Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P3454 - Impact of Novel Advanced Therapies on Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Patients With Comorbid Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Zehra Naseem, MD
Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Sarah Khan, MD1, Zehra Naseem, MD1, Mohamed Tausif Siddiqui, MD2, Laura Sahyoun, MD3, Dana J. Lukin, MD4, Muyiwa Awoniyi, MD2, Florian Rieder, MD5, Katherine Falloon, MD6
1Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 2Digestive Disease Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 3New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 4Jill Roberts Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, New York Presbyterian Hospital-Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY; 5Digestive Diseases and Surgery Institute; Lerner Research Institute, Program for Global Translational Inflammatory Bowel Diseases; Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 6Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Shaker Heights, OH
Introduction: Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is an idiopathic stricturing biliary disease affecting 1-16/100k person-years linked with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Although there are existing studies on lack of liver response to biological agents like infliximab and vedolizumab, information on new advanced therapies and their effects on liver outcomes is sparse for PSC. This study aims to investigate the safety and clinical outcomes of novel therapies for IBD in PSC-IBD patients, comparing traditional treatments (anti-TNF agents, vedolizumab) to newer therapies (ustekinumab, tofacitinib, and upadacitinib).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study (1/2009-12/2022) assessing the impact of novel therapies (ustekinumab, tofacitinib, upadacitinib) compared to traditional IBD medications (vedolizumab, anti-TNF agents) on the clinical course of patients with PSC-IBD. We analyzed trends in biochemical tests (Table 1), in validated Mayo and UK-PSC scores, and in development/worsening of advanced liver fibrosis (on fibroscan) at the time of drug initiation and after 6-16 weeks of follow-up. Adverse events were also documented. Data were summarized using means (continuous variables) and percentages (categorical variables).
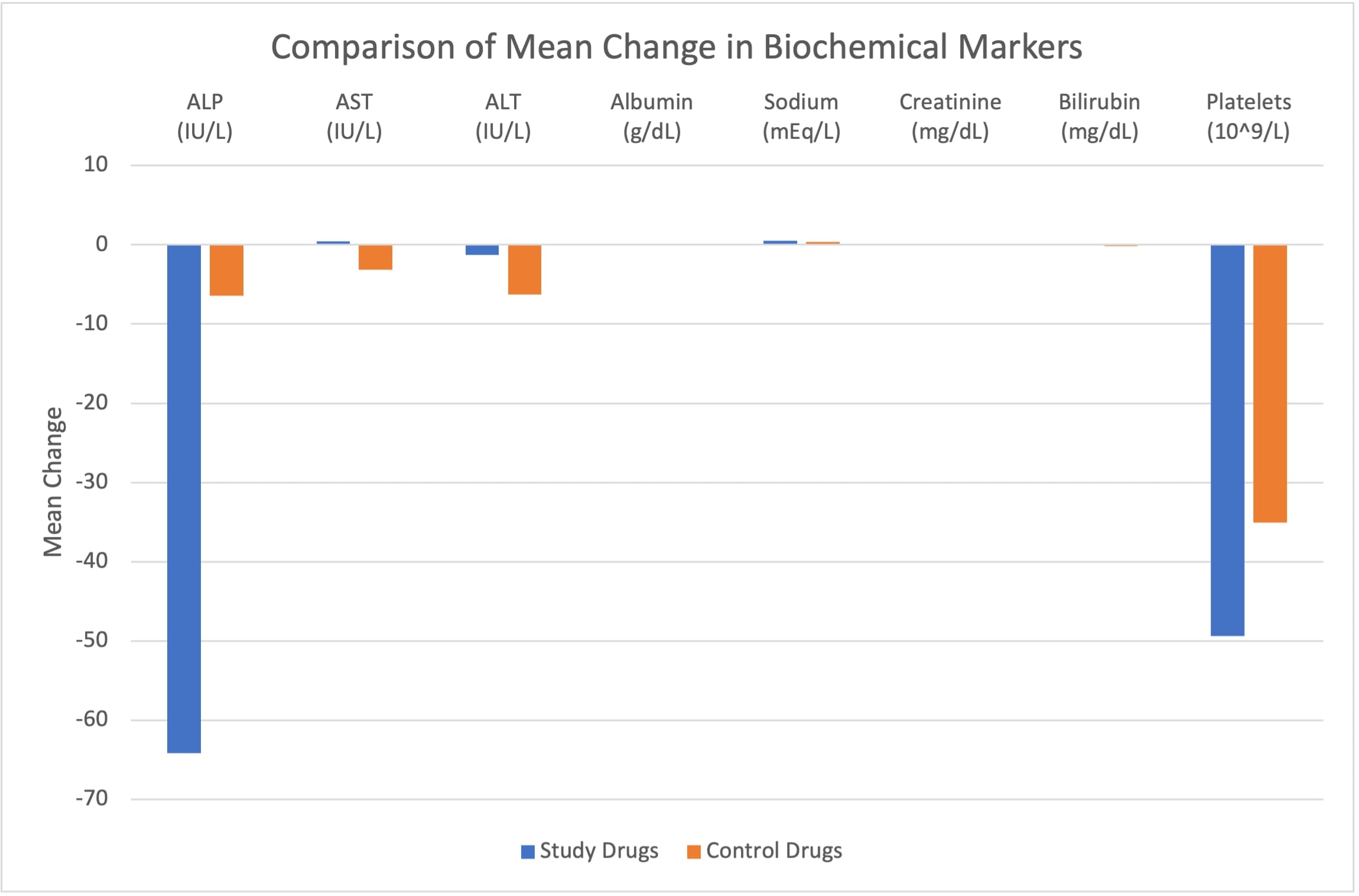
Results: Among 104 PSC-IBD patients, 49 received study drugs (42: ustekinumab, 4: tofacitinib, and 3: upadacitinib) and 55 received control drugs (14: vedolizumab and 41: anti-TNF agents). Age was the only demographic variable that was significant between the two cohorts (p=0.04) (Table 1). There was no statistically significant change in biochemical parameters between groups, though the study group showed the largest mean decrease in alkaline phosphatase compared to the control group (-64.16 vs. -6.41, p = 0.20) (Figure 1). A statistically significant improvement in the UK-PSC score was observed in the study group compared to the control group (-0.93 vs. 0.13; p = 0.02). More patients on control drugs had development/worsening of advanced liver fibrosis during the study (not statistically significant between the cohorts). The incidence of adverse events (decompensated cirrhosis, hepatotoxicity, and cholangiocarcinoma) was similar between the two cohorts. However, a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving study drugs experienced improvement in pruritus compared to controls (p < 0.001).
Discussion: Our findings support statistically significant improvement in PSC severity score and pruritis with novel advanced therapies as compared to traditional IBD therapies.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Sarah Khan, MD1, Zehra Naseem, MD1, Mohamed Tausif Siddiqui, MD2, Laura Sahyoun, MD3, Dana J. Lukin, MD4, Muyiwa Awoniyi, MD2, Florian Rieder, MD5, Katherine Falloon, MD6. P3454 - Impact of Novel Advanced Therapies on Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Patients With Comorbid Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 2Digestive Disease Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 3New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY; 4Jill Roberts Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease, New York Presbyterian Hospital-Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY; 5Digestive Diseases and Surgery Institute; Lerner Research Institute, Program for Global Translational Inflammatory Bowel Diseases; Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 6Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Shaker Heights, OH
Introduction: Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is an idiopathic stricturing biliary disease affecting 1-16/100k person-years linked with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Although there are existing studies on lack of liver response to biological agents like infliximab and vedolizumab, information on new advanced therapies and their effects on liver outcomes is sparse for PSC. This study aims to investigate the safety and clinical outcomes of novel therapies for IBD in PSC-IBD patients, comparing traditional treatments (anti-TNF agents, vedolizumab) to newer therapies (ustekinumab, tofacitinib, and upadacitinib).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study (1/2009-12/2022) assessing the impact of novel therapies (ustekinumab, tofacitinib, upadacitinib) compared to traditional IBD medications (vedolizumab, anti-TNF agents) on the clinical course of patients with PSC-IBD. We analyzed trends in biochemical tests (Table 1), in validated Mayo and UK-PSC scores, and in development/worsening of advanced liver fibrosis (on fibroscan) at the time of drug initiation and after 6-16 weeks of follow-up. Adverse events were also documented. Data were summarized using means (continuous variables) and percentages (categorical variables).
Results: Among 104 PSC-IBD patients, 49 received study drugs (42: ustekinumab, 4: tofacitinib, and 3: upadacitinib) and 55 received control drugs (14: vedolizumab and 41: anti-TNF agents). Age was the only demographic variable that was significant between the two cohorts (p=0.04) (Table 1). There was no statistically significant change in biochemical parameters between groups, though the study group showed the largest mean decrease in alkaline phosphatase compared to the control group (-64.16 vs. -6.41, p = 0.20) (Figure 1). A statistically significant improvement in the UK-PSC score was observed in the study group compared to the control group (-0.93 vs. 0.13; p = 0.02). More patients on control drugs had development/worsening of advanced liver fibrosis during the study (not statistically significant between the cohorts). The incidence of adverse events (decompensated cirrhosis, hepatotoxicity, and cholangiocarcinoma) was similar between the two cohorts. However, a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving study drugs experienced improvement in pruritus compared to controls (p < 0.001).
Discussion: Our findings support statistically significant improvement in PSC severity score and pruritis with novel advanced therapies as compared to traditional IBD therapies.

Figure: Figure 1: Comparison of mean change in biochemical markers from drug initiation to 6-16 weeks of drug initiation between study and control drugs. ALP: alkaline phosphatase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase. P > 0.05 for all markers.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Sarah Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zehra Naseem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Tausif Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Laura Sahyoun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dana J. Lukin: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. AltruBio – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Magellan Health – Consultant. Palatin Technologies – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Prometheus Laboratories – Consultant. PSI – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support.
Muyiwa Awoniyi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Florian Rieder: 89Bio – Consultant. AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Adiso – Consultant. Adnovate – Consultant. Agomab – Consultant. Allergan – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Arena – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. AstraZeneca – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Bausch & Lomb – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. CDISC – Consultant. Celgene/BMS – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Celltrion – Consultant. Celsius – Consultant. Cowen – Consultant. Eugit – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant. Galmed – Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Gilead – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Gossamer – Consultant. Granite – Consultant. Guidepoint – Consultant. Helmsley – Consultant. Horizon Therapeutics – Consultant. Image Analysis Limited – Consultant. Index Pharma – Consultant. Jannsen – Consultant. Koutif – Consultant. Landos – Consultant. Mestag – Consultant. Metacrine – Consultant. Mirum – Consultant. Mopec – Consultant. Morphic – Consultant. Myka Labs – Consultant. Organovo – Consultant. Origo – Consultant. Palisade Bio – Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Pliant – Consultant. Prometheus Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Receptos – Consultant. RedX – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Samsung – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Sanofi – Consultant. Surmodics – Consultant. Surrozen – Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Techlab – Consultant. Teva – Consultant. Theravance – Consultant. Thetis – Consultant. Trix Bio – Consultant. UCB – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Ysios – Consultant.
Katherine Falloon: Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Pfizer – Grant/Research Support.
Sarah Khan, MD1, Zehra Naseem, MD1, Mohamed Tausif Siddiqui, MD2, Laura Sahyoun, MD3, Dana J. Lukin, MD4, Muyiwa Awoniyi, MD2, Florian Rieder, MD5, Katherine Falloon, MD6. P3454 - Impact of Novel Advanced Therapies on Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Patients With Comorbid Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
