rise in liver enzymes and Creatinine. She was started on hemodialysis (HD), and the workup for viral hepatitis, Wilson's disease, and other autoimmune conditions was negative. Her liver enzymes remained stable and improved for a month, then started to worsen. A liver biopsy showed cholestatic injury, more prominent in zone 3, with marked macrovesicular steatosis. No periductal inflammation, florid duct lesions, granulomas, onion skinning fibrosis, or fibro-obliterative lesions were identified. Marked cholestatic hepatitis in this patient, with a history of NSAID use, is consistent with drug-induced liver injury. She underwent expedited liver/kidney transplant evaluation and eventually received DDLT for subacute liver failure from DILI and DDKT for anuric biopsy-proven ATN requiring HD.
Discussion: The incidence of hepatotoxicity associated with non-narcotic analgesics is low, with an incidence of < 0.1%, but results in 2.2 hospitalizations per 100,000 population per year. OTC analgesics increase the risk of hepatotoxicity and renal toxicity, increasing medical and economic costs. Aspirin causes dose-dependent toxicity and is an intrinsic hepatotoxin. Hepatotoxicity occurs with 1,800 to 3,200 mg daily ( >100mg/kg) and salicylate levels greater than 25 mg/dL. Severe acute toxicity occurs at a dose of 300mg/kg, and a dose of 500 mg/kg is potentially lethal. Hepatocellular injury is the most common, but cholestatic and mixed injury with steatosis and granulomatous changes were reported. Adult Liver transplant candidates who meet the criteria of CKD, AKI, and metabolic disease are eligible for SLK transplant per the Organ Procurement and Transplant Network/United Network for Organ Sharing OPTN/UNOS policy implemented in August 2017.

Figure: Figure 1: The liver explant shows marked zone 3 damage with cholestasis (a, H&E, 40X). Occasional portal tracts lack an identifiable bile duct; background macrovesicular steatosis is present (b, H&E, 200x).
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Neha Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Naga Venkata Rama Krishna Vura indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faris Shweikeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anamay Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raja Chandra Chakinala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Courtney Thomas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carmen Landaverde indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neha Sharma, MD1, Naga Venkata Rama Krishna Vura, MD2, Faris Shweikeh, MD3, Anamay N. Sharma, MD4, Raja Chandra Chakinala, MD5, Courtney Thomas, DO2, Carmen Landaverde, MD6. P3108 - Simultaneous Liver and Kidney Transplant After Over-the-Counter Aspirin Overuse, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
