Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P3621 - Concurrent Development of Diabetes Mellitus, Splenic Vein Thrombosis, and Portal Vein Thrombosis Following a First Episode of Idiopathic Acute Pancreatitis: A Rare Triadic Presentation
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E


Saira Shah, MD
Brooklyn Hospital Center
Naugatuck, CT
Presenting Author(s)
Saira Shah, MD1, Iyad Al-bustami, MD, MPH(c)2, Salman Haider, MD1, Amin Shah, MBBS3, Moazzam Hussain, MBBS4, Fatima Zohra, MBBS5, Kiran Zaman, MD6
1Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 2Brooklyn Hospital Center, Houston, TX; 3Khyber Medical University, Brooklyn, NY; 4Khyber Medical College, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 5Khyber Girls Medical College, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 6The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: Acute pancreatitis (AP) can lead to significant complications, including vascular issues like splenic and portal vein thrombosis, and metabolic disturbances such as transient hyperglycemia or overt diabetes. This case highlights a patient who experienced their first episode of idiopathic AP and simultaneously developed new-onset diabetes mellitus (DM), along with thrombosis in both the splenic and portal veins during their initial hospitalization without prior pancreatic disease history.
Case Description/Methods: A 44-year-old male with no significant medical history presented to ED with severe LUQ abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting for three days. Physical examination showed tenderness in LUQ and RUQ but was otherwise unremarkable. Vitals were stable. The patient reported social alcohol use, no smoking, or illicit drug use, and was not on any medications.
Laboratory tests revealed elevated lipase (267 U/L), creatinine (1.6 mg/dL), glucose (154 mg/dL), hemoglobin A1c (5.7%), and triglycerides (270 mg/dL), with a normal hepatic panel. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis indicated AP at the pancreatic tail without necrosis and concurrent splenic and portal vein thrombosis. A right upper quadrant ultrasound showed fatty liver and no gallstones, with a common bile duct measuring 2.9 mm.
The initial workup was inconclusive for the etiology of AP. The patient developed impaired glucose tolerance with glucose levels peaking in the 400s mg/dL during his hospital stay. He was started on insulin but remained hyperglycemic, with glucose consistently above 200 mg/dL. Repeat CT imaging showed increased pancreatic edema but no necrosis.
The patient was discharged with clinical improvement, continued on Apixaban for thrombosis, and basal-bolus insulin for newly diagnosed DM. Outpatient follow-up with hematology-oncology has shown all hypercoagulable workup to be unremarkable.
Discussion: This case is particularly noteworthy because no pancreatic necrosis was evident on the CT scan, challenging the prevailing assumption that such complications predominantly accompany severe AP. This finding underscores the necessity of considering these complications even in mild to moderate cases of AP. Physicians need to be aware of both acute and long-term complications associated with AP, whether they occur individually or in combination. Given the significant risk of AP-related diabetes, as demonstrated by evolving evidence and our patient's experience, screening for diabetes in all AP patients may be advisable.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Saira Shah, MD1, Iyad Al-bustami, MD, MPH(c)2, Salman Haider, MD1, Amin Shah, MBBS3, Moazzam Hussain, MBBS4, Fatima Zohra, MBBS5, Kiran Zaman, MD6. P3621 - Concurrent Development of Diabetes Mellitus, Splenic Vein Thrombosis, and Portal Vein Thrombosis Following a First Episode of Idiopathic Acute Pancreatitis: A Rare Triadic Presentation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY; 2Brooklyn Hospital Center, Houston, TX; 3Khyber Medical University, Brooklyn, NY; 4Khyber Medical College, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 5Khyber Girls Medical College, Peshawar, North-West Frontier, Pakistan; 6The Brooklyn Hospital Center, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: Acute pancreatitis (AP) can lead to significant complications, including vascular issues like splenic and portal vein thrombosis, and metabolic disturbances such as transient hyperglycemia or overt diabetes. This case highlights a patient who experienced their first episode of idiopathic AP and simultaneously developed new-onset diabetes mellitus (DM), along with thrombosis in both the splenic and portal veins during their initial hospitalization without prior pancreatic disease history.
Case Description/Methods: A 44-year-old male with no significant medical history presented to ED with severe LUQ abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting for three days. Physical examination showed tenderness in LUQ and RUQ but was otherwise unremarkable. Vitals were stable. The patient reported social alcohol use, no smoking, or illicit drug use, and was not on any medications.
Laboratory tests revealed elevated lipase (267 U/L), creatinine (1.6 mg/dL), glucose (154 mg/dL), hemoglobin A1c (5.7%), and triglycerides (270 mg/dL), with a normal hepatic panel. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis indicated AP at the pancreatic tail without necrosis and concurrent splenic and portal vein thrombosis. A right upper quadrant ultrasound showed fatty liver and no gallstones, with a common bile duct measuring 2.9 mm.
The initial workup was inconclusive for the etiology of AP. The patient developed impaired glucose tolerance with glucose levels peaking in the 400s mg/dL during his hospital stay. He was started on insulin but remained hyperglycemic, with glucose consistently above 200 mg/dL. Repeat CT imaging showed increased pancreatic edema but no necrosis.
The patient was discharged with clinical improvement, continued on Apixaban for thrombosis, and basal-bolus insulin for newly diagnosed DM. Outpatient follow-up with hematology-oncology has shown all hypercoagulable workup to be unremarkable.
Discussion: This case is particularly noteworthy because no pancreatic necrosis was evident on the CT scan, challenging the prevailing assumption that such complications predominantly accompany severe AP. This finding underscores the necessity of considering these complications even in mild to moderate cases of AP. Physicians need to be aware of both acute and long-term complications associated with AP, whether they occur individually or in combination. Given the significant risk of AP-related diabetes, as demonstrated by evolving evidence and our patient's experience, screening for diabetes in all AP patients may be advisable.

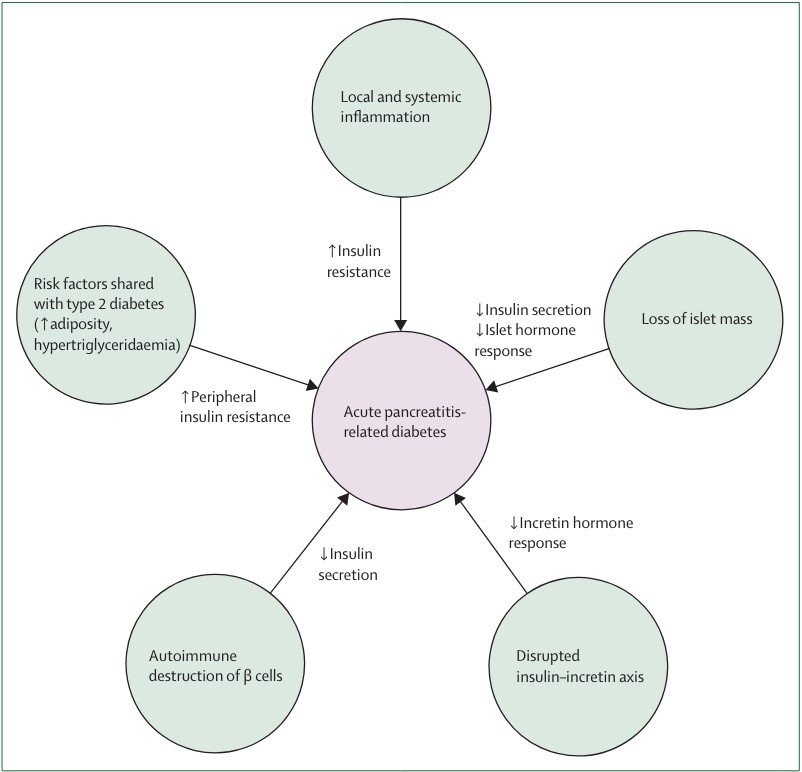
Figure: Proposed contributing factors to the pathophysiology of diabetes following acute pancreatitis
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Saira Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iyad Al-bustami indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Salman Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amin Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Moazzam Hussain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fatima Zohra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kiran Zaman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saira Shah, MD1, Iyad Al-bustami, MD, MPH(c)2, Salman Haider, MD1, Amin Shah, MBBS3, Moazzam Hussain, MBBS4, Fatima Zohra, MBBS5, Kiran Zaman, MD6. P3621 - Concurrent Development of Diabetes Mellitus, Splenic Vein Thrombosis, and Portal Vein Thrombosis Following a First Episode of Idiopathic Acute Pancreatitis: A Rare Triadic Presentation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
