Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach
P3324 - Predictive Value of Gastric Myoelectrical Activity in Patient Satisfaction after Gastric Per-Oral Myotomy
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- SK
Sulman Khan, DO
Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Sulman Khan, DO1, Jack Loesch, BA1, Eyad Hamza, MS1, Justin M. Foreman, DO2, Matthew Allemang, MD1, Andrew D. Grubic, DO1, Michael Cline, DO3
1Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 2Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Mayfield Heights, OH; 3Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Gastric per-oral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) has emerged as a promising approach for managing refractory gastroparesis. Factors predicting its success remain uncertain. Our study aims to investigate whether features of electrogastrography (EGG) can serve as predictive markers for patient outcomes following G-POEM. By analyzing the relationship between specific gastric myoelectrical activity (GMA) subgroups and patient symptoms post-G-POEM, we seek to understand factors influencing the therapeutic efficacy of G-POEM in treating gastroparesis.
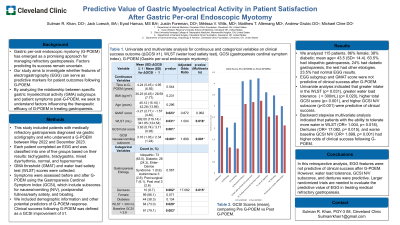
Methods: This study included patients with medically refractory gastroparesis diagnosed via gastric scintigraphy and who underwent a G-POEM between May 2022 and December 2023. Each patient completed an EGG and was classified into one of five groups based on their results: tachygastria, bradygastria, mixed dysrhythmia, normal, and hypernormal. GMA threshold (GMAT) and water load satiety test (WLST) scores were collected. Symptoms were assessed before and after G-POEM using the Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI), which include subscores for nausea/vomiting (N/V), postprandial fullness/early satiety, and bloating. We included demographic information and other potential predictors of G-POEM response. Clinical success following G-POEM was defined as a GCSI improvement of ≥1.
Results: We analyzed 130 patients. 85.4% female; 36% diabetic; mean age= 43.7 (SD= 14.8). 64.6% had idiopathic gastroparesis, 23.1% had diabetic gastroparesis, the rest had other etiologies. 24.6% had normal EGG results. EGG subgroup and GMAT score were not predictive of clinical success after G-POEM. Univariate analysis indicated that greater intake in the WLST (p= 0.049), greater water load tolerance ( > 300mL) (p= 0.028), higher total GCSI score (p= 0.006), and higher GCSI N/V subscore (p= 0.003) were predictive of clinical success. Backward stepwise multivariate analysis indicated that patients with the ability to tolerate more water in WLST (OR= 1.004, p= 0.019), less time between G-POEM and the follow-up GCSI (OR= 0.993, p= 0.038), and worse baseline GCSI N/V (OR= 1.880, p< 0.001) had higher odds of clinical success following G-POEM.
Discussion: In this retrospective analysis, EGG features were not predictive of clinical success after G-POEM. However, water load tolerance, GCSI N/V subscores, and time between G-POEM and GCSI were predictive. Larger randomized trials are needed to evaluate the predictive value of EGG in treating medical refractory gastroparesis.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Sulman Khan, DO1, Jack Loesch, BA1, Eyad Hamza, MS1, Justin M. Foreman, DO2, Matthew Allemang, MD1, Andrew D. Grubic, DO1, Michael Cline, DO3. P3324 - Predictive Value of Gastric Myoelectrical Activity in Patient Satisfaction after Gastric Per-Oral Myotomy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Sulman Khan, DO1, Jack Loesch, BA1, Eyad Hamza, MS1, Justin M. Foreman, DO2, Matthew Allemang, MD1, Andrew D. Grubic, DO1, Michael Cline, DO3
1Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 2Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Mayfield Heights, OH; 3Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Gastric per-oral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) has emerged as a promising approach for managing refractory gastroparesis. Factors predicting its success remain uncertain. Our study aims to investigate whether features of electrogastrography (EGG) can serve as predictive markers for patient outcomes following G-POEM. By analyzing the relationship between specific gastric myoelectrical activity (GMA) subgroups and patient symptoms post-G-POEM, we seek to understand factors influencing the therapeutic efficacy of G-POEM in treating gastroparesis.
Methods: This study included patients with medically refractory gastroparesis diagnosed via gastric scintigraphy and who underwent a G-POEM between May 2022 and December 2023. Each patient completed an EGG and was classified into one of five groups based on their results: tachygastria, bradygastria, mixed dysrhythmia, normal, and hypernormal. GMA threshold (GMAT) and water load satiety test (WLST) scores were collected. Symptoms were assessed before and after G-POEM using the Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index (GCSI), which include subscores for nausea/vomiting (N/V), postprandial fullness/early satiety, and bloating. We included demographic information and other potential predictors of G-POEM response. Clinical success following G-POEM was defined as a GCSI improvement of ≥1.
Results: We analyzed 130 patients. 85.4% female; 36% diabetic; mean age= 43.7 (SD= 14.8). 64.6% had idiopathic gastroparesis, 23.1% had diabetic gastroparesis, the rest had other etiologies. 24.6% had normal EGG results. EGG subgroup and GMAT score were not predictive of clinical success after G-POEM. Univariate analysis indicated that greater intake in the WLST (p= 0.049), greater water load tolerance ( > 300mL) (p= 0.028), higher total GCSI score (p= 0.006), and higher GCSI N/V subscore (p= 0.003) were predictive of clinical success. Backward stepwise multivariate analysis indicated that patients with the ability to tolerate more water in WLST (OR= 1.004, p= 0.019), less time between G-POEM and the follow-up GCSI (OR= 0.993, p= 0.038), and worse baseline GCSI N/V (OR= 1.880, p< 0.001) had higher odds of clinical success following G-POEM.
Discussion: In this retrospective analysis, EGG features were not predictive of clinical success after G-POEM. However, water load tolerance, GCSI N/V subscores, and time between G-POEM and GCSI were predictive. Larger randomized trials are needed to evaluate the predictive value of EGG in treating medical refractory gastroparesis.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Sulman Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jack Loesch: Eli Lilly and Company – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Eyad Hamza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Justin Foreman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Allemang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Grubic indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Cline indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sulman Khan, DO1, Jack Loesch, BA1, Eyad Hamza, MS1, Justin M. Foreman, DO2, Matthew Allemang, MD1, Andrew D. Grubic, DO1, Michael Cline, DO3. P3324 - Predictive Value of Gastric Myoelectrical Activity in Patient Satisfaction after Gastric Per-Oral Myotomy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

