Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3141 - Leptospirosis as a Cause of Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia in an Urban Community Hospital
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Faryal Altaf, MD
BronxCare Health System
Bronx, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Haider Ghazanfar, MD1, Faryal Altaf, MD1, Ali Ghazanfar, MBBS2, Srikaran Bojja, MD1, Abhilasha Jyala, MD1, Elona Shehi, MD1
1BronxCare Health System, Bronx, NY; 2Fauji Foundation Hospital, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: The global incidence of leptospirosis is around 1.9 cases per 100,000 population. Leptospirosis is a zoonotic disease, and its presentation can vary from mild influenza-like illness to multiorgan failure and pulmonary hemorrhage. Leptospirosis can spread to humans through contact with water or soil contaminated by urine or body fluids from infected animals or by directly touching body fluids from an infected animal. There have been a few cases of leptospirosis reported in homeless people in New York City due to contact with rat urine.
Case Description/Methods: We present a case of a 48-year-old homeless man who presented to the Emergency Department with complaints of fatigue, weight loss, and jaundice for the past 2 weeks. The patient denied any past medical or surgical history. His social history was significant for smoking and marijuana use. His physical examination was significant for hepatomegaly and jaundice. His initial laboratory workup was significant for conjugated hyperbilirubinemia with transaminitis, thrombocytopenia, and elevated creatinine. Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography did not show any biliary abnormality. The hepatitis, autoimmune, and metabolic workup was unremarkable. The patient tested positive for Leptospirosis and was started on Ceftriaxone. He developed a diffuse rash on the body after 3 days on ceftriaxone, and the antibiotic was switched to intravenous doxycycline. Following the initiation of antibiotic therapy, the patient's bilirubin levels showed notable improvement, and his liver chemistries were fully resolved within one month.
Discussion: There has been a significant increase in the number of Leptospirosis cases. In 2023, New York State reported a record 24 cases, surpassing any previous year's count as per the NYC Health Department. Although Leptospirosis is more common in rural areas and developing countries, its prevalence in urban and developed countries has increased with time. Physicians need to include leptospirosis in their differential diagnosis in high-risk patients presenting with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Our case highlights the importance of early diagnosis and prompt treatment for these patients.
Disclosures:
Haider Ghazanfar, MD1, Faryal Altaf, MD1, Ali Ghazanfar, MBBS2, Srikaran Bojja, MD1, Abhilasha Jyala, MD1, Elona Shehi, MD1. P3141 - Leptospirosis as a Cause of Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia in an Urban Community Hospital, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1BronxCare Health System, Bronx, NY; 2Fauji Foundation Hospital, Rawalpindi, Punjab, Pakistan
Introduction: The global incidence of leptospirosis is around 1.9 cases per 100,000 population. Leptospirosis is a zoonotic disease, and its presentation can vary from mild influenza-like illness to multiorgan failure and pulmonary hemorrhage. Leptospirosis can spread to humans through contact with water or soil contaminated by urine or body fluids from infected animals or by directly touching body fluids from an infected animal. There have been a few cases of leptospirosis reported in homeless people in New York City due to contact with rat urine.
Case Description/Methods: We present a case of a 48-year-old homeless man who presented to the Emergency Department with complaints of fatigue, weight loss, and jaundice for the past 2 weeks. The patient denied any past medical or surgical history. His social history was significant for smoking and marijuana use. His physical examination was significant for hepatomegaly and jaundice. His initial laboratory workup was significant for conjugated hyperbilirubinemia with transaminitis, thrombocytopenia, and elevated creatinine. Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography did not show any biliary abnormality. The hepatitis, autoimmune, and metabolic workup was unremarkable. The patient tested positive for Leptospirosis and was started on Ceftriaxone. He developed a diffuse rash on the body after 3 days on ceftriaxone, and the antibiotic was switched to intravenous doxycycline. Following the initiation of antibiotic therapy, the patient's bilirubin levels showed notable improvement, and his liver chemistries were fully resolved within one month.
Discussion: There has been a significant increase in the number of Leptospirosis cases. In 2023, New York State reported a record 24 cases, surpassing any previous year's count as per the NYC Health Department. Although Leptospirosis is more common in rural areas and developing countries, its prevalence in urban and developed countries has increased with time. Physicians need to include leptospirosis in their differential diagnosis in high-risk patients presenting with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Our case highlights the importance of early diagnosis and prompt treatment for these patients.

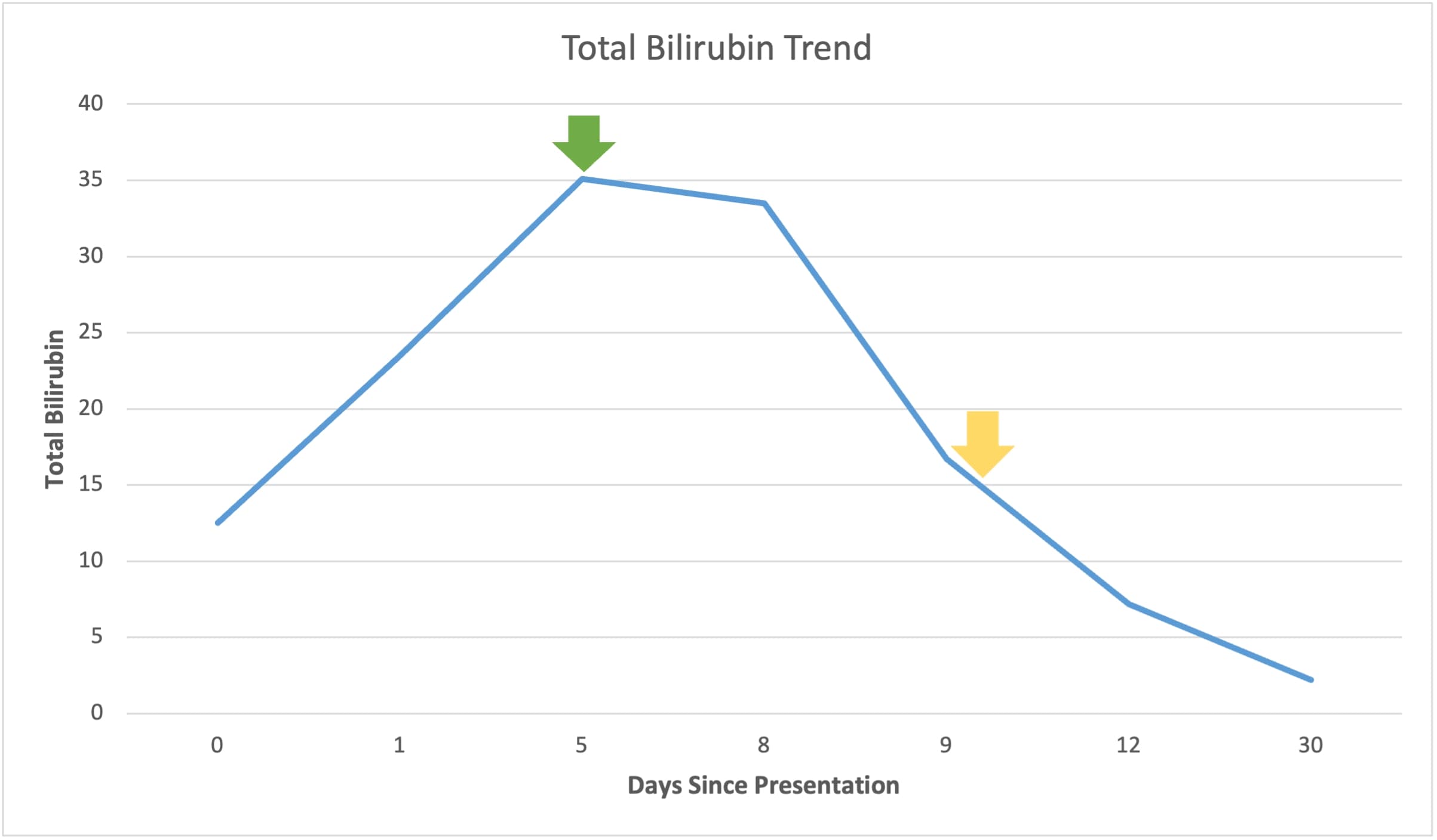
Figure: Total Bilirubin Trend Since Presentation. The Green Arrow indicates the start day for Ceftriaxone, and the Yellow Arrow indicates the start day for Doxycycline.
Disclosures:
Haider Ghazanfar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faryal Altaf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ali Ghazanfar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Srikaran Bojja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhilasha Jyala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elona Shehi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Haider Ghazanfar, MD1, Faryal Altaf, MD1, Ali Ghazanfar, MBBS2, Srikaran Bojja, MD1, Abhilasha Jyala, MD1, Elona Shehi, MD1. P3141 - Leptospirosis as a Cause of Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia in an Urban Community Hospital, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
