Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P3487 - Risk Factors for High Grade Dysplasia or Pancreatic Cancer in Patients With Mucinous Pancreatic Cystic Lesions
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Stacy Menees, MD
Michigan Medicine
Ann Arbor, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Stacy Menees, MD1, Brian Derstine, MS1, Jiaqi Shi, MD, PhD2, Grace Su, MD1
1Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI; 2University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
Introduction: Improving risk prediction for cancer in mucinous pancreatic cystic lesions (PCL) is urgently needed. Standard qualitative review of imaging is insufficient. Akin to radiomics, analytic morphomics is a novel technology which utilizes high throughput extraction of quantitative imaging data from standard radiologic images. We hypothesize that by using analytic morphomics, we can better predict the likelihood of cancer in routine pre-operative abdominal CT scans
Methods: We performed a retrospective study of patients with a pre-operative CT scan who underwent surgery for a mucinous PCL at the University of Michigan from 01/01/2000 - 11/18/2019. We extracted demographic, clinical history, cyst characteristics, and histologic data. De-identified CT scans were loaded into the morphomics server and analyzed with a blinded, semi-automated process. Univariate and multivariable analysis (MV) were performed utilizing 3-fold cross-validation of variables with a p < 0.05 or a priori selected based on clinical relevance.
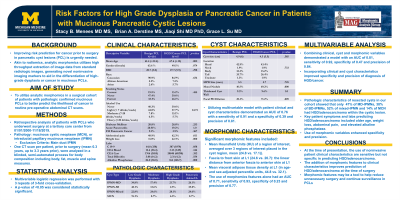
Results: 207 patients were included in this analysis (161 intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm [IPMN], 48 mucinous cystic neoplasm [MCN]). For those with IPMN, 14.2% were main duct, 50.3% side branch and 35 % mixed type (48% female, 66.2 yrs mean age). Patients with MCN were 100% female with a mean age 51.8 yrs. Prevalence of dysplasia and cancer are shown in Table 1. On univariate analysis, the presence of weight loss, higher mean alkaline phosphatase (164.4.1 vs. 86.1), older age (67.5 vs. 61.4), and being an IPMN compared to MCN were associated with risk of cancer at time of surgery. Morphomics variables that were significant on univariate analysis included mean hounsfield units (24.8 vs. 17.1), fascia to front skin at L1 (24.6 vs. 20.7) and mean visceral adipose tissue density at L1 (in age- and sex-adjusted percentile units, 44.8 vs. 32.1). On MV, the use of clinical factors had an AUC of 0.76 with a sensitivity of 0.91 and a specificity of 0.39 and precision of 0.81. The use of morphomics features alone had an AUC of 0.71, sensitivity of 0.93, specificity of 0.23 and precision of 0.77. Combining both clinical and morphomic variables had an AUC of 0.81, sensitivity of 0.92, specificity of 0.47 and precision of 0.84.
Discussion: A combined model of clinical and morphomic features extracted from pre-operative scans had a higher AUC compared to either model alone. Morphomic features may provide clinicians incremental tools to aid in surveillance of mucinous cysts.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Stacy Menees, MD1, Brian Derstine, MS1, Jiaqi Shi, MD, PhD2, Grace Su, MD1. P3487 - Risk Factors for High Grade Dysplasia or Pancreatic Cancer in Patients With Mucinous Pancreatic Cystic Lesions, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI; 2University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
Introduction: Improving risk prediction for cancer in mucinous pancreatic cystic lesions (PCL) is urgently needed. Standard qualitative review of imaging is insufficient. Akin to radiomics, analytic morphomics is a novel technology which utilizes high throughput extraction of quantitative imaging data from standard radiologic images. We hypothesize that by using analytic morphomics, we can better predict the likelihood of cancer in routine pre-operative abdominal CT scans
Methods: We performed a retrospective study of patients with a pre-operative CT scan who underwent surgery for a mucinous PCL at the University of Michigan from 01/01/2000 - 11/18/2019. We extracted demographic, clinical history, cyst characteristics, and histologic data. De-identified CT scans were loaded into the morphomics server and analyzed with a blinded, semi-automated process. Univariate and multivariable analysis (MV) were performed utilizing 3-fold cross-validation of variables with a p < 0.05 or a priori selected based on clinical relevance.
Results: 207 patients were included in this analysis (161 intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm [IPMN], 48 mucinous cystic neoplasm [MCN]). For those with IPMN, 14.2% were main duct, 50.3% side branch and 35 % mixed type (48% female, 66.2 yrs mean age). Patients with MCN were 100% female with a mean age 51.8 yrs. Prevalence of dysplasia and cancer are shown in Table 1. On univariate analysis, the presence of weight loss, higher mean alkaline phosphatase (164.4.1 vs. 86.1), older age (67.5 vs. 61.4), and being an IPMN compared to MCN were associated with risk of cancer at time of surgery. Morphomics variables that were significant on univariate analysis included mean hounsfield units (24.8 vs. 17.1), fascia to front skin at L1 (24.6 vs. 20.7) and mean visceral adipose tissue density at L1 (in age- and sex-adjusted percentile units, 44.8 vs. 32.1). On MV, the use of clinical factors had an AUC of 0.76 with a sensitivity of 0.91 and a specificity of 0.39 and precision of 0.81. The use of morphomics features alone had an AUC of 0.71, sensitivity of 0.93, specificity of 0.23 and precision of 0.77. Combining both clinical and morphomic variables had an AUC of 0.81, sensitivity of 0.92, specificity of 0.47 and precision of 0.84.
Discussion: A combined model of clinical and morphomic features extracted from pre-operative scans had a higher AUC compared to either model alone. Morphomic features may provide clinicians incremental tools to aid in surveillance of mucinous cysts.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Stacy Menees indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brian Derstine indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jiaqi Shi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Grace Su indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stacy Menees, MD1, Brian Derstine, MS1, Jiaqi Shi, MD, PhD2, Grace Su, MD1. P3487 - Risk Factors for High Grade Dysplasia or Pancreatic Cancer in Patients With Mucinous Pancreatic Cystic Lesions, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
