Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3132 - Severe Hyperammonemia and Hepatic Encephalopathy Precipitated by Routine Difelikefalin Administration: A Relatively Unknown Adverse Effect
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
.jpg)
Ruona Ebiai, MD
Ochsner Health Clinic Foundation
New Orleans, LA
Presenting Author(s)
Ruona Ebiai, MD1, Jasmine McNair, MD1, Ian Tobal, DO2, Paula Cacioppo, MD1, Adil Memon, MBBS3
1Ochsner Health Clinic Foundation, New Orleans, LA; 2Ochsner Medical Center, Jefferson, LA; 3Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, LA
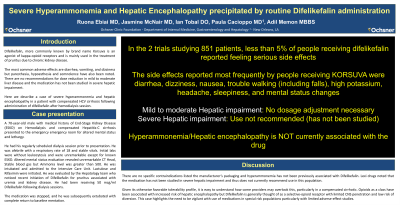
Introduction: Difelikefalin, more commonly known by brand name Korsuva is an agonist of kappa-opioid receptors, and is mainly used in the treatment of pruritus due to chronic kidney disease. The most common adverse effects are diarrhea, vomiting, and dizziness but paresthesia, hypoesthesia and somnolence have also been noted. There are no recommendations for dose reduction in mild to moderate liver disease and the medication has not been studied in severe hepatic impairment. Here we describe a case of severe hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy following administration of difelikefalin after hemodialysis session.
Case Description/Methods: A 70-year-old male with medical history of End-Stage Kidney Disease (ESKD) on Hemodialysis and Hepatitis-C cirrhosis without previous hepatic encephalopathy and had never been on lactulose or rifaximin presented to the emergency emergency room for altered mental status and lethargy. He had his regularly scheduled dialysis session prior to presentation. He was afebrile with a respiratory rate of 18 and stable vitals. Initial labs were without leukocytosis and were unremarkable except for known ESKD. Altered mental status evaluation revealed unremarkable CT Head, Stable blood gas but Ammonia level was greater than 500. He was intubated and admitted to the Intensive Care Unit. Lactulose and Rifaximin were initiated. He was evaluated by the Hepatology team who noticed recent initiation of Difelikefalin for pruritus associated with uremia and kidney disease. He had been receiving 50 mcg/ml Difelikefalin following dialysis sessions. The medication was discontinued and he was subsequently extubated with complete return to baseline mentation.
Discussion: There are no specific contraindications listed the manufacturer’s packaging and hyperammonemia has not been previously associated with Difelikefalin. Lexidrugs noted that the medication has not been studied in severe hepatic impairment and thus does not currently recommend use in this population. Given its otherwise favorable tolerability profile, it is easy to understand how some providers may overlook this. Opioids as a class have been associated with increased risk of hepatic encephalopathy but Difelikefalin is generally thought of as a selective-opioid receptor with limited CNS penetration and low risk of diversion. This case highlights the need to be vigilant with use of medications in special risk populations particularly with limited adverse-effect studies.
Disclosures:
Ruona Ebiai, MD1, Jasmine McNair, MD1, Ian Tobal, DO2, Paula Cacioppo, MD1, Adil Memon, MBBS3. P3132 - Severe Hyperammonemia and Hepatic Encephalopathy Precipitated by Routine Difelikefalin Administration: A Relatively Unknown Adverse Effect, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Ochsner Health Clinic Foundation, New Orleans, LA; 2Ochsner Medical Center, Jefferson, LA; 3Ochsner Medical Center, New Orleans, LA
Introduction: Difelikefalin, more commonly known by brand name Korsuva is an agonist of kappa-opioid receptors, and is mainly used in the treatment of pruritus due to chronic kidney disease. The most common adverse effects are diarrhea, vomiting, and dizziness but paresthesia, hypoesthesia and somnolence have also been noted. There are no recommendations for dose reduction in mild to moderate liver disease and the medication has not been studied in severe hepatic impairment. Here we describe a case of severe hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy following administration of difelikefalin after hemodialysis session.
Case Description/Methods: A 70-year-old male with medical history of End-Stage Kidney Disease (ESKD) on Hemodialysis and Hepatitis-C cirrhosis without previous hepatic encephalopathy and had never been on lactulose or rifaximin presented to the emergency emergency room for altered mental status and lethargy. He had his regularly scheduled dialysis session prior to presentation. He was afebrile with a respiratory rate of 18 and stable vitals. Initial labs were without leukocytosis and were unremarkable except for known ESKD. Altered mental status evaluation revealed unremarkable CT Head, Stable blood gas but Ammonia level was greater than 500. He was intubated and admitted to the Intensive Care Unit. Lactulose and Rifaximin were initiated. He was evaluated by the Hepatology team who noticed recent initiation of Difelikefalin for pruritus associated with uremia and kidney disease. He had been receiving 50 mcg/ml Difelikefalin following dialysis sessions. The medication was discontinued and he was subsequently extubated with complete return to baseline mentation.
Discussion: There are no specific contraindications listed the manufacturer’s packaging and hyperammonemia has not been previously associated with Difelikefalin. Lexidrugs noted that the medication has not been studied in severe hepatic impairment and thus does not currently recommend use in this population. Given its otherwise favorable tolerability profile, it is easy to understand how some providers may overlook this. Opioids as a class have been associated with increased risk of hepatic encephalopathy but Difelikefalin is generally thought of as a selective-opioid receptor with limited CNS penetration and low risk of diversion. This case highlights the need to be vigilant with use of medications in special risk populations particularly with limited adverse-effect studies.
Disclosures:
Ruona Ebiai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jasmine McNair indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ian Tobal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paula Cacioppo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adil Memon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ruona Ebiai, MD1, Jasmine McNair, MD1, Ian Tobal, DO2, Paula Cacioppo, MD1, Adil Memon, MBBS3. P3132 - Severe Hyperammonemia and Hepatic Encephalopathy Precipitated by Routine Difelikefalin Administration: A Relatively Unknown Adverse Effect, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
