Monday Poster Session
Category: Obesity
P3169 - Assessing Longer Term Efficacy of Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) on Glycemic Control and Weight Loss: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
- SC
Sahithi Chinnam, DO
University of Toledo
Toledo, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Sahithi Chinnam, DO1, Sudheer Dhoop, MD1, Rayna Patel, MD2, Zohaib Ahmed, MD2, Yaseen Alastal, MD2
1University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 2University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) is a an endoscopic procedure involving thermal ablation of mucosal tissue to result in subsequent mucosal regeneration. This produces effects such as improved metabolic effects. We aim to do meta-analysis to assess DMR effect on metabolic outcomes including HBa1c and weight loss over longer duration.
Methods: We performed a search in the databases of PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Web of Science from inception through November 25th, 2023. Four manuscripts from three-open labels, single arm studies and a randomized controlled trial were included, all only evaluating the Revita procedure device. The primary outcome was mean weight loss at 12 months after DMR and the secondary outcomes were mean change in Hba1c at 12 months as well as mean change of HBa1c at 6 months after DMR. The random-effects model was used to calculate the mean differences (MDs) and confidence intervals (CI). A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Heterogeneity was assessed using the Higgins I2 index. We used tabular and graphical displays in Review Manager (RevMan).
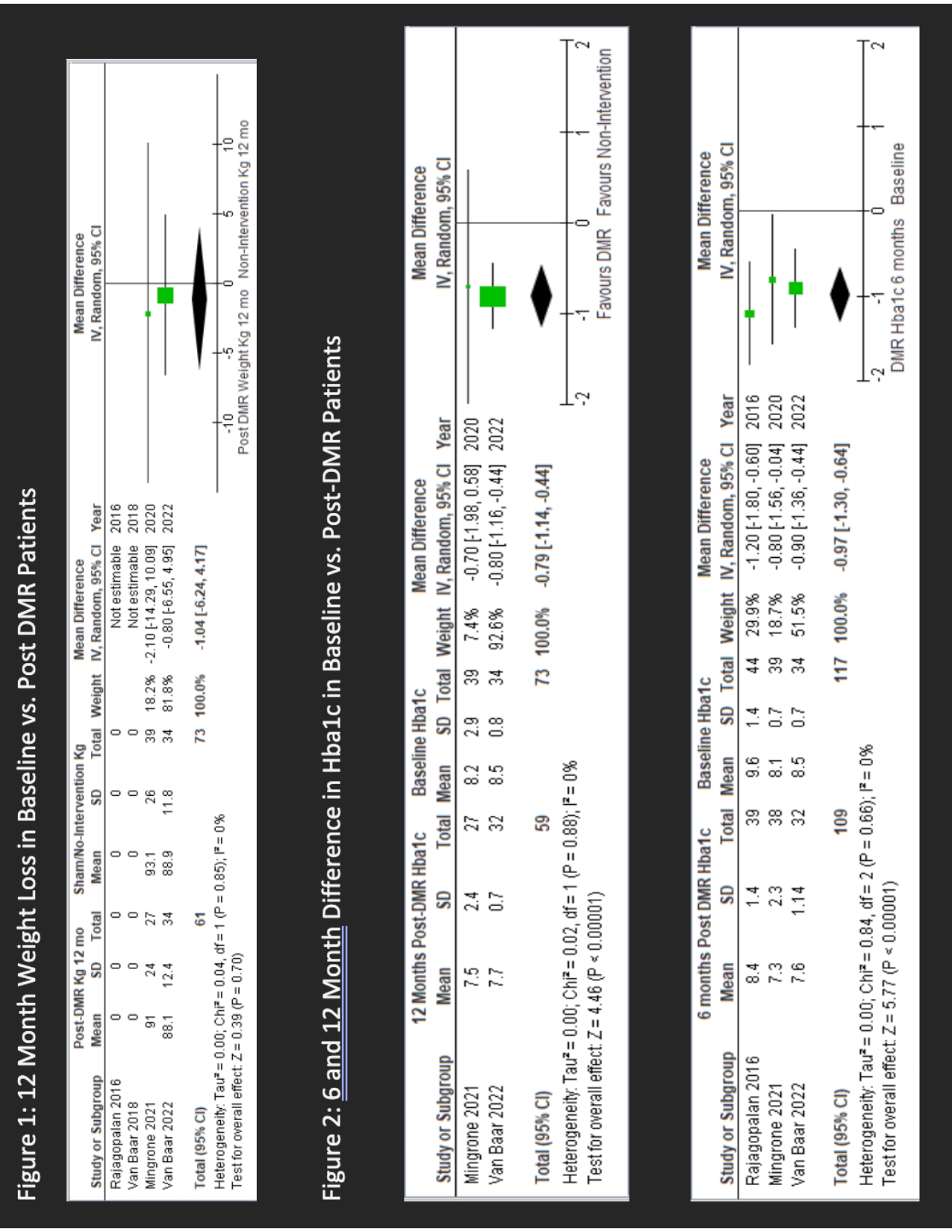
Results: Four studies including 1 non-randomized single-center study, 2 prospective studies, and 1 RCT were included for a total of 145 patients were included in this meta-analysis. 2 trials recorded the weight loss at 12 months, and did not demonstrate a statistically significant difference in weight change from baseline after 12 months DMR (MD: -1.04, 95% CI: -6.24 to 4.17, p=0.70, I2 =0). In terms of the change in HbA1c, 2 trials recorded mean HBa1c change after 12 months and demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in mean Hba1c in the DMR group relative to a screening baseline (MD: -0.79, 95% CI: -1.14 to -0.44, p< 0.01, I2 =0) and 2 trials recorded HBa1c at 6 months and demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in mean Hba1c in the DMR group relative to baseline (MD: -0.97,95% CI:-1.30 to -0.64,p< 0.01, I2 =0)
Discussion: Our meta-analysis demonstrates that there was no significant reduction in mean weight (kg) at 12 months in the post DMR group relative to the baseline group, but there was a statistically significant reduction of Hba1c at 6 months, maintained at 12 months. This suggests that the DMR procedure may not result in long-term weight loss but can result in long term reductions in Hba1c levels and improvement in glycemic control. Future experimental studies and randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm our findings.
Disclosures:
Sahithi Chinnam, DO1, Sudheer Dhoop, MD1, Rayna Patel, MD2, Zohaib Ahmed, MD2, Yaseen Alastal, MD2. P3169 - Assessing Longer Term Efficacy of Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) on Glycemic Control and Weight Loss: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 2University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH
Introduction: Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) is a an endoscopic procedure involving thermal ablation of mucosal tissue to result in subsequent mucosal regeneration. This produces effects such as improved metabolic effects. We aim to do meta-analysis to assess DMR effect on metabolic outcomes including HBa1c and weight loss over longer duration.
Methods: We performed a search in the databases of PubMed/MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Web of Science from inception through November 25th, 2023. Four manuscripts from three-open labels, single arm studies and a randomized controlled trial were included, all only evaluating the Revita procedure device. The primary outcome was mean weight loss at 12 months after DMR and the secondary outcomes were mean change in Hba1c at 12 months as well as mean change of HBa1c at 6 months after DMR. The random-effects model was used to calculate the mean differences (MDs) and confidence intervals (CI). A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Heterogeneity was assessed using the Higgins I2 index. We used tabular and graphical displays in Review Manager (RevMan).
Results: Four studies including 1 non-randomized single-center study, 2 prospective studies, and 1 RCT were included for a total of 145 patients were included in this meta-analysis. 2 trials recorded the weight loss at 12 months, and did not demonstrate a statistically significant difference in weight change from baseline after 12 months DMR (MD: -1.04, 95% CI: -6.24 to 4.17, p=0.70, I2 =0). In terms of the change in HbA1c, 2 trials recorded mean HBa1c change after 12 months and demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in mean Hba1c in the DMR group relative to a screening baseline (MD: -0.79, 95% CI: -1.14 to -0.44, p< 0.01, I2 =0) and 2 trials recorded HBa1c at 6 months and demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in mean Hba1c in the DMR group relative to baseline (MD: -0.97,95% CI:-1.30 to -0.64,p< 0.01, I2 =0)
Discussion: Our meta-analysis demonstrates that there was no significant reduction in mean weight (kg) at 12 months in the post DMR group relative to the baseline group, but there was a statistically significant reduction of Hba1c at 6 months, maintained at 12 months. This suggests that the DMR procedure may not result in long-term weight loss but can result in long term reductions in Hba1c levels and improvement in glycemic control. Future experimental studies and randomized controlled trials are needed to confirm our findings.

Figure: Comparing weight loss and Hba1c in baseline versus post DMR patients
Disclosures:
Sahithi Chinnam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sudheer Dhoop indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rayna Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zohaib Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yaseen Alastal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sahithi Chinnam, DO1, Sudheer Dhoop, MD1, Rayna Patel, MD2, Zohaib Ahmed, MD2, Yaseen Alastal, MD2. P3169 - Assessing Longer Term Efficacy of Duodenal Mucosal Resurfacing (DMR) on Glycemic Control and Weight Loss: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
