Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P3609 - Biopsy Confirmed IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis - A Cryptogenic Case Report
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ethan Abrishamian, DO
NYC Health + Hospitals/South Brooklyn Health
Brooklyn, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Ethan Abrishamian, DO1, Akil Olliverrie, MD1, Jarin Prasa, MD1, Syed Karim, DO1, Jingwei Ren, 2
1NYC Health + Hospitals/South Brooklyn Health, Brooklyn, NY; 2Touro College of Osteopathic Medicine, Brooklyn, NY
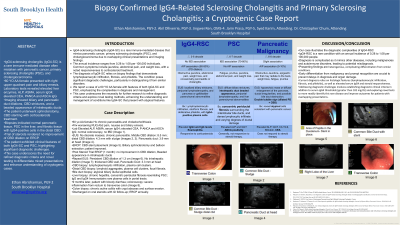
Introduction: IgG4-sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) is an immune-mediated disease that mimics pancreatic cancer (PCa), primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), and cholangiocarcinoma in symptoms and imaging.1,2 The annual incidence is 0.28 to 1.08 per 100,000 individuals.3 Patients present with jaundice, abdominal pain, weight loss, and steroid responsiveness. IgG4-SC is confirmed via biopsy exhibiting lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, fibrosis, and phlebitis.4,5,6
Case Description/Methods: A 60-year-old African American female with a medical history of gastroesophageal reflux disease, asthma, bladder incontinence with neurostimulator implantation, and aortic insufficiency presented with right upper quadrant abdominal pain and biliary emesis. Lab tests revealed the following testing: ALT of 144 U/L, AST of 118 U/L, CEA of 13.9 ng/mL, AFP of 13 ng/mL, serum IgG4 of 357 mg/dL, and positive P-ANCA 1:160. CA 19-9 and bilirubin levels were normal. Abdominal CT demonstrated cholelithiasis, common bile duct (CBD) dilation of 1.2 cm, and pancreatic duct dilation of 0.5 cm. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) denoted chronic pancreatitis with a 3.9 mm dilation of the pancreatic duct at the head, mid-CBD dilation of 8.5 mm, distal CBD narrowing of 4.3 mm, CBD strictures, and a beaded appearance in the intrahepatic ducts. Subsequently, sphincterotomy and bile duct stenting were performed.
The patient tolerated the procedures well and improved. Pancreatic head biopsy was normal. Liver biopsy indicated PSC and distal CBD biopsy showed fibrotic tissue, lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with IgG4-positive cells, and lymphoid aggregates. Biliary duct biopsy revealed atypical epithelial cells. She was discharged with corticosteroids and scheduled for outpatient follow-up with ERCP.
Discussion: IgG4-SC often co-presents with autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP).7 Early steroid treatment prevents organ damage and differentiates IgG4-SC from PSC.1,7 Serum IgG4 levels greater than 182 mg/dL distinguishes IgG4-SC from PCa and PSC.5 Despite receiving steroids, the patient did not improve on cholangiogram which showed persistent findings, possibly due to a delayed response to treatment.4 The patient showed P-ANCA positivity, AIP, biopsy-confirmed PSC and IgG4-SC, elevated IgG4 levels, and beaded intrahepatic ducts. This is significant as the patient displays characteristics of both IgG4-SC and PSC and underscores the need for further research to refine diagnostic criteria.
Disclosures:
Ethan Abrishamian, DO1, Akil Olliverrie, MD1, Jarin Prasa, MD1, Syed Karim, DO1, Jingwei Ren, 2. P3609 - Biopsy Confirmed IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis - A Cryptogenic Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1NYC Health + Hospitals/South Brooklyn Health, Brooklyn, NY; 2Touro College of Osteopathic Medicine, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: IgG4-sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) is an immune-mediated disease that mimics pancreatic cancer (PCa), primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), and cholangiocarcinoma in symptoms and imaging.1,2 The annual incidence is 0.28 to 1.08 per 100,000 individuals.3 Patients present with jaundice, abdominal pain, weight loss, and steroid responsiveness. IgG4-SC is confirmed via biopsy exhibiting lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, fibrosis, and phlebitis.4,5,6
Case Description/Methods: A 60-year-old African American female with a medical history of gastroesophageal reflux disease, asthma, bladder incontinence with neurostimulator implantation, and aortic insufficiency presented with right upper quadrant abdominal pain and biliary emesis. Lab tests revealed the following testing: ALT of 144 U/L, AST of 118 U/L, CEA of 13.9 ng/mL, AFP of 13 ng/mL, serum IgG4 of 357 mg/dL, and positive P-ANCA 1:160. CA 19-9 and bilirubin levels were normal. Abdominal CT demonstrated cholelithiasis, common bile duct (CBD) dilation of 1.2 cm, and pancreatic duct dilation of 0.5 cm. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) denoted chronic pancreatitis with a 3.9 mm dilation of the pancreatic duct at the head, mid-CBD dilation of 8.5 mm, distal CBD narrowing of 4.3 mm, CBD strictures, and a beaded appearance in the intrahepatic ducts. Subsequently, sphincterotomy and bile duct stenting were performed.
The patient tolerated the procedures well and improved. Pancreatic head biopsy was normal. Liver biopsy indicated PSC and distal CBD biopsy showed fibrotic tissue, lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with IgG4-positive cells, and lymphoid aggregates. Biliary duct biopsy revealed atypical epithelial cells. She was discharged with corticosteroids and scheduled for outpatient follow-up with ERCP.
Discussion: IgG4-SC often co-presents with autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP).7 Early steroid treatment prevents organ damage and differentiates IgG4-SC from PSC.1,7 Serum IgG4 levels greater than 182 mg/dL distinguishes IgG4-SC from PCa and PSC.5 Despite receiving steroids, the patient did not improve on cholangiogram which showed persistent findings, possibly due to a delayed response to treatment.4 The patient showed P-ANCA positivity, AIP, biopsy-confirmed PSC and IgG4-SC, elevated IgG4 levels, and beaded intrahepatic ducts. This is significant as the patient displays characteristics of both IgG4-SC and PSC and underscores the need for further research to refine diagnostic criteria.
Disclosures:
Ethan Abrishamian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akil Olliverrie indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jarin Prasa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Karim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jingwei Ren indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ethan Abrishamian, DO1, Akil Olliverrie, MD1, Jarin Prasa, MD1, Syed Karim, DO1, Jingwei Ren, 2. P3609 - Biopsy Confirmed IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis and Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis - A Cryptogenic Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
